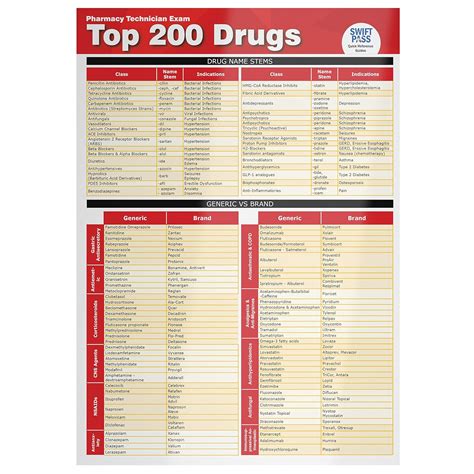
The pharmaceutical landscape is vast and complex, with numerous prescription drugs available to treat a wide range of medical conditions. Among these, there are certain medications that stand out due to their widespread use, therapeutic importance, and impact on public health. This article will delve into the top 200 prescription drugs, exploring their classifications, uses, and significance in modern medicine.
Introduction to Prescription Drugs
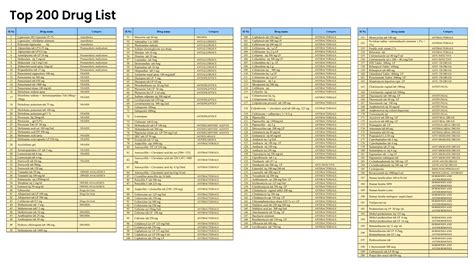
Prescription drugs are medications that can only be dispensed by a licensed healthcare provider. They are developed and tested for their safety and efficacy in treating specific conditions, and their use is strictly regulated by health authorities worldwide. The development of new prescription drugs is a costly and time-consuming process, involving extensive research, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals.
Key Points
- The top 200 prescription drugs include a wide range of therapeutic classes, such as analgesics, antibiotics, antihypertensives, and antidiabetics.
- These medications are used to treat common conditions like pain, infections, hypertension, diabetes, and various chronic diseases.
- The list of top prescription drugs can vary by region, reflecting differences in disease prevalence, healthcare systems, and prescribing practices.
- Understanding the top 200 prescription drugs is essential for healthcare professionals, patients, and policymakers to ensure appropriate use, manage side effects, and allocate healthcare resources effectively.
- The development and use of prescription drugs are strictly regulated, with ongoing monitoring for safety and efficacy.
Therapeutic Categories of Top Prescription Drugs

The top 200 prescription drugs can be broadly categorized into several therapeutic classes based on their primary uses. These include:
Analgesics and Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Analgesics, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, are used to relieve pain, while anti-inflammatory drugs, including corticosteroids and NSAIDs, reduce inflammation and swelling. These medications are commonly prescribed for acute and chronic pain management, as well as for treating conditions like arthritis.
Antibiotics and Antimicrobials
Antibiotics, such as amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin, are crucial in treating bacterial infections. Antimicrobials, including antivirals and antifungals, target viral and fungal infections, respectively. The appropriate use of these drugs is vital to combat microbial resistance and ensure effective infection control.
Cardiovascular Drugs
Medications for cardiovascular diseases, including antihypertensives (e.g., lisinopril), antiplatelets (e.g., aspirin), and statins (e.g., atorvastatin), are among the most prescribed drugs. They are essential for managing hypertension, preventing heart attacks and strokes, and controlling cholesterol levels.
Diabetes Medications
With the increasing prevalence of diabetes, medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin are critical for blood sugar control. These drugs help manage diabetes symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the quality of life for diabetic patients.
| Therapeutic Category | Examples of Drugs | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Analgesics | Acetaminophen, Ibuprofen | Pain relief |
| Antibiotics | Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin | Treating bacterial infections |
| Antihypertensives | Lisinopril, Amlodipine | Managing hypertension |
| Antidiabetics | Metformin, Insulin | Controlling blood sugar levels |

Factors Influencing the List of Top Prescription Drugs
The list of top 200 prescription drugs can vary significantly depending on several factors, including:
Disease Prevalence
Regions with higher prevalence rates of certain diseases will have different top prescription drugs compared to areas with lower rates. For example, in regions with a high prevalence of diabetes, antidiabetic medications will be more commonly prescribed.
Healthcare Policies and Guidelines
Healthcare policies, treatment guidelines, and formulary listings influence which medications are prescribed. These factors can lead to variations in the most commonly used drugs between different countries or healthcare systems.
Pharmaceutical Market and Availability
The availability of drugs, their pricing, and marketing strategies can affect their prescription rates. Newly approved medications or generic versions of existing drugs can also shift the landscape of commonly prescribed medications.
Implications and Future Directions
Understanding the top 200 prescription drugs has significant implications for healthcare practice, policy, and research. It highlights the need for:
Appropriate Prescribing Practices
Healthcare providers must be knowledgeable about the most effective and safe medications for various conditions, ensuring that patients receive optimal care while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
Continuous Monitoring and Research
Ongoing surveillance of drug safety and efficacy, as well as research into new therapeutic agents, is essential to address emerging health challenges and improve patient outcomes.
Public Health Initiatives
Public health strategies, including education campaigns and preventive measures, can reduce the burden of chronic diseases and infectious conditions, thereby influencing the demand for certain prescription drugs.
What are the most commonly prescribed analgesics?
+The most commonly prescribed analgesics include acetaminophen and ibuprofen, which are used for pain relief and to reduce inflammation.
How do antibiotics work?
+Antibiotics work by targeting and killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria that cause infections, thereby helping the body's immune system to recover from the infection.
What are the benefits of using statins for cholesterol management?
+Statins are beneficial for cholesterol management as they reduce the levels of "bad" LDL cholesterol in the blood, thereby lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke.
In conclusion, the top 200 prescription drugs represent a crucial component of modern healthcare, offering effective treatments for a wide range of medical conditions. Understanding these medications, their uses, and their implications is vital for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and the general public. As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve, ongoing education, research, and public health initiatives will be essential in ensuring the appropriate use of these drugs and improving patient outcomes.