The American system, a complex and multifaceted entity, operates on various principles and mechanisms that have evolved over time. At its core, the system is designed to balance power, protect individual rights, and promote the general welfare of its citizens. Understanding how the American system works requires delving into its foundational elements, including its democratic framework, the role of institutions, the impact of policies, and the interactions between different branches of government. This article will explore five key ways the American system functions, highlighting its strengths, challenges, and the ongoing efforts to refine and improve it.
Key Points
- The American system is based on a democratic republic framework, where power is divided among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
- The Constitution and the Bill of Rights play crucial roles in outlining the powers of the government and the rights of the citizens.
- The system of checks and balances is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
- Federalism, or the division of power between the federal government and the states, allows for a balance between national unity and regional autonomy.
- Civic engagement and participation are essential for the functioning of the American system, as they ensure that the government remains accountable to the people.
The Framework of Democracy

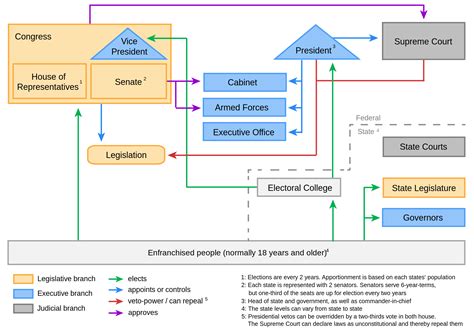
The American system is rooted in democracy, with a governmental structure that includes the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. This tripartite system is fundamental to the functioning of the country, as it ensures that power is distributed evenly and that no single entity dominates the others. The legislative branch, composed of Congress, is responsible for making the laws. The executive branch, headed by the President, is tasked with enforcing these laws. Meanwhile, the judicial branch, comprising the Supreme Court and other federal courts, interprets the laws and ensures they align with the Constitution. This division of power is a cornerstone of the American system, designed to protect individual rights and prevent the concentration of power.
The Role of the Constitution and the Bill of Rights
The Constitution, adopted in 1787, and the Bill of Rights, ratified in 1791, are foundational documents of the American system. The Constitution outlines the framework of the federal government and the relationship between the government and the citizens. It establishes the principles of federalism, individual rights, and the rule of law. The Bill of Rights, comprising the first ten amendments to the Constitution, enumerates specific individual liberties and protections, such as freedom of speech, the right to bear arms, and protection against unreasonable searches and seizures. These documents are not only historical relics but living, breathing components of the American system, shaping legal precedents, political discourse, and social norms.
Checks and Balances
A critical mechanism within the American system is the principle of checks and balances. This system is designed to prevent any one branch of government from abusing its power. For instance, Congress can impeach and remove the President, thereby checking the executive branch’s power. Similarly, the President can veto laws passed by Congress, which can then be overridden by a two-thirds majority in both the House and the Senate. The Supreme Court, on the other hand, can declare laws passed by Congress or actions taken by the President as unconstitutional, thus exercising its judicial review power. This delicate balance of power ensures that the government remains accountable and that no branch becomes omnipotent.
Federalism and the Division of Power
Federalism is another key aspect of the American system, where power is divided between the federal government and the states. This division allows for a balance between national unity and regional autonomy, enabling states to address local issues while the federal government focuses on national and international matters. The Tenth Amendment to the Constitution, part of the Bill of Rights, explicitly states that any powers not delegated to the federal government are reserved to the states or the people. This principle of federalism has been a subject of ongoing debate and interpretation, particularly in areas such as healthcare, education, and environmental regulation, where the boundaries between federal and state authority are often blurred.
| Branch of Government | Powers | Checks |
|---|---|---|
| Legislative | Making laws | Can be vetoed by the President, judicial review by the Supreme Court |
| Executive | Enforcing laws, Commander-in-Chief | Impeachment by Congress, laws can be declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court |
| Judicial | Interpreting laws | Justices can be appointed or impeached by Congress and the President |
Civic Engagement and Participation
Civic engagement and participation are vital components of the American system, ensuring that the government remains accountable to the people. Through elections, public debates, and activism, citizens can influence policy decisions and hold their elected representatives accountable. The First Amendment’s protection of freedom of speech, assembly, and the press further facilitates this engagement, allowing for the free exchange of ideas and the organization of public movements. In essence, the health of the American system depends on an informed and active citizenry, capable of participating in the democratic process and contributing to the ongoing dialogue about the direction of the country.
What is the main purpose of the system of checks and balances in the American government?
+The main purpose of the system of checks and balances is to prevent any one branch of the government from becoming too powerful, thereby protecting individual rights and promoting accountability within the government.
How does federalism contribute to the functioning of the American system?
+Federalism allows for a division of power between the federal government and the states, enabling the addressing of national issues at the federal level while allowing states to handle local matters. This balance between national unity and regional autonomy is crucial for the country's governance and development.
Why is civic engagement important for the American system?
+Civic engagement is essential because it ensures that the government remains accountable to the people. Through participation in elections, public debates, and activism, citizens can influence policy decisions and contribute to the democratic process, thereby safeguarding the principles of democracy and individual rights.
In conclusion, the American system is a complex and dynamic entity, characterized by its democratic framework, the system of checks and balances, federalism, and the protection of individual rights. Understanding these components and how they interact is crucial for appreciating the strengths and challenges of the system. As the country continues to evolve, the American system must also adapt, balancing tradition with the need for innovation and reform. Through civic engagement, a deep understanding of its foundational principles, and a commitment to the values of democracy, the American system can continue to thrive, serving as a model of governance and a beacon of freedom and opportunity for generations to come.



