The gas laws are a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, describing the behavior of gases under various conditions. Understanding these laws is crucial for students, researchers, and professionals in fields such as chemistry, physics, and engineering. In this article, we will explore five essential tips for mastering the gas laws, including the ideal gas law, Charles' law, Boyle's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law.
Key Points
- Understand the ideal gas law and its applications
- Recognize the importance of Charles' law in describing temperature-volume relationships
- Apply Boyle's law to predict pressure-volume changes
- Use Avogadro's law to relate volume and amount of gas
- Analyze Gay-Lussac's law to understand pressure-temperature relationships
Navigating the Ideal Gas Law

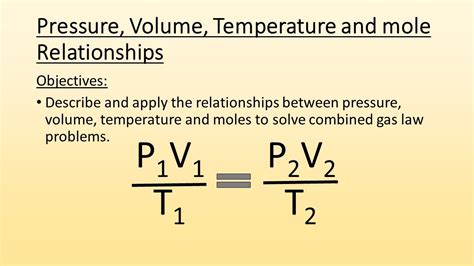
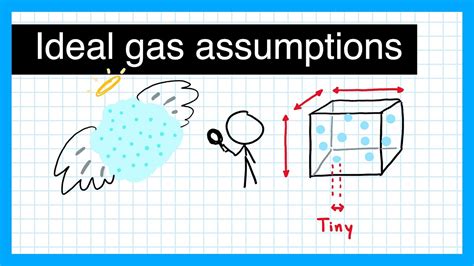
The ideal gas law, also known as the combined gas law, is a fundamental principle that describes the behavior of ideal gases. It is expressed by the equation PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature. To apply the ideal gas law effectively, it is essential to understand the assumptions and limitations of the ideal gas model. For instance, the ideal gas law assumes that gas molecules have no intermolecular forces and occupy no volume, which is not true for real gases. However, the ideal gas law provides a useful approximation for many real-world applications.
Charles’ Law: Temperature-Volume Relationships
Charles’ law states that, at constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature. This law is often expressed by the equation V1 / T1 = V2 / T2, where V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes, and T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures. Understanding Charles’ law is crucial for predicting the behavior of gases in various temperature conditions. For example, if the temperature of a gas increases, its volume will also increase, assuming constant pressure.
| Gas Law | Equation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ideal Gas Law | PV = nRT | Relates pressure, volume, and temperature of an ideal gas |
| Charles' Law | V1 / T1 = V2 / T2 | Describes temperature-volume relationships at constant pressure |
| Boyle's Law | P1V1 = P2V2 | Relates pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature |
| Avogadro's Law | V1 / n1 = V2 / n2 | Describes the relationship between volume and amount of gas |
| Gay-Lussac's Law | P1 / T1 = P2 / T2 | Relates pressure and temperature of a gas at constant volume |
Applying Boyle’s Law and Avogadro’s Law

Boyle’s law states that, at constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume. This law is often expressed by the equation P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and P2 are the initial and final pressures, and V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes. Avogadro’s law, on the other hand, states that, at constant temperature and pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles. Understanding these laws is crucial for predicting the behavior of gases in various conditions. For example, if the pressure of a gas increases, its volume will decrease, assuming constant temperature.
Gay-Lussac’s Law: Pressure-Temperature Relationships
Gay-Lussac’s law states that, at constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature. This law is often expressed by the equation P1 / T1 = P2 / T2, where P1 and P2 are the initial and final pressures, and T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures. Understanding Gay-Lussac’s law is essential for predicting the behavior of gases in various temperature conditions. For instance, if the temperature of a gas increases, its pressure will also increase, assuming constant volume.
What is the difference between the ideal gas law and the combined gas law?
+The ideal gas law and the combined gas law are often used interchangeably, but they refer to the same principle. The combined gas law is a more general form of the ideal gas law, which relates the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas.
How do I apply the gas laws in real-world scenarios?
+The gas laws have numerous applications in fields such as chemistry, physics, and engineering. To apply the gas laws in real-world scenarios, it is essential to understand the assumptions and limitations of each law and to pay attention to the units of measurement.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with the gas laws?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when working with the gas laws include using inconsistent units of measurement, neglecting to consider the assumptions and limitations of each law, and failing to pay attention to the conditions under which the laws are applied.
In conclusion, mastering the gas laws is essential for understanding the behavior of gases under various conditions. By applying the ideal gas law, Charles’ law, Boyle’s law, Avogadro’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law, individuals can predict the behavior of gases and make informed decisions in fields such as chemistry, physics, and engineering. Remember to pay attention to the units of measurement, understand the assumptions and limitations of each law, and apply the laws correctly in real-world scenarios.