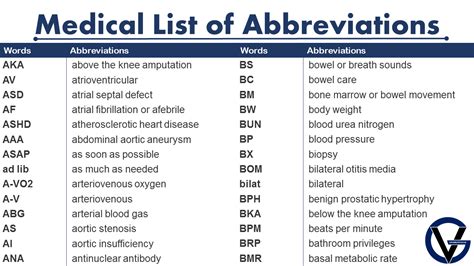
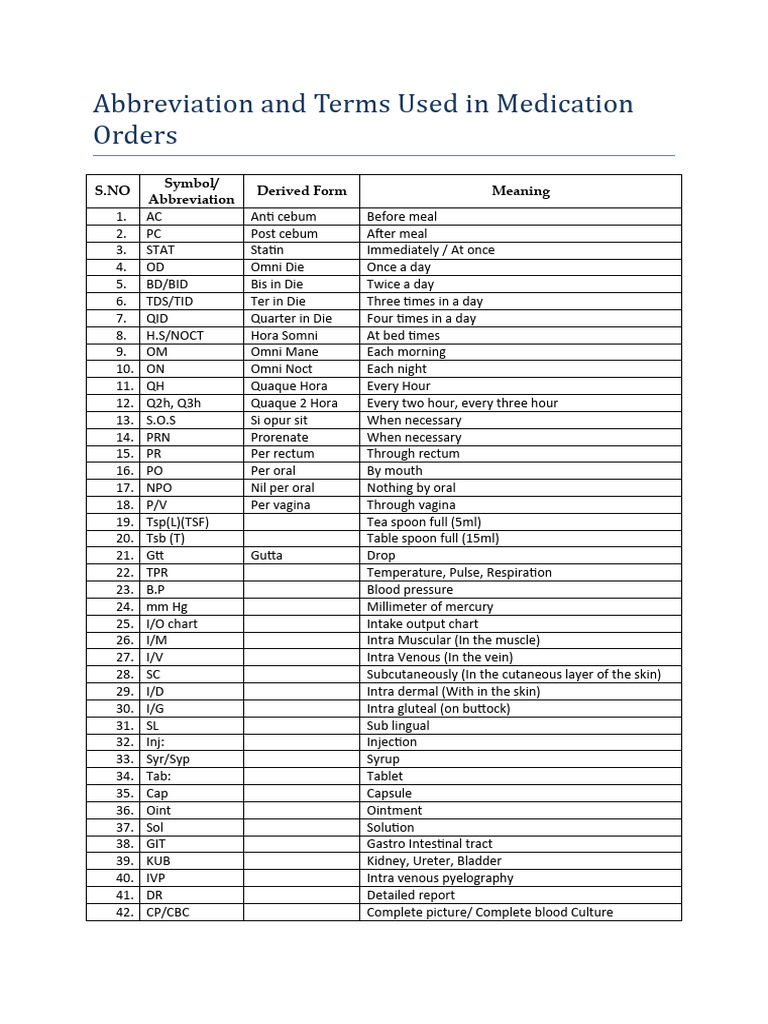
Texas medical professionals rely heavily on a wide range of medical abbreviations to efficiently communicate patient information, diagnoses, and treatment plans. The use of these abbreviations is not only limited to Texas but is a common practice across the United States and globally in the medical field. Understanding these abbreviations is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure accurate and timely patient care.
Common Medical Abbreviations Used in Texas
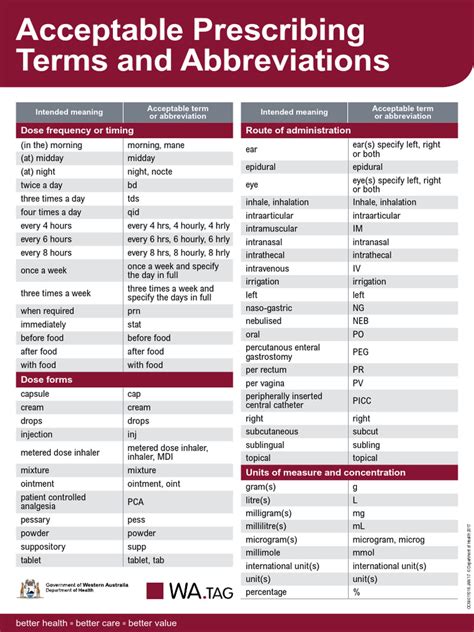
Medical abbreviations are used in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and medical offices. Some common medical abbreviations used in Texas include:
- BP: Blood Pressure
- HR: Heart Rate
- RR: Respiratory Rate
- Temp: Temperature
- Wt: Weight
- Ht: Height
- ALL: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- CAD: Coronary Artery Disease
- CHF: Congestive Heart Failure
- COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- DM: Diabetes Mellitus
- HTN: Hypertension
Medication-Related Abbreviations
Medication-related abbreviations are also commonly used in Texas medical settings. These abbreviations help healthcare providers quickly identify medication names, dosages, and administration routes. Some examples include:
- PO: By Mouth
- IV: Intravenous
- IM: Intramuscular
- SC: Subcutaneous
- bid: Twice a Day
- tid: Three Times a Day
- qid: Four Times a Day
- HS: At Bedtime
- PRN: As Needed
| Medication Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| mg | Milligram |
| mL | Milliliter |
| mcg | Microgram |
| UI | Unit |
Key Points
- Medical abbreviations are widely used in Texas healthcare settings to facilitate efficient communication.
- Common medical abbreviations include those related to patient vital signs, diagnoses, and treatment plans.
- Medication-related abbreviations help healthcare providers quickly identify medication names, dosages, and administration routes.
- Staying current with medical abbreviations is crucial for accurate and efficient communication among healthcare professionals.
- The Joint Commission and other healthcare organizations provide guidelines for using medical abbreviations to minimize errors and improve patient safety.
Importance of Accurate Medical Abbreviation Usage

The accurate use of medical abbreviations is critical in Texas healthcare settings to prevent medication errors, misdiagnoses, and other adverse events. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), medication errors affect an estimated 1.5 million people in the United States each year, resulting in significant morbidity, mortality, and economic burden. The Joint Commission recommends that healthcare organizations establish clear policies and procedures for using medical abbreviations to minimize errors and improve patient safety.
Best Practices for Using Medical Abbreviations
To ensure accurate and efficient communication, Texas medical professionals should follow best practices for using medical abbreviations. These include:
- Using only approved medical abbreviations
- Avoiding ambiguous or unclear abbreviations
- Documenting medication orders and treatment plans clearly and accurately
- Verifying patient information and medication orders with colleagues and patients
- Staying current with updates and changes to medical abbreviations
What are some common medical abbreviations used in Texas?
+Common medical abbreviations used in Texas include BP (Blood Pressure), HR (Heart Rate), and RR (Respiratory Rate), among others.
Why is accurate medical abbreviation usage important?
+Accurate medical abbreviation usage is critical to prevent medication errors, misdiagnoses, and other adverse events, ultimately improving patient safety and outcomes.
How can Texas medical professionals stay current with medical abbreviations?
+Texas medical professionals can stay current with medical abbreviations by attending continuing education courses, reviewing updates from healthcare organizations, and participating in peer discussions and training sessions.
Meta Description: Discover the common medical abbreviations used in Texas, their importance in healthcare settings, and best practices for accurate usage to improve patient safety and outcomes. (149 characters)