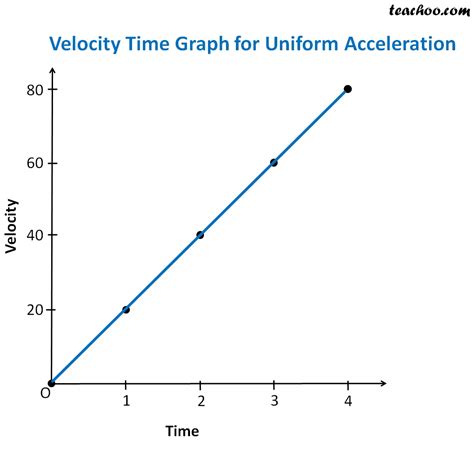
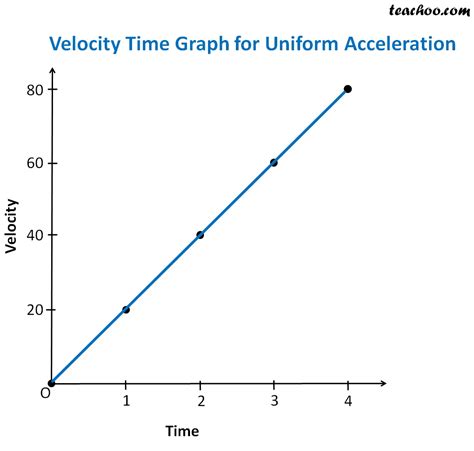
Velocity graphs are a crucial component in the realm of physics and engineering, serving as a visual representation of an object's velocity over time. The velocity of an object is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude (amount of movement) and direction. Understanding how velocity graphs work is essential for analyzing and predicting the motion of objects in various fields, from mechanics to aerospace engineering. In this article, we'll delve into the five primary ways velocity graphs operate, exploring their construction, interpretation, and application in real-world scenarios.
Key Points
- Velocity graphs are used to represent the velocity of an object as a function of time.
- The slope of a velocity graph represents the acceleration of the object.
- Velocity graphs can be used to analyze the motion of objects in one dimension.
- The area under a velocity graph represents the displacement of the object.
- Velocity graphs are essential in understanding and predicting the motion of objects in various fields.
Construction of Velocity Graphs
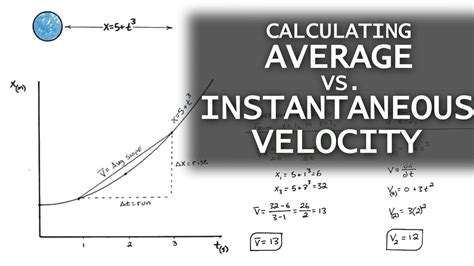
The construction of a velocity graph involves plotting the velocity of an object against time. The velocity is typically represented on the y-axis, while time is represented on the x-axis. The resulting graph can take various forms, depending on the nature of the motion. For instance, if an object is moving at a constant velocity, its velocity graph will be a straight line parallel to the x-axis. On the other hand, if the object is accelerating, the velocity graph will be a curve or a series of connected lines, indicating the change in velocity over time.
Interpreting Velocity Graphs
Interpreting velocity graphs is crucial for understanding the motion of an object. The slope of a velocity graph at any point represents the acceleration of the object at that instant. A positive slope indicates that the object is accelerating in the positive direction, while a negative slope indicates acceleration in the negative direction. If the slope is zero, the object is moving at a constant velocity. Furthermore, the area under a velocity graph represents the displacement of the object over a given time interval. This means that by calculating the area under the curve, one can determine how far the object has traveled.
| Velocity Graph Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Constant Velocity | Straight line parallel to the x-axis |
| Acceleration | Curve or series of connected lines |
| Deceleration | Negative slope |
| Displacement | Area under the velocity graph |
Applications of Velocity Graphs
Velocity graphs have numerous applications across various fields, including physics, engineering, and transportation. They are used to design safer vehicles, optimize traffic flow, and predict the motion of projectiles. In aerospace engineering, velocity graphs are critical for planning trajectories and ensuring the safe launch and recovery of spacecraft. Additionally, velocity graphs are used in the development of autonomous vehicles, allowing them to navigate complex environments and avoid obstacles.
Real-World Examples
A practical example of the application of velocity graphs can be seen in the analysis of a car’s motion. By plotting the car’s velocity against time, one can determine its acceleration, deceleration, and displacement. This information is vital for understanding the car’s performance and safety features. Another example is in the field of sports, where velocity graphs can be used to analyze the motion of athletes, helping coaches to optimize training programs and improve performance.
In conclusion, velocity graphs are a powerful tool for analyzing and predicting the motion of objects. By understanding how to construct, interpret, and apply velocity graphs, individuals in various fields can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of motion, ultimately leading to advancements in technology, safety, and performance.
What is the primary purpose of a velocity graph?
+The primary purpose of a velocity graph is to represent the velocity of an object as a function of time, allowing for the analysis of its motion and the calculation of displacement and acceleration.
How do you calculate the displacement of an object using a velocity graph?
+The displacement of an object can be calculated by determining the area under the velocity graph over a given time interval. This can be done using integration in calculus or by approximating the area using geometric shapes.
What does the slope of a velocity graph represent?
+The slope of a velocity graph at any point represents the acceleration of the object at that instant. A positive slope indicates acceleration in the positive direction, while a negative slope indicates acceleration in the negative direction.