The concept of a two-column proof is a fundamental aspect of geometry and mathematical reasoning. It provides a structured approach to proving the validity of geometric statements, allowing individuals to organize their thoughts and clearly demonstrate the logical flow of their arguments. In this explanation, we will delve into the world of two-column proofs, exploring their components, benefits, and applications, while highlighting the importance of rigorous mathematical reasoning.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic structure of a two-column proof, including statements and reasons.
- Recognizing the importance of logical reasoning and argumentation in geometric proofs.
- Applying two-column proofs to various geometric theorems and problems.
- Developing critical thinking skills through the creation and evaluation of proofs.
- Utilizing two-column proofs as a tool for enhancing mathematical communication and clarity.
Introduction to Two-Column Proofs
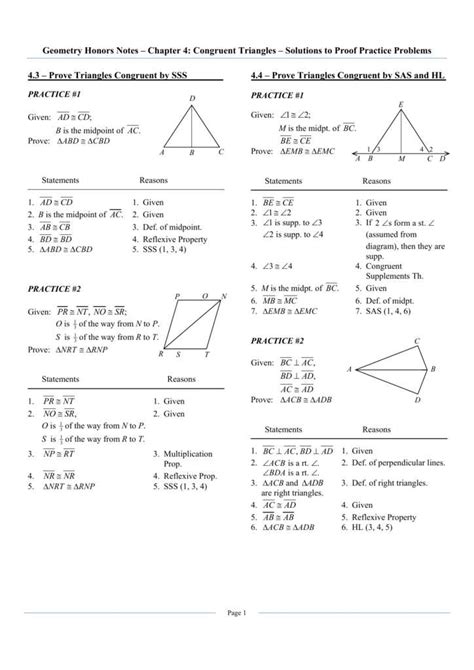
A two-column proof is a methodical way of presenting a geometric proof, where statements and their corresponding reasons are listed in two separate columns. The left column typically contains the statements, which are the steps or conclusions being made, while the right column provides the reasons or justifications for each statement. This format helps in maintaining clarity and ensures that each step of the proof is well-supported and logically connected to the previous steps.
Components of a Two-Column Proof
A standard two-column proof includes several key components: the statement, which is the assertion being made; the reason, which explains why the statement is true; and sometimes, a diagram, which can help illustrate the geometric configuration being discussed. The statements are usually numbered for reference, and the reasons may cite specific theorems, postulates, or previously proven statements. Understanding these components is crucial for constructing and evaluating two-column proofs.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Statement | The assertion or step being made in the proof. |
| Reason | The justification or explanation for why the statement is true. |
| Diagram | A visual representation of the geometric figures involved. |
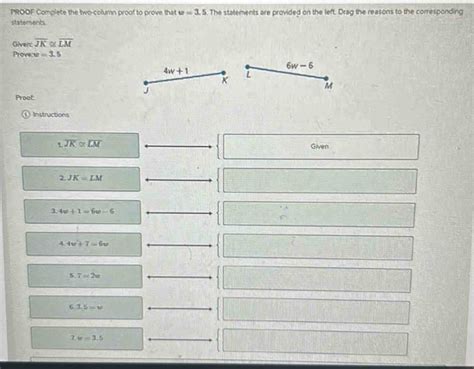
Benefits and Applications of Two-Column Proofs
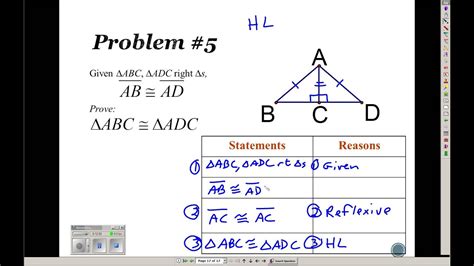
Two-column proofs offer several benefits in the learning and practice of geometry. They promote a systematic approach to problem-solving, enhancing the ability to break down complex problems into manageable steps. Furthermore, they foster critical thinking and logical reasoning, as each step must be carefully justified. The clarity and structure provided by two-column proofs also make them an excellent tool for communication among mathematicians and students, facilitating the sharing and verification of mathematical ideas.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Engaging with two-column proofs, whether by creating them or evaluating existing ones, is an effective way to develop critical thinking skills. It requires analyzing each statement and its corresponding reason, assessing whether the logic is sound, and considering potential flaws or alternative arguments. This process not only deepens one’s understanding of geometric concepts but also cultivates a more nuanced and rigorous approach to mathematical reasoning.
As we explore the realm of two-column proofs, it becomes evident that they are not merely a tool for geometric problem-solving but also a gateway to understanding the underlying principles of logic and argumentation in mathematics. By embracing this structured method of proof, individuals can enhance their mathematical literacy, foster a deeper appreciation for the subject, and develop a set of skills that are transferable to a wide range of intellectual pursuits.
What is the primary purpose of using a two-column proof in geometry?
+The primary purpose of a two-column proof is to provide a clear, step-by-step justification for a geometric statement, ensuring that each assertion is logically supported and easy to follow.
How do two-column proofs contribute to the development of critical thinking skills?
+Two-column proofs contribute to the development of critical thinking skills by requiring individuals to evaluate the logical coherence of each step in a proof, consider the validity of the reasons provided, and potentially identify flaws or alternative arguments.
What role do diagrams play in two-column proofs?
+Diagrams in two-column proofs serve as visual aids, helping to illustrate the geometric configurations and relationships being discussed. They can make the proof more intuitive and easier to understand, especially for complex geometric concepts.
In conclusion, two-column proofs are a powerful tool in the realm of geometry, offering a structured approach to mathematical reasoning and proof. By understanding and applying this method, individuals can deepen their grasp of geometric concepts, enhance their critical thinking skills, and develop a more nuanced appreciation for the logic and beauty of mathematics. As we continue to explore and apply two-column proofs, we not only refine our mathematical literacy but also cultivate a mindset that values rigor, clarity, and logical argumentation.