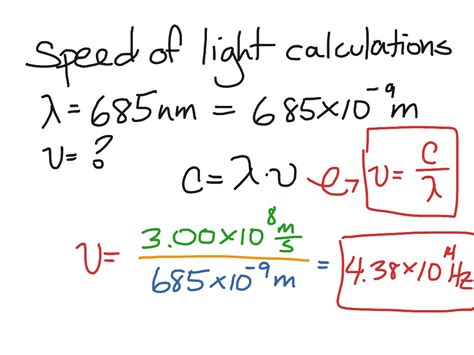The velocity of light, a fundamental constant in physics, has been a subject of fascination for centuries. The speed of light, denoted by the symbol c, is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum. This constant has far-reaching implications in various fields, including electromagnetism, relativity, and quantum mechanics. In this article, we will delve into the velocity of light formula, its derivation, and its significance in the realm of physics.
Historical Background and Development
The concept of the speed of light dates back to ancient Greece, where philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle proposed that light travels at a finite speed. However, it wasn’t until the 17th century that the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light were made by Ole Rømer, a Danish astronomer. Rømer’s experiment involved observing the eclipses of Jupiter’s moons and measuring the time delay between the eclipses. This led to an estimate of the speed of light, which was remarkably close to the actual value.
Derivation of the Velocity of Light Formula
The velocity of light formula is derived from Maxwell’s equations, which describe the behavior of electromagnetic fields. The speed of light is a fundamental constant that relates the electric and magnetic fields. The formula is given by:c = 1 / √(μ₀ε₀)
where c is the speed of light, μ₀ is the magnetic constant (also known as the permeability of free space), and ε₀ is the electric constant (also known as the permittivity of free space). This formula shows that the speed of light is a function of the fundamental constants of the universe.
Key Points
- The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics, approximately equal to 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum.
- The velocity of light formula is derived from Maxwell's equations, which describe the behavior of electromagnetic fields.
- The formula relates the electric and magnetic fields, showing that the speed of light is a function of the fundamental constants of the universe.
- The speed of light has far-reaching implications in various fields, including electromagnetism, relativity, and quantum mechanics.
- Understanding the velocity of light formula is crucial for applications in telecommunications, navigation, and astronomy.
Significance of the Velocity of Light Formula

The velocity of light formula has significant implications in various fields of physics. In electromagnetism, the speed of light is used to describe the behavior of electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, microwaves, and light itself. In relativity, the speed of light is a fundamental constant that relates space and time, and its constancy is a cornerstone of the theory of special relativity. In quantum mechanics, the speed of light is used to describe the behavior of particles, such as photons, and their interactions with matter.
Applications of the Velocity of Light Formula
The velocity of light formula has numerous applications in various fields, including:- Telecommunications: The speed of light is used to design optical communication systems, such as fiber optic cables, which transmit data at high speeds.
- Navigation: The speed of light is used in GPS technology to provide location and time information.
- Astronomy: The speed of light is used to measure the distance to celestial objects, such as stars and galaxies.
| Field of Application | Significance of Velocity of Light Formula |
|---|---|
| Electromagnetism | Describes the behavior of electromagnetic waves |
| Relativity | Relates space and time, and is a cornerstone of special relativity |
| Quantum Mechanics | Describes the behavior of particles, such as photons, and their interactions with matter |
| Telecommunications | Used to design optical communication systems, such as fiber optic cables |
| Navigation | Used in GPS technology to provide location and time information |
| Astronomy | Used to measure the distance to celestial objects, such as stars and galaxies |

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the velocity of light formula is a fundamental concept in physics, with significant implications in various fields. The formula, derived from Maxwell’s equations, relates the electric and magnetic fields and shows that the speed of light is a function of the fundamental constants of the universe. Understanding this formula is crucial for applications in telecommunications, navigation, and astronomy. As we continue to explore the universe and push the boundaries of human knowledge, the velocity of light formula will remain a cornerstone of our understanding of the physical world.What is the significance of the velocity of light formula in physics?
+The velocity of light formula is a fundamental concept in physics, with significant implications in various fields, including electromagnetism, relativity, and quantum mechanics. It relates the electric and magnetic fields and shows that the speed of light is a function of the fundamental constants of the universe.
What are the applications of the velocity of light formula?
+The velocity of light formula has numerous applications in various fields, including telecommunications, navigation, and astronomy. It is used to design optical communication systems, provide location and time information, and measure the distance to celestial objects.
Why is the velocity of light formula important in understanding the universe?
+The velocity of light formula is important in understanding the universe because it provides a fundamental constant that relates space and time. It is a cornerstone of the theory of special relativity and has significant implications for our understanding of the behavior of particles and the structure of the universe.
Meta Description: Learn about the velocity of light formula, its derivation, and its significance in physics. Discover the applications of this fundamental concept in telecommunications, navigation, and astronomy.