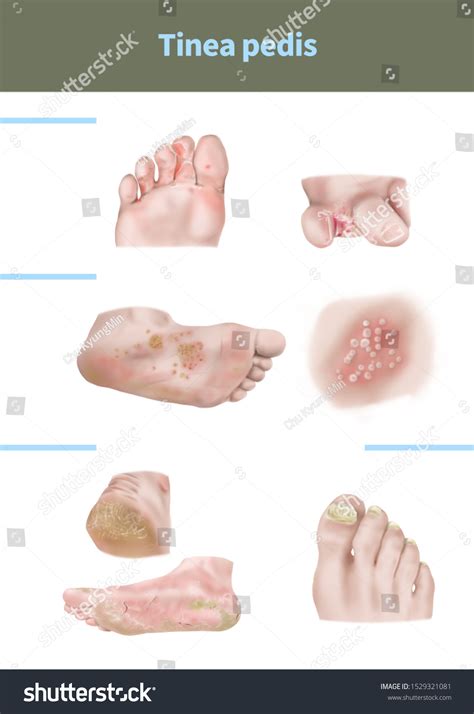
Tinea pedis, commonly known as athlete's foot, is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It is a widespread condition that can cause discomfort, itching, and cracking of the skin. The treatment of tinea pedis typically involves the use of antifungal medications, which can be applied topically or taken orally. In this article, we will discuss the various medications available for the treatment of tinea pedis, their effectiveness, and potential side effects.
Key Points
- Tinea pedis is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet.
- Antifungal medications are the primary treatment for tinea pedis.
- Topical antifungal medications are effective for mild to moderate cases of tinea pedis.
- Oral antifungal medications are prescribed for more severe cases of tinea pedis.
- Combination therapy, which involves the use of both topical and oral antifungal medications, can be effective for treating tinea pedis.
Topical Antifungal Medications

Topical antifungal medications are creams, ointments, or powders that are applied directly to the affected area. They are effective for treating mild to moderate cases of tinea pedis. Some common topical antifungal medications include:
- Clotrimazole (Lotrimin)
- Miconazole (Micatin)
- Terbinafine (Lamisil)
- Butenafine (Mentax)
These medications work by inhibiting the growth of fungi, thereby reducing the severity of symptoms. They are generally well-tolerated and have few side effects. However, they may cause skin irritation, such as redness, itching, or burning, in some individuals.
Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal medications are prescribed for more severe cases of tinea pedis, such as those that do not respond to topical treatment or that involve a large area of the foot. Some common oral antifungal medications include:
- Terbinafine (Lamisil)
- Fluconazole (Diflucan)
- Griseofulvin (Fulvicin)
- Itraconazole (Sporanox)
These medications work by inhibiting the growth of fungi in the body, thereby reducing the severity of symptoms. They are generally effective, but may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or abdominal pain. In rare cases, they may also cause more serious side effects, such as liver damage or allergic reactions.
| Medication | Dosage | Duration of Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Terbinafine (Lamisil) | 250 mg/day | 6-12 weeks |
| Fluconazole (Diflucan) | 150 mg/day | 6-12 weeks |
| Griseofulvin (Fulvicin) | 500 mg/day | 12-24 weeks |
| Itraconazole (Sporanox) | 200 mg/day | 6-12 weeks |

Combination Therapy
Combination therapy, which involves the use of both topical and oral antifungal medications, can be effective for treating tinea pedis. This approach can help to improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of recurrence. For example, using a topical antifungal medication, such as clotrimazole, in combination with an oral antifungal medication, such as terbinafine, may be more effective than using either medication alone.
Prevention
Preventing tinea pedis involves practicing good foot hygiene, such as washing the feet daily, drying them thoroughly, and wearing clean socks. It is also essential to wear shoes that fit well and to change them regularly to prevent moisture buildup. Additionally, using antifungal powders or sprays can help to prevent the growth of fungi on the feet.
What is the most effective treatment for tinea pedis?
+The most effective treatment for tinea pedis depends on the severity of the infection. For mild cases, topical antifungal medications may be sufficient, while more severe cases may require oral antifungal medications or combination therapy.
How long does it take to treat tinea pedis?
+The duration of treatment for tinea pedis varies depending on the severity of the infection and the type of medication used. Topical antifungal medications may take 2-6 weeks to clear the infection, while oral antifungal medications may take 6-12 weeks.
Can tinea pedis be prevented?
+Yes, tinea pedis can be prevented by practicing good foot hygiene, wearing clean socks, and using antifungal powders or sprays. It is also essential to wear shoes that fit well and to change them regularly to prevent moisture buildup.
In conclusion, tinea pedis is a common fungal infection that can be treated with antifungal medications. Topical antifungal medications are effective for mild to moderate cases, while oral antifungal medications are prescribed for more severe cases. Combination therapy, which involves the use of both topical and oral antifungal medications, can be effective for treating tinea pedis. Preventing tinea pedis involves practicing good foot hygiene and using antifungal powders or sprays. By understanding the treatment options and prevention strategies, individuals can effectively manage tinea pedis and reduce the risk of recurrence.



