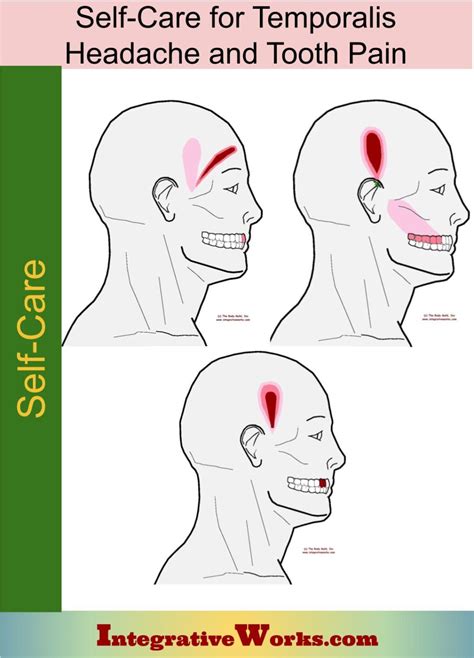
Tooth pain and headache are two common complaints that can be related in various ways. While they can occur independently, there are instances where tooth pain can trigger or exacerbate headaches, and vice versa. Understanding the potential connections between these two conditions can help in diagnosing and treating the underlying causes effectively. The relationship between tooth pain and headache is complex and can involve multiple factors, including dental issues, neurological conditions, and even systemic diseases.
The most direct connection between tooth pain and headache is through the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for sensation in the face, including the teeth, and also plays a role in headache pathways. When a tooth becomes problematic due to decay, infection, or other dental issues, it can stimulate the trigeminal nerve, leading to pain that is not only localized to the tooth but can also radiate to other areas of the face and head, manifesting as a headache. This phenomenon is often seen in cases of severe tooth decay, abscesses, or gum disease, where the infection or inflammation can irritate the nerve endings and cause referred pain.
Key Points
- Tooth pain can be a direct cause of headache due to the stimulation of the trigeminal nerve.
- Dental issues such as tooth decay, abscesses, and gum disease are common causes of tooth pain that can lead to headaches.
- The connection between tooth pain and headache is bidirectional, with some headaches also potentially causing or exacerbating tooth pain.
- Diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause are crucial for relieving both tooth pain and headache.
- Preventive dental care, including regular check-ups and good oral hygiene practices, can help in minimizing the risk of developing tooth pain and related headaches.
Understanding the Trigeminal Nerve’s Role
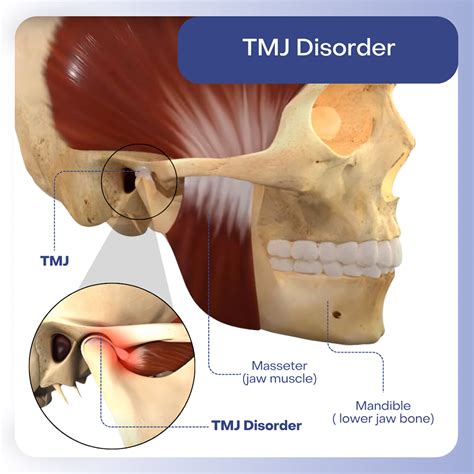
The trigeminal nerve is a crucial component in understanding the relationship between tooth pain and headache. It is the fifth cranial nerve and has three major branches that supply sensation to different parts of the face, including the teeth. When any part of the face or teeth is stimulated, such as by pain or pressure, it can activate the trigeminal nerve. In the context of tooth pain, this activation can lead to the sensation of pain being referred to other areas innervated by the trigeminal nerve, including parts of the head, thereby causing a headache.
Dental Conditions Leading to Tooth Pain and Headache
Several dental conditions can lead to tooth pain and subsequently cause or exacerbate headaches. These include:
- Tooth Decay and Abscesses: Bacterial infection of the tooth pulp can cause severe pain and lead to the formation of an abscess, which can irritate the surrounding tissues and nerves, including the trigeminal nerve.
- Gum Disease: Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) or the supporting tissues of the teeth (periodontitis) can cause pain and discomfort, potentially triggering headaches.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders: The TMJ connects the jawbone to the skull and plays a role in jaw movement. Disorders of the TMJ can cause pain in the jaw, face, and head, and are often associated with tooth grinding or clenching, which can also contribute to tooth pain.
| Dental Condition | Association with Headache |
|---|---|
| Tooth Decay and Abscesses | Direct stimulation of the trigeminal nerve due to infection or inflammation |
| Gum Disease | Potential for referred pain to the head due to widespread inflammation |
| TMJ Disorders | Contribution to both tooth pain and headache through jaw dysfunction and muscle tension |

Treatment and Prevention Strategies

Treatment for tooth pain and related headaches depends on the underlying cause. For dental issues, this may involve:
- Fillings or Crowns: To address tooth decay and prevent further complications.
- Root Canal Therapy: To treat infections of the tooth pulp.
- Periodontal Treatment: To manage gum disease and prevent its progression.
- TMJ Therapy: Which can include jaw exercises, oral appliances to reduce grinding, and in some cases, surgery.
Prevention is also key, with regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, and a balanced diet contributing to minimizing the risk of dental issues that can lead to tooth pain and headaches.
Systemic Conditions and Headaches
While the focus has been on dental causes, it’s also important to recognize that some systemic conditions and other factors can contribute to both tooth pain and headaches. These include sinus infections, migraines, tension headaches, and even conditions like fibromyalgia. A thorough medical and dental history, along with a physical examination, can help in identifying such conditions and guiding appropriate management.
What are the common causes of tooth pain that can lead to headaches?
+
How can I prevent tooth pain and related headaches?
+Prevention involves regular dental check-ups, practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding foods and drinks that can contribute to tooth decay, and managing stress to reduce teeth grinding and clenching.
When should I seek professional help for tooth pain and headaches?
+You should seek help if you experience severe, persistent, or recurring tooth pain or headaches, as these could be signs of underlying conditions that need medical or dental attention.
In conclusion, the relationship between tooth pain and headache is intricate, involving direct and indirect pathways. Understanding these connections is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment. By recognizing the potential causes and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of experiencing these painful conditions. For those already affected, seeking professional advice from a dentist or healthcare provider is the first step towards relief and recovery.