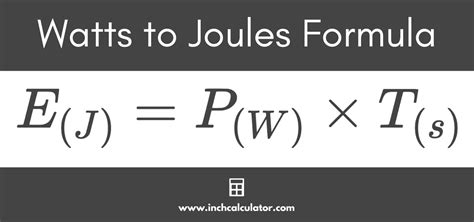The conversion of watts to joules is a fundamental concept in physics, particularly in the context of energy and power. Watts are a unit of power, indicating the rate at which energy is transferred or converted, while joules are a unit of energy, representing the amount of energy expended or work done. Understanding how to convert between these two units is crucial for a wide range of applications, from electrical engineering to mechanical engineering and beyond. In this article, we will explore five ways to convert watts to joules, each providing a unique perspective on this important conversion.
Key Points
- Understanding the basic formula for converting watts to joules, which involves time as a critical factor.
- Using the concept of energy as the product of power and time to perform conversions.
- Applying the formula in various contexts, such as electrical circuits and mechanical systems.
- Recognizing the importance of unit consistency during conversions.
- Practicing conversions with different values to reinforce understanding and proficiency.
Basic Conversion Formula
The most straightforward way to convert watts to joules is by using the formula: Energy (in joules) = Power (in watts) * Time (in seconds). This formula is derived from the definition of power as the rate of energy transfer. For instance, if a device operates at 100 watts for 10 seconds, the total energy it consumes can be calculated as 100 watts * 10 seconds = 1000 joules.
Conversion in Electrical Circuits
In the context of electrical circuits, converting watts to joules can help in understanding how much energy is consumed by a device over a period. For example, a light bulb rated at 20 watts, used for 5 hours (18000 seconds), would consume 20 watts * 18000 seconds = 360,000 joules of energy. This calculation is essential for estimating the energy efficiency of devices and planning electrical supply systems.
| Device Power | Operational Time | Total Energy Consumed |
|---|---|---|
| 100 watts | 10 seconds | 1000 joules |
| 20 watts | 18000 seconds | 360,000 joules |

Conversion in Mechanical Systems
In mechanical systems, the conversion of watts to joules can be applied to understand the work done by a machine. For instance, a motor producing 500 watts of power and operating for 2 minutes (120 seconds) would do 500 watts * 120 seconds = 60,000 joules of work. This calculation is vital for assessing the efficiency and capability of mechanical systems.
Practical Applications and Considerations
Beyond the basic conversion formula, it’s essential to consider the practical aspects of watts to joules conversions. This includes understanding the efficiency of energy conversion, recognizing potential losses, and ensuring that the units used are consistent. In real-world scenarios, the actual energy consumed or work done may differ from theoretical calculations due to various factors such as resistance in electrical circuits or friction in mechanical systems.
The conversion of watts to joules is not just a mathematical exercise but has significant implications for the design, operation, and efficiency of systems across various domains. By mastering this conversion, professionals and enthusiasts alike can better understand and optimize energy usage, leading to more efficient, sustainable, and innovative solutions.
What is the basic formula for converting watts to joules?
+The basic formula is Energy (in joules) = Power (in watts) * Time (in seconds).
How is the conversion applied in electrical circuits?
+In electrical circuits, the conversion helps in understanding how much energy a device consumes over time, calculated as the product of the device’s power rating and the duration of its operation.
What factors can affect the actual energy conversion in practical applications?
+Factors such as efficiency of energy conversion, potential losses, and consistency of units can significantly affect the actual energy conversion in practical applications.