The concepts of union and intersection are fundamental in set theory, a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of sets, which are collections of unique objects. Understanding these concepts is crucial for various applications in mathematics, computer science, and data analysis. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, examples, and applications of union and intersection, providing a comprehensive overview of these essential mathematical operations.
Definition of Union
The union of two sets, denoted as A ∪ B, is the set of all elements that are in A, in B, or in both. In other words, it is the combination of all elements from both sets without duplicates. For instance, if A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {3, 4, 5}, then A ∪ B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}. The union operation is commutative, meaning that A ∪ B = B ∪ A, and associative, meaning that (A ∪ B) ∪ C = A ∪ (B ∪ C).
Properties of Union
The union operation has several important properties. It is idempotent, meaning that A ∪ A = A. Additionally, the union of a set with the empty set results in the original set, i.e., A ∪ ∅ = A. These properties make the union operation a powerful tool for combining sets in various mathematical and computational contexts.
Key Points
- The union of two sets contains all elements from both sets without duplicates.
- The union operation is commutative and associative.
- The union of a set with itself results in the original set (idempotent property).
- The union of a set with the empty set results in the original set.
- Union is a fundamental operation in set theory with applications in mathematics, computer science, and data analysis.
Definition of Intersection
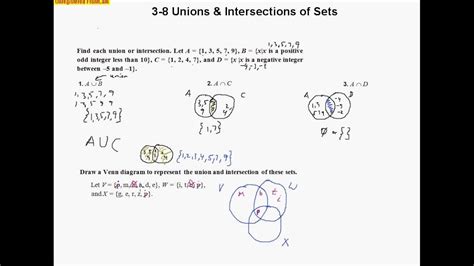
The intersection of two sets, denoted as A ∩ B, is the set of all elements that are common to both A and B. In other words, it is the set of elements that are simultaneously in A and in B. For example, if A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {3, 4, 5}, then A ∩ B = {3}. The intersection operation is also commutative, meaning that A ∩ B = B ∩ A, and associative, meaning that (A ∩ B) ∩ C = A ∩ (B ∩ C).
Properties of Intersection
The intersection operation has several key properties. It is idempotent, meaning that A ∩ A = A. The intersection of a set with the empty set results in the empty set, i.e., A ∩ ∅ = ∅. Additionally, the intersection of a set with the universal set (the set containing all elements under consideration) results in the original set, i.e., A ∩ U = A. These properties highlight the importance of intersection in identifying common elements between sets.
| Operation | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Union (A ∪ B) | Set of all elements in A, B, or both | A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {3, 4, 5}, A ∪ B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} |
| Intersection (A ∩ B) | Set of all elements common to both A and B | A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {3, 4, 5}, A ∩ B = {3} |

Applications of Union and Intersection
The union and intersection operations have numerous applications in mathematics, computer science, and data analysis. In database management, these operations are used in SQL queries to combine or find common data between different tables. In data analysis, union and intersection are used to combine datasets or find overlapping data points. In mathematical modeling, these operations are used to represent complex relationships between sets of variables or entities.
Real-World Examples
In a social media platform, the union operation can be used to combine the friends lists of two users, while the intersection operation can be used to find the common friends between them. In a marketing database, the union of customer lists from different campaigns can help identify the total reach, while the intersection can help identify customers who responded to multiple campaigns.
What is the difference between the union and intersection of two sets?
+The union of two sets contains all elements from both sets without duplicates, while the intersection contains only the elements common to both sets.
How are union and intersection used in real-world applications?
+These operations are used in database querying, data analysis, and mathematical modeling to combine or find common data between different sets or datasets.
What are the key properties of the union and intersection operations?
+Both operations are commutative and associative. The union operation is idempotent, and the union of a set with the empty set results in the original set. The intersection operation is also idempotent, and the intersection of a set with the empty set results in the empty set.
In conclusion, the union and intersection operations are fundamental concepts in set theory, with far-reaching applications in mathematics, computer science, and data analysis. Understanding these operations and their properties is essential for solving problems and making informed decisions in various fields. By applying these concepts, professionals and researchers can efficiently combine and analyze data, identify patterns, and model complex relationships, ultimately driving innovation and progress.