The temperate forest, characterized by its moderate climate and distinct seasonal changes, is home to a diverse array of animal species. These forests, found in regions such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, provide a unique habitat for animals that have adapted to the changing seasons and the availability of food sources. From the majestic predators that roam the forest floor to the tiny insects that inhabit the trees, the temperate forest is teeming with life. In this article, we will explore the various animal species that can be found in temperate forests, highlighting their unique characteristics, adaptations, and roles within the ecosystem.
Primary Species Found in Temperate Forests

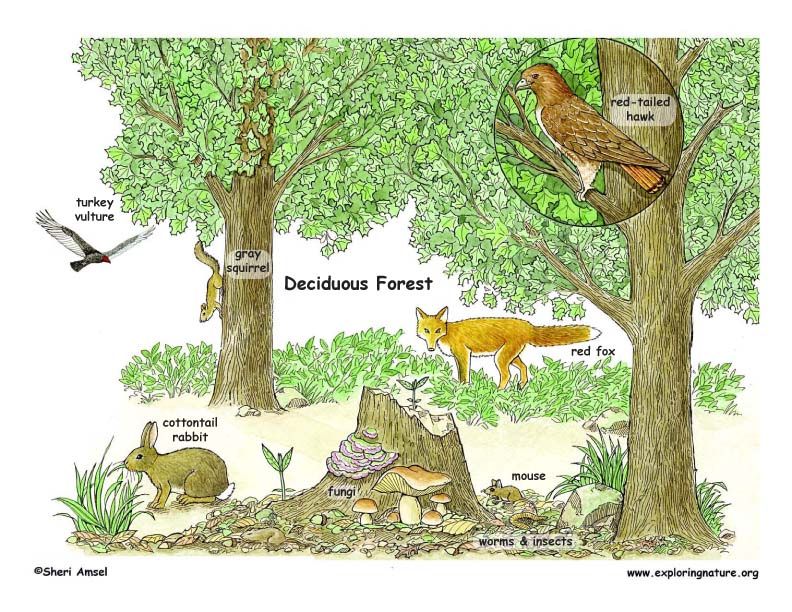
Temperate forests are home to a wide range of animal species, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects. Some of the primary species found in these forests include white-tailed deer, black bears, and gray wolves. These large mammals play a crucial role in shaping the forest ecosystem, with deer and other herbivores helping to disperse seeds and create pathways, while predators like wolves and bears regulate prey populations and maintain the balance of the ecosystem. Forest fragmentation, which occurs when forests are divided into smaller patches due to human activities like deforestation and urbanization, can have significant impacts on these species, making it essential to conserve and manage temperate forests effectively.
Key Points
- The temperate forest is home to a diverse array of animal species, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects.
- Primary species found in temperate forests include white-tailed deer, black bears, and gray wolves.
- Forest fragmentation can have significant impacts on animal species, emphasizing the need for effective conservation and management strategies.
- Temperate forests provide a unique habitat for animals that have adapted to the changing seasons and the availability of food sources.
- Conservation efforts should focus on preserving large, contiguous areas of forest habitat to support the long-term viability of animal populations.
Adaptations of Temperate Forest Animals
Animals that inhabit temperate forests have evolved a range of adaptations to survive and thrive in this environment. For example, many species of birds migrate to warmer climates during the winter months, while others, like the black-capped chickadee, remain in the forest year-round, relying on their ability to find food and shelter in the snowy landscape. Hibernation is another adaptation used by some species, such as black bears and chipmunks, to conserve energy during the winter months when food is scarce. These adaptations are crucial for the survival of animal species in temperate forests, allowing them to cope with the challenges posed by the changing seasons.
| Animal Species | Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Black bears | Hibernation |
| White-tailed deer | Migration to lower elevations during winter |
| Gray wolves | Highly developed sense of smell and hearing to locate prey |
| Black-capped chickadee | Ability to find food and shelter in snowy landscapes |
Conservation Efforts and Management Strategies

Conservation efforts and management strategies are essential for preserving the integrity of temperate forests and the animal species that inhabit them. This can involve habitat preservation, species reintroduction, and ecosystem management practices. For example, the reintroduction of gray wolves to Yellowstone National Park in the 1990s had a significant impact on the ecosystem, helping to regulate elk populations and maintain the balance of the forest ecosystem. Additionally, forest certification programs can help to promote sustainable forestry practices, ensuring that timber harvesting and other human activities are carried out in a way that minimizes harm to the environment and the animal species that depend on it.
Challenges and Opportunities for Conservation
Despite the importance of conservation efforts, there are many challenges and opportunities that must be addressed. Climate change is one of the most significant threats facing temperate forests, as it can alter the distribution and abundance of animal species, and disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem. Human-wildlife conflict is another challenge, as the expansion of human settlements and agricultural activities can lead to conflicts between humans and animals, such as deer and wolves. However, there are also opportunities for conservation, such as the use of ecological corridors to connect fragmented habitats and promote the movement of animal species, and the development of sustainable forestry practices that balance human needs with environmental protection.
What are some of the primary species found in temperate forests?
+Some of the primary species found in temperate forests include white-tailed deer, black bears, and gray wolves. These large mammals play a crucial role in shaping the forest ecosystem.
How do animals adapt to the changing seasons in temperate forests?
+Animals that inhabit temperate forests have evolved a range of adaptations to survive and thrive in this environment, including hibernation, migration, and the ability to find food and shelter in snowy landscapes.
What are some of the challenges and opportunities for conservation in temperate forests?
+Despite the importance of conservation efforts, there are many challenges and opportunities that must be addressed, including climate change, human-wildlife conflict, and the use of ecological corridors to connect fragmented habitats and promote the movement of animal species.
In conclusion, temperate forests are complex and dynamic ecosystems that support a wide range of animal species. The adaptations exhibited by these species are a testament to their ability to thrive in this environment, and highlight the importance of preserving and managing temperate forests to support biodiversity. By addressing the challenges and opportunities for conservation, we can work to protect and preserve these ecosystems for future generations.



