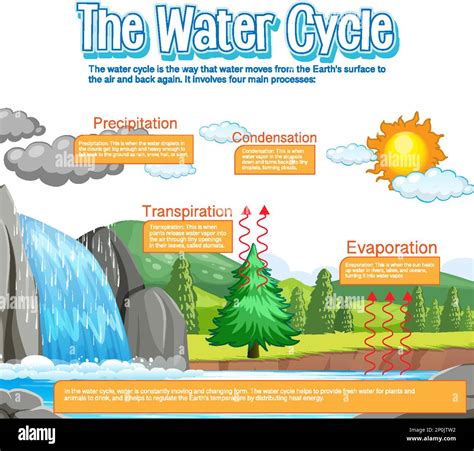
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, is the continuous process by which water is circulated between the Earth's oceans, atmosphere, and land. It is a vital component of the Earth's system, supporting life and regulating the planet's climate. The water cycle diagram is a visual representation of this process, illustrating the various stages and pathways that water takes as it moves through the environment. In this article, we will delve into the details of the water cycle diagram, exploring its key components, processes, and significance.
Introduction to the Water Cycle Diagram
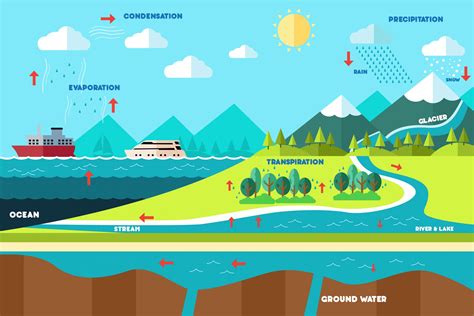
The water cycle diagram typically consists of a series of interconnected arrows and circles, representing the different stages of the water cycle. The diagram is often simplified, but it effectively conveys the complex interactions between the atmosphere, oceans, lakes, rivers, and land. The water cycle diagram is an essential tool for understanding the Earth’s water system, as it helps to identify the various pathways and processes that water undergoes as it circulates through the environment.
Key Components of the Water Cycle Diagram
The water cycle diagram includes several key components, each representing a critical stage or process in the water cycle. These components include:
- Evaporation: The process by which water is converted from a liquid to a gas, typically occurring at the surface of oceans, lakes, and rivers.
- Condensation: The process by which water vapor in the atmosphere cools and condenses into liquid water, forming clouds, fog, or dew.
- Precipitation: The process by which water falls to the Earth’s surface, including rain, snow, sleet, and hail.
- Runoff: The flow of water over the land, often collecting in streams, rivers, and lakes.
- Infiltration: The process by which water seeps into the soil, recharging groundwater aquifers.
| Water Cycle Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Evaporation | Conversion of liquid water to water vapor |
| Condensation | Cooling and condensation of water vapor into liquid water |
| Precipitation | Falling of water to the Earth's surface |
| Runoff | Flow of water over the land |
| Infiltration | Seepage of water into the soil |
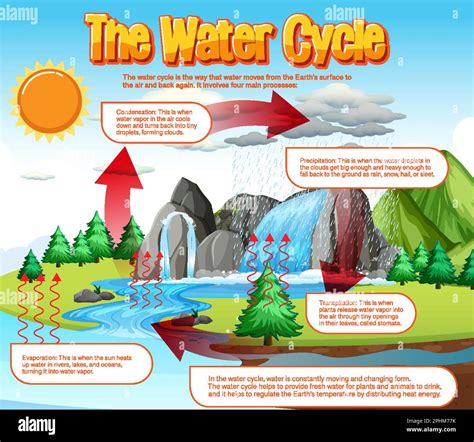
Processes and Pathways in the Water Cycle Diagram
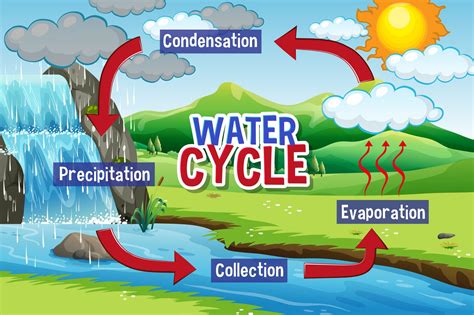
The water cycle diagram illustrates the various processes and pathways that water takes as it circulates through the environment. These processes include:
- Transpiration: The process by which plants release water vapor into the atmosphere through their leaves.
- Evapotranspiration: The combination of evaporation and transpiration, representing the total amount of water lost from the land surface to the atmosphere.
- Groundwater flow: The movement of water through the soil and underlying rock, often feeding into streams, rivers, and lakes.
Significance of the Water Cycle Diagram
The water cycle diagram is a crucial tool for understanding the Earth’s water system, with significant implications for:
- Water resource management: Understanding the water cycle diagram helps to identify areas of water scarcity, inform water conservation strategies, and optimize water allocation.
- Climate regulation: The water cycle plays a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate, with changes in the water cycle impacting temperature, precipitation patterns, and weather extremes.
- Ecosystem health: The water cycle diagram highlights the interconnectedness of ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of maintaining healthy watersheds, wetlands, and aquatic ecosystems.
Key Points
- The water cycle diagram illustrates the continuous process of water circulation between the Earth's oceans, atmosphere, and land.
- The diagram includes key components such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, and infiltration.
- Understanding the water cycle diagram is essential for managing water resources, predicting weather patterns, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- The water cycle diagram highlights the interconnectedness of ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of maintaining healthy watersheds, wetlands, and aquatic ecosystems.
- The water cycle plays a critical role in regulating the Earth's climate, with changes in the water cycle impacting temperature, precipitation patterns, and weather extremes.
FAQs
What is the water cycle diagram?
+The water cycle diagram is a visual representation of the continuous process of water circulation between the Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and land.
What are the key components of the water cycle diagram?
+The key components of the water cycle diagram include evaporation, condensation, precipitation, runoff, and infiltration.
Why is the water cycle diagram important?
+The water cycle diagram is important for understanding the Earth’s water system, managing water resources, predicting weather patterns, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Meta Description: “The water cycle diagram is a vital tool for understanding the Earth’s water system. Learn about the key components, processes, and significance of the water cycle diagram, and discover its importance for managing water resources, predicting weather patterns, and mitigating climate change.” (149 characters)