The management of pleural space issues, such as pneumothorax or pleural effusion, often requires the insertion of a chest tube to drain air or fluid from the pleural cavity. A water seal chest tube, also known as an underwater seal drain, is a type of chest drainage system that utilizes a water seal to prevent air from entering the pleural space while allowing fluid or air to escape. This device plays a critical role in the treatment of various thoracic conditions, providing a safe and effective means of managing pleural space pathology.
Principle of Operation
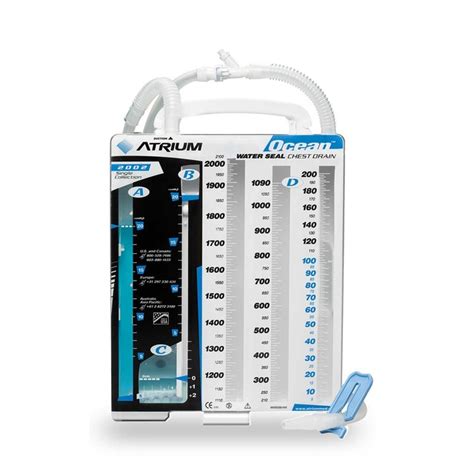
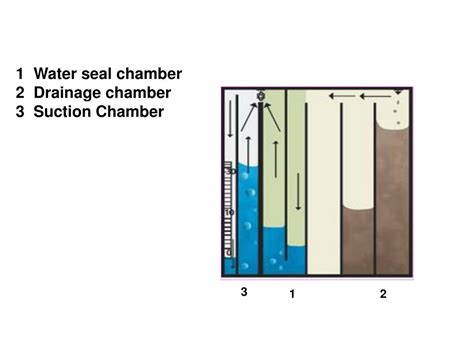
A water seal chest tube functions on the principle of creating a one-way valve effect using a water seal chamber. The chest tube is connected to a drainage system that includes a water seal chamber, a collection chamber, and sometimes a suction control chamber. When the patient inhales, the pressure in the pleural space becomes more negative relative to the atmospheric pressure, allowing fluid or air to escape from the pleural space into the water seal chamber. The water seal acts as a barrier, preventing air from entering the pleural space through the tube, thus maintaining a negative pressure environment within the thoracic cavity.
Components and Setup
The setup of a water seal chest tube includes several key components. The chest tube itself is inserted into the pleural space through a small incision in the chest wall. The tube is then connected to the drainage system, which consists of the water seal chamber, the collection chamber for fluid drainage, and possibly a suction chamber to apply controlled negative pressure. The water seal chamber is filled with a specific amount of water, typically to a level that creates a water seal of about 2 cm. This setup allows for the visualization of air bubbles escaping from the pleural space, providing a means to monitor the resolution of pneumothorax or the drainage of fluid.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Chest Tube | Inserted into the pleural space for drainage |
| Water Seal Chamber | Prevents air from entering the pleural space while allowing fluid/air to escape |
| Collection Chamber | Collects drained fluid for measurement and disposal |
| Suction Chamber (optional) | Applies controlled negative pressure to facilitate drainage |

Clinical Applications and Indications
The water seal chest tube has a broad range of clinical applications, primarily in the management of conditions that affect the pleural space. These include pneumothorax, where air leaks into the space between the lung and chest wall; pleural effusion, characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space; and hemothorax, which involves blood accumulation in the pleural space. The device is also used post-operatively in thoracic surgery to drain fluid and air from the pleural space, facilitating lung expansion and reducing the risk of complications.
Management and Monitoring
The management of a water seal chest tube involves regular monitoring of the drainage system, including the amount and characteristics of the fluid drained, the presence of air leaks, and the patient’s clinical status. It is crucial to maintain the integrity of the system, ensuring that all connections are secure and that the water seal chamber is filled to the appropriate level. Patients with a water seal chest tube require close observation for signs of complications, such as infection, bleeding, or the development of a persistent air leak.
Key Points
- The water seal chest tube is a critical device in the management of pleural space conditions, including pneumothorax and pleural effusion.
- Proper setup and maintenance of the drainage system are essential for its effectiveness and the prevention of complications.
- Clinical applications include post-operative care in thoracic surgery, as well as the treatment of various pleural space pathologies.
- Regular monitoring of the drainage system and the patient's clinical status is vital for optimal management.
- The device operates on the principle of a one-way valve, using a water seal to prevent air entry into the pleural space while allowing fluid or air to escape.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its effectiveness, the use of water seal chest tubes is not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is the risk of complications, such as infection or the development of a persistent air leak. Moreover, the management of these devices requires a significant amount of healthcare resources, including trained personnel and dedicated facilities. Future directions in the development of chest drainage systems may include the incorporation of digital technology to enhance monitoring and management, as well as the development of more sophisticated materials and designs to reduce the risk of complications and improve patient outcomes.
What is the primary function of a water seal chest tube?
+The primary function of a water seal chest tube is to drain fluid or air from the pleural space while preventing air from entering, thus helping to re-expand the lung and restore normal intrathoracic pressure.
How is the water seal chamber maintained?
+The water seal chamber is maintained by ensuring it is filled to the appropriate water level, usually 2 cm, and that all connections are secure to prevent air leaks and maintain the negative pressure environment within the thoracic cavity.
What are the common indications for the use of a water seal chest tube?
+Common indications include the management of pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and hemothorax, as well as post-operative drainage in thoracic surgery.
In conclusion, the water seal chest tube is a vital component in the management of pleural space conditions, offering a reliable and effective means of draining fluid and air while preventing air entry into the pleural space. Its proper use and management are critical for optimal patient outcomes, and ongoing advancements in technology and design are expected to further enhance its efficacy and safety.