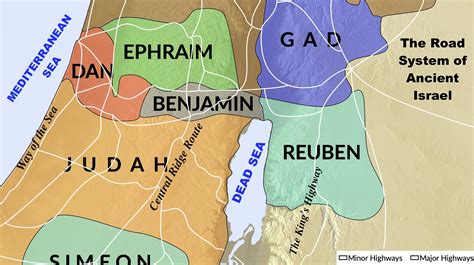
The Tribe of Benjamin, one of the twelve tribes of Israel, has a rich and complex history that spans over three millennia. As the youngest son of Jacob and Rachel, Benjamin's story is deeply intertwined with the biblical narrative, playing a significant role in the formation of the Israelite nation. To understand the history of the Tribe of Benjamin, it is essential to delve into the biblical account, exploring their origins, migration, and eventual settlement in the Promised Land.
Origins and Early History
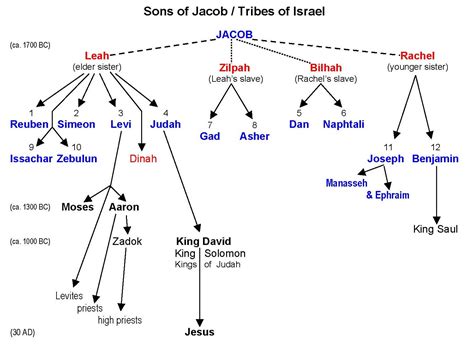
The Tribe of Benjamin originated from the patriarch Jacob’s youngest son, Benjamin, born to his favorite wife, Rachel. The name Benjamin, meaning “son of the right hand,” signifies his birth as the youngest and most beloved child. According to the biblical account in Genesis 35:18, Benjamin’s birth occurred near Bethlehem, and his mother, Rachel, died shortly after. Jacob’s love for Benjamin and his mother, Rachel, is evident in the biblical narrative, highlighting the significance of this tribe in the early history of Israel.
Migration to Egypt and the Exodus
As the Israelites faced famine and hardship, Jacob’s sons, including Benjamin, migrated to Egypt, where they were eventually enslaved. The biblical account in Genesis 46:21 and Numbers 26:38-41 provides a detailed description of the Benjaminite clans and their population during this period. The Tribe of Benjamin played a crucial role in the Exodus, with their military prowess and strategic location contributing to the Israelites’ success. The biblical narrative highlights the bravery and loyalty of the Benjaminites, particularly in the battle against the Philistines, as recorded in 1 Samuel 4:1-11.
| Benjaminite Clans | Population (Exodus) |
|---|---|
| Bela | 27,200 |
| Ashbel | 26,000 |
| Aharah | 24,400 |
| Nohah | 22,600 |
| Rapha | 21,300 |
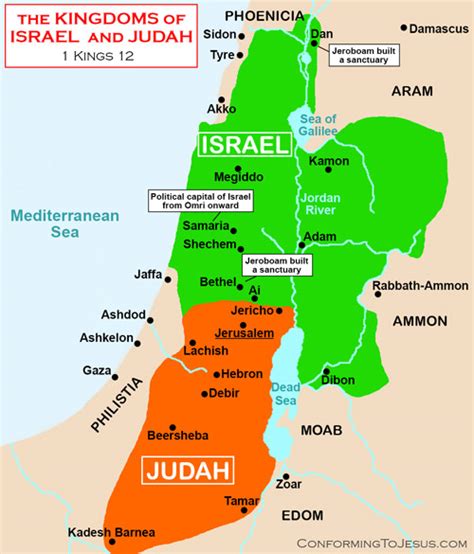
Settlement in Canaan and the Monarchy
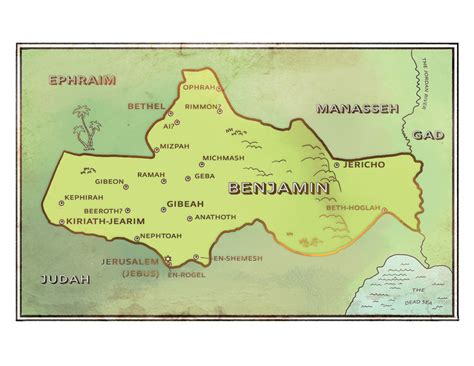
Following the Exodus, the Tribe of Benjamin settled in the central region of Canaan, bordering the tribes of Ephraim and Judah. The biblical account in Joshua 18:11-28 describes the Benjaminite territory, which included the cities of Jerusalem, Gibeah, and Bethel. The Tribe of Benjamin played a crucial role in the Israelite monarchy, with King Saul, the first king of Israel, hailing from the Benjaminite clan of Matri (1 Samuel 9:1-2). The Benjaminites’ loyalty to the monarchy and their military prowess were instrumental in the early successes of the Israelite kingdom.
Division and Assyrian Conquest
As the Israelite kingdom divided into two, with the northern kingdom of Israel and the southern kingdom of Judah, the Tribe of Benjamin remained loyal to the Davidic dynasty in Judah. The biblical account in 1 Kings 12:21-24 describes the Benjaminites’ decision to remain with the southern kingdom, ensuring their continued influence in the region. However, the Tribe of Benjamin eventually fell to the Assyrian conquest, as recorded in 2 Kings 15:29 and 17:1-6, leading to their dispersal and assimilation into the surrounding cultures.
Key Points
- The Tribe of Benjamin originated from the youngest son of Jacob, Benjamin, and played a significant role in the formation of the Israelite nation.
- The Benjaminites were known for their military prowess, strategic location, and loyal dedication to the Israelite monarchy.
- The Tribe of Benjamin settled in the central region of Canaan, bordering the tribes of Ephraim and Judah, and included the cities of Jerusalem, Gibeah, and Bethel.
- The Benjaminites remained loyal to the Davidic dynasty in Judah, ensuring their continued influence in the region, but eventually fell to the Assyrian conquest.
- The Tribe of Benjamin's history is marked by their bravery, loyalty, and strategic contributions to the Israelite nation, leaving a lasting legacy in the biblical narrative.
Legacy and Modern Relevance
The Tribe of Benjamin’s legacy extends beyond their historical contributions to the Israelite nation. Their story serves as a testament to the importance of loyalty, bravery, and strategic thinking. In modern times, the Tribe of Benjamin’s history has been the subject of extensive research and debate, with scholars seeking to understand the complexities of their origins, migration, and settlement in Canaan. The Benjaminites’ experience also serves as a reminder of the enduring power of faith and community, as they navigated the challenges of their time, ultimately leaving a lasting impact on the biblical narrative.
What is the significance of the Tribe of Benjamin in the biblical narrative?
+The Tribe of Benjamin played a crucial role in the formation of the Israelite nation, contributing to the Exodus, the conquest of Canaan, and the Israelite monarchy. Their loyalty, bravery, and strategic thinking were instrumental in the early successes of the Israelite kingdom.
What was the relationship between the Tribe of Benjamin and the Israelite monarchy?
+The Tribe of Benjamin was closely tied to the Israelite monarchy, with King Saul, the first king of Israel, hailing from the Benjaminite clan of Matri. The Benjaminites remained loyal to the Davidic dynasty in Judah, ensuring their continued influence in the region.
What is the modern relevance of the Tribe of Benjamin’s history?
+The Tribe of Benjamin’s history serves as a testament to the importance of loyalty, bravery, and strategic thinking. Their experience also reminds us of the enduring power of faith and community, as they navigated the challenges of their time, ultimately leaving a lasting impact on the biblical narrative.