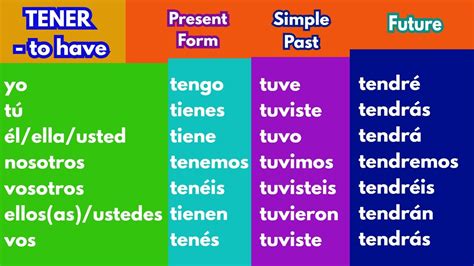
Mastering the conjugation of the verb "tener" in the past tense is essential for communicating effectively in Spanish. The verb "tener," which translates to "to have" in English, is one of the most commonly used verbs in Spanish, and its past tense conjugation is crucial for describing past possession, age, or characteristics. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the specifics of conjugating "tener" in the preterite and imperfect past tenses, providing you with the knowledge to express yourself accurately about past events or conditions.
Introduction to Tener
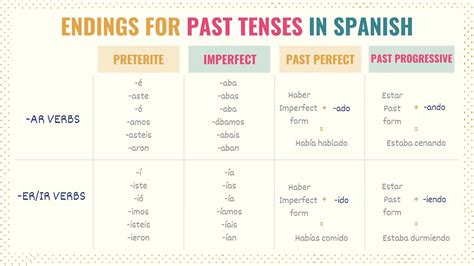
The verb “tener” is a regular -er verb, but it has an irregular stem in the present tense (tengo, tienes, tiene, tenemos, tenéis, tienen). However, in the past tense, it follows a more predictable pattern. Understanding the conjugation of “tener” in the past tense will significantly enhance your ability to convey complex ideas and narratives in Spanish.
Preterite Tense of Tener
The preterite tense, also known as the simple past, is used to describe completed actions in the past. The conjugation of “tener” in the preterite tense is as follows:
| Subject | Preterite Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | tuve |
| Tú | tuve |
| Él/ella/usted | tuvo |
| Nosotros/as | tuvimos |
| Vosotros/as | tuvisteis |
| Ellos/as | tuvieron |

For example, "Yo tuve un perro cuando era niño" means "I had a dog when I was a child." This tense is used to talk about finished actions in the past.
Imperfect Tense of Tener
The imperfect tense is used to describe ongoing or repeated actions in the past. The conjugation of “tener” in the imperfect tense is as follows:
| Subject | Imperfect Conjugation |
|---|---|
| Yo | tenía |
| Tú | tenías |
| Él/ella/usted | tenía |
| Nosotros/as | teníamos |
| Vosotros/as | teníais |
| Ellos/as | tenían |
For example, "Yo tenía diez años cuando comencé a aprender español" means "I was ten years old when I started learning Spanish." This tense is useful for describing background information or setting the scene for a story.
Key Points
- The verb "tener" is crucial for expressing possession, age, or characteristics in the past.
- The preterite tense of "tener" is used for completed actions (e.g., tuve, tuviste, tuvo, tuvimos, tuvisteis, tuvieron).
- The imperfect tense of "tener" is used for ongoing or repeated actions (e.g., tenía, tenías, tenía, teníamos, teníais, tenían).
- Understanding the conjugation of "tener" in the past tense enhances your ability to tell stories and describe past events in Spanish.
- Practice using both the preterite and imperfect tenses in context to improve your Spanish storytelling skills.
Practical Applications and Examples
To solidify your understanding of “tener” in the past tense, consider the following examples and practice incorporating them into your own sentences:
- Yo tuve una bicicleta roja cuando era niño. (I had a red bicycle when I was a child.)
- Ella tenía un libro muy interesante que leí durante mis vacaciones. (She had a very interesting book that I read during my vacation.)
- Nosotros tuvimos que estudiar mucho para el examen. (We had to study a lot for the exam.)
These examples illustrate how "tener" in the past tense can be used to describe past possession, obligations, or conditions. By practicing with these conjugations, you will become more comfortable expressing yourself about past events in Spanish.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Mastering the past tense conjugation of “tener” is a significant step in advancing your Spanish language skills. By understanding and practicing the preterite and imperfect tenses, you will be able to communicate more effectively about past experiences, possessions, and conditions. Remember to practice using these tenses in context to improve your fluency and comprehension. With consistent practice and exposure to the language, you will find yourself more confident in expressing complex ideas and narratives in Spanish.
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre el pretérito y el imperfecto de “tener”?
+El pretérito se usa para acciones completadas en el pasado, mientras que el imperfecto se usa para acciones en curso o repetidas en el pasado.
¿Cómo se conjuga “tener” en el pretérito?
+La conjugación de “tener” en el pretérito es: yo tuve, tú tuviste, él/ella/usted tuvo, nosotros/as tuvimos, vosotros/as tuvisteis, ellos/as tuvieron.
¿Por qué es importante entender “tener” en el pasado?
+Entender “tener” en el pasado es crucial para describir posesiones, edades o características en el pasado, lo que te permite contar historias y describir eventos de manera más efectiva en español.