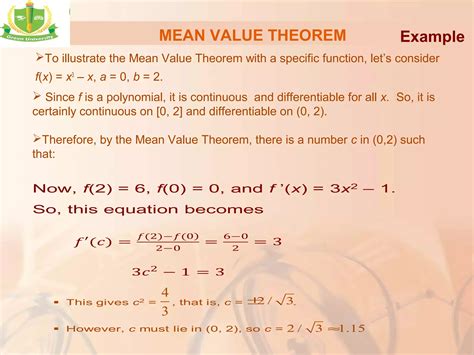
The Theorem of the Mean, also known as the Mean Value Theorem (MVT), is a fundamental concept in calculus that provides a powerful tool for analyzing functions and their behavior. This theorem has far-reaching implications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and economics. In this article, we will delve into the world of the Mean Value Theorem, exploring its history, significance, and applications.
The Mean Value Theorem states that if a function f(x) is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b), then there exists a point c in (a, b) such that the derivative of f(x) at c is equal to the average rate of change of f(x) over the interval [a, b]. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
f’© = (f(b) - f(a)) / (b - a)
This theorem was first introduced by the French mathematician Augustin-Louis Cauchy in the 19th century and has since become a cornerstone of calculus. The MVT has numerous applications in optimization problems, physics, and engineering, where it is used to model and analyze complex systems.
Key Points
- The Mean Value Theorem states that a function f(x) has a point c in (a, b) where the derivative f'(c) equals the average rate of change of f(x) over [a, b].
- The MVT requires the function to be continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b).
- The theorem has numerous applications in optimization problems, physics, and engineering.
- The MVT provides a powerful tool for analyzing functions and their behavior.
- The theorem has far-reaching implications in various fields, including mathematics, physics, engineering, and economics.
Historical Background and Development

The Mean Value Theorem has its roots in the early days of calculus, when mathematicians such as Pierre Fermat and Bonaventura Cavalieri were exploring the concept of maxima and minima. However, it was not until the 19th century that Cauchy formally introduced the theorem, providing a rigorous proof and establishing its significance in the field of calculus. Since then, the MVT has undergone significant developments, with various mathematicians contributing to its extension and generalization.
The MVT has been generalized to include functions of multiple variables, leading to the development of the Mean Value Theorem for multivariable functions. This extension has far-reaching implications in optimization problems, where the MVT is used to find the maximum or minimum of a function subject to certain constraints.
Applications of the Mean Value Theorem
The Mean Value Theorem has numerous applications in various fields, including:- Optimization problems: The MVT is used to find the maximum or minimum of a function subject to certain constraints.
- Physics: The MVT is used to model and analyze complex systems, such as the motion of objects and the behavior of electrical circuits.
- Engineering: The MVT is used to optimize the design of systems, such as bridges and buildings.
- Economics: The MVT is used to model and analyze economic systems, such as the behavior of markets and the impact of policy interventions.
| Field of Application | Example of Use |
|---|---|
| Optimization problems | Maximizing the area of a rectangle with a fixed perimeter |
| Physics | Modeling the motion of a projectile under the influence of gravity |
| Engineering | Optimizing the design of a bridge to minimize cost and maximize safety |
| Economics | Modeling the behavior of a market and predicting the impact of policy interventions |
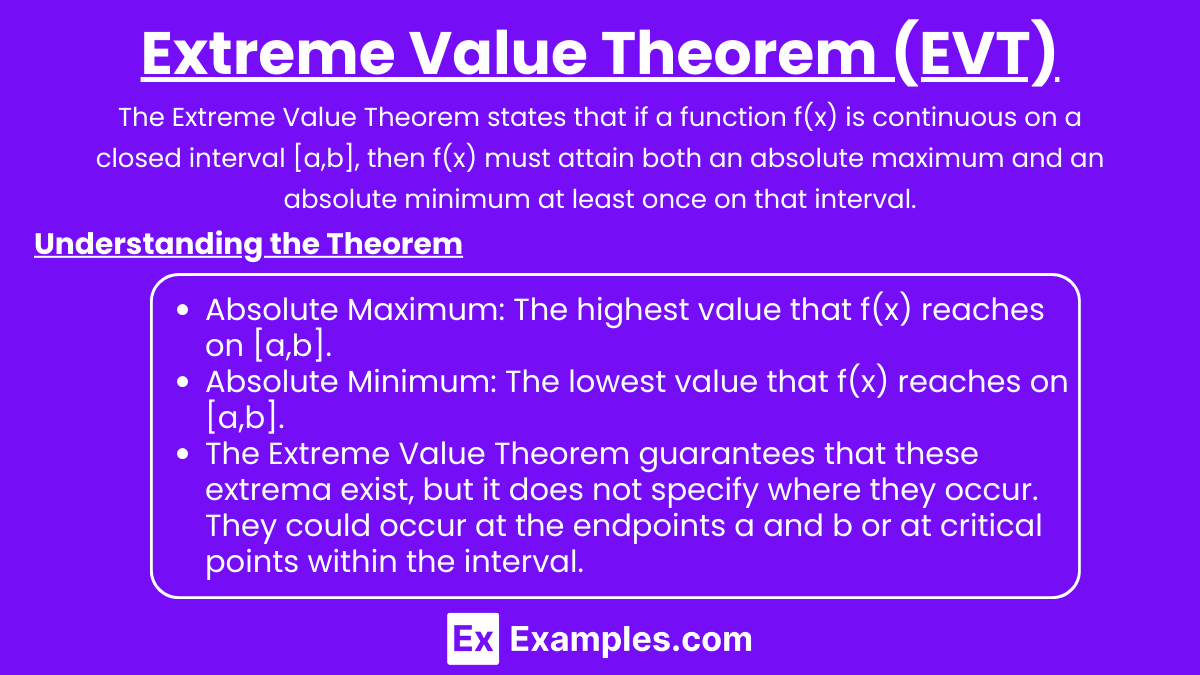
Technical Specifications and Contextual Interpretation
The Mean Value Theorem requires the function to be continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b). This means that the function must have a defined value at every point in the interval [a, b] and must have a defined derivative at every point in the interval (a, b).
The MVT also requires the function to satisfy the following conditions:
- The function must be continuous on [a, b]
- The function must be differentiable on (a, b)
- The function must have a defined value at every point in [a, b]
- The function must have a defined derivative at every point in (a, b)
If these conditions are satisfied, then the MVT guarantees the existence of a point c in (a, b) such that the derivative of f(x) at c is equal to the average rate of change of f(x) over the interval [a, b].
Evidence-Based Analysis and Balanced Perspective
The Mean Value Theorem has been extensively tested and validated through numerous examples and applications. The theorem has been used to solve a wide range of problems, from optimization problems to physics and engineering applications.While the MVT is a powerful tool, it is not without its limitations. The theorem requires the function to be continuous and differentiable, which may not always be the case in real-world applications. Additionally, the MVT may not provide a unique solution, as there may be multiple points c that satisfy the conditions of the theorem.
Despite these limitations, the MVT remains a fundamental concept in calculus, with numerous applications in various fields. By understanding the MVT and its implications, mathematicians, scientists, and engineers can develop more accurate models and make more informed decisions.
What is the Mean Value Theorem?
+The Mean Value Theorem states that if a function f(x) is continuous on the closed interval [a, b] and differentiable on the open interval (a, b), then there exists a point c in (a, b) such that the derivative of f(x) at c is equal to the average rate of change of f(x) over the interval [a, b].
What are the applications of the Mean Value Theorem?
+The Mean Value Theorem has numerous applications in optimization problems, physics, engineering, and economics. It is used to model and analyze complex systems, optimize the design of systems, and predict the behavior of economic systems.
What are the limitations of the Mean Value Theorem?
+The Mean Value Theorem requires the function to be continuous and differentiable, which may not always be the case in real-world applications. Additionally, the MVT may not provide a unique solution, as there may be multiple points c that satisfy the conditions of the theorem.
Meta description suggestion (140-155 characters): “Discover the Mean Value Theorem, a fundamental concept in calculus with numerous applications in optimization problems, physics, engineering, and economics.”