The Pythagorean trigonometric identity is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in the field of trigonometry. This identity is based on the Pythagorean theorem and is used to describe the relationship between the sine and cosine of an angle in a right-angled triangle. The Pythagorean identity states that for any angle θ, the sum of the squares of the sine and cosine of θ is equal to 1. This can be expressed mathematically as: sin²θ + cos²θ = 1.
Derivation of the Pythagorean Identity
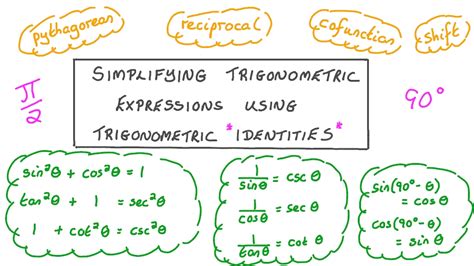
The Pythagorean identity can be derived from the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. By defining the sine and cosine of an angle in terms of the ratios of the sides of a right triangle, we can derive the Pythagorean identity. Specifically, if we consider a right triangle with an angle θ, and define the sine of θ as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse, and the cosine of θ as the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the angle to the length of the hypotenuse, then the Pythagorean theorem can be expressed in terms of these ratios.
Mathematical Representation
Mathematically, the Pythagorean identity can be represented as: sin²θ + cos²θ = 1. This equation shows that the sum of the squares of the sine and cosine of any angle θ is always equal to 1. This identity is useful in a wide range of applications, including solving trigonometric equations, simplifying complex expressions, and proving other trigonometric identities.
| Trigonometric Function | Definition |
|---|---|
| Sine (sin) | Opposite side / Hypotenuse |
| Cosine (cos) | Adjacent side / Hypotenuse |

Key Points
- The Pythagorean identity states that sin²θ + cos²θ = 1 for any angle θ.
- This identity is derived from the Pythagorean theorem and the definitions of sine and cosine in a right triangle.
- The Pythagorean identity is useful for simplifying trigonometric expressions and solving equations.
- This identity is a fundamental concept in trigonometry and has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering.
- Understanding the Pythagorean identity is essential for working with trigonometric functions and solving problems in these fields.
Applications of the Pythagorean Identity
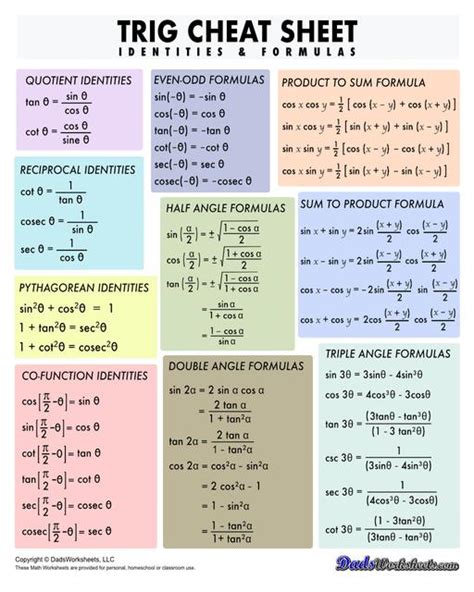
The Pythagorean identity has numerous applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering. It is used to simplify trigonometric expressions, solve equations, and prove other trigonometric identities. In physics, the Pythagorean identity is used to describe the relationship between the components of vectors and the magnitude of the resultant vector. In engineering, it is used to solve problems involving right triangles and trigonometric functions.
Real-World Examples
In real-world applications, the Pythagorean identity is used in a wide range of fields, including navigation, physics, and engineering. For example, in navigation, the Pythagorean identity is used to calculate distances and directions between locations. In physics, it is used to describe the motion of objects and the forces acting upon them. In engineering, it is used to design and optimize systems, such as bridges, buildings, and electronic circuits.
| Field of Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Navigation | Calculating distances and directions between locations |
| Physics | Describing the motion of objects and the forces acting upon them |
| Engineering | Designing and optimizing systems, such as bridges, buildings, and electronic circuits |
What is the Pythagorean identity?
+The Pythagorean identity is a mathematical equation that states that the sum of the squares of the sine and cosine of an angle is always equal to 1. This can be expressed mathematically as: sin²θ + cos²θ = 1.
Where is the Pythagorean identity used?
+The Pythagorean identity is used in a wide range of fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering. It is used to simplify trigonometric expressions, solve equations, and prove other trigonometric identities.
Why is the Pythagorean identity important?
+The Pythagorean identity is important because it provides a fundamental relationship between the sine and cosine of an angle. This relationship is used to solve a wide range of problems in mathematics, physics, and engineering, and is a key concept in trigonometry.



