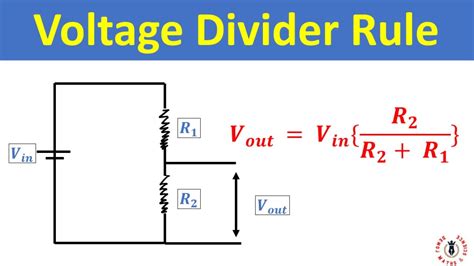
The voltage divider is a fundamental concept in electronics, widely used for reducing voltage levels in circuits. It's a simple yet versatile circuit that consists of two resistors connected in series, with the input voltage applied across the entire series and the output voltage taken across one of the resistors. In this article, we will delve into the world of voltage dividers, exploring five key tips that can help you design, apply, and troubleshoot these circuits more effectively.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic principle of voltage division and its application in circuit design
- Calculating the output voltage of a voltage divider using the voltage divider rule
- Considering the loading effect of the circuit connected to the voltage divider output
- Using voltage dividers in conjunction with other components for more complex circuit functions
- Troubleshooting common issues in voltage divider circuits, such as inaccurate output voltages
Voltage Divider Basics and Applications
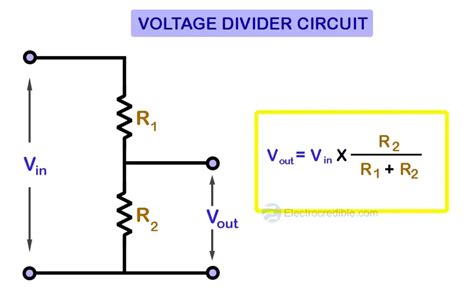
A voltage divider works on the principle that the voltage across each resistor in a series circuit is proportional to the resistance of that resistor. The total resistance (R_total) of the circuit is the sum of the individual resistances (R1 and R2), and the output voltage (V_out) is determined by the ratio of R2 to R_total. This principle is encapsulated in the voltage divider rule: V_out = V_in * (R2 / (R1 + R2)), where V_in is the input voltage.
Calculating Output Voltage and Resistance Values
To calculate the output voltage of a voltage divider, you need to know the input voltage and the values of the two resistors. For example, if you have a 12V input and you want to divide it down to 4V, you can choose appropriate values for R1 and R2. A common approach is to select a value for R2 that will give you the desired output voltage, then calculate R1 based on the desired voltage division ratio. However, it’s crucial to consider the current that will flow through the divider, as high currents can lead to excessive power dissipation in the resistors.
| Resistor Value | Percentage of Total Resistance |
|---|---|
| R1 = 6kΩ | 60% |
| R2 = 4kΩ | 40% |
Practical Considerations: Loading Effect and Component Selection
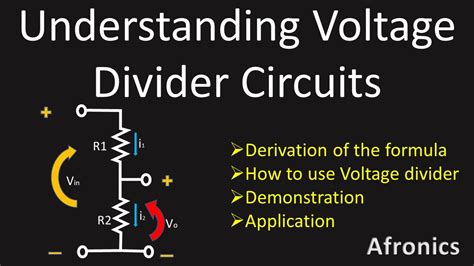
A critical aspect of using voltage dividers is understanding the loading effect. The circuit that the voltage divider is driving (the load) will have its own input resistance, which can affect the voltage divider’s output. If the load resistance is too low, it can significantly alter the voltage division ratio, leading to inaccurate output voltages. To mitigate this, you can use a buffer amplifier or ensure that the load resistance is much higher than the output resistance of the voltage divider.
Advanced Applications and Component Combinations
Voltage dividers are not limited to simple voltage reduction; they can be combined with other components to create more complex circuits. For instance, adding a capacitor in parallel with R2 can create a low-pass filter, useful for filtering out high-frequency noise from the output voltage. Similarly, using a voltage divider as part of a feedback loop in an operational amplifier can allow for precise voltage regulation.
In terms of component selection, choosing the right resistors is crucial. Considerations include the power rating (to ensure the resistors can handle the voltage and current without overheating), tolerance (to ensure the resistance values are close enough to the calculated values), and temperature coefficient (to minimize drift in the output voltage due to temperature changes).
Troubleshooting Voltage Divider Circuits
Troubleshooting a voltage divider circuit often involves checking the basic parameters: ensuring that the input voltage is as expected, verifying that the resistor values are correct, and checking for any signs of overload or damage to the resistors. A common mistake is not accounting for the loading effect of the circuit connected to the output, which can lead to a lower than expected output voltage. Using a multimeter to measure the voltages across each resistor can help identify where the issue lies.
What is the primary function of a voltage divider in electronic circuits?
+The primary function of a voltage divider is to reduce the voltage level from a higher voltage to a lower voltage, which can then be used to power components or circuits that require lower voltages.
How do you calculate the output voltage of a voltage divider circuit?
+The output voltage (V_out) of a voltage divider can be calculated using the formula: V_out = V_in * (R2 / (R1 + R2)), where V_in is the input voltage, and R1 and R2 are the resistances of the two resistors in the divider.
What is the loading effect in voltage divider circuits, and how does it affect the output voltage?
+The loading effect refers to the impact of the load resistance on the output voltage of the voltage divider. If the load resistance is too low, it can draw too much current, reducing the output voltage. This effect can be mitigated by ensuring the load resistance is significantly higher than the output resistance of the divider or by using a buffer amplifier.
In conclusion, voltage dividers are a powerful tool in electronic circuit design, offering a simple and effective way to reduce voltage levels. By understanding the principles behind voltage division, considering practical aspects such as loading effect and component selection, and applying troubleshooting techniques, designers and engineers can harness the full potential of voltage dividers in a wide range of applications.