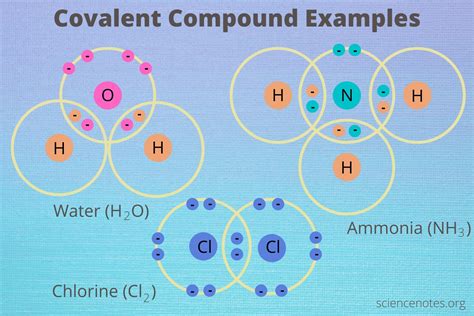
Covalent bonds are a fundamental aspect of chemistry, representing the sharing of electron pairs between atoms to form a stable molecule. The properties of covalent bonds are crucial in understanding the behavior, structure, and reactivity of molecules. In this context, we will delve into the key properties of covalent bonds, exploring their characteristics, types, and the factors that influence their strength and reactivity.
Key Points
- Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
- The strength and length of covalent bonds are influenced by the atoms involved and their electronegativities.
- Polarity in covalent bonds arises from differences in electronegativity between the bonded atoms.
- The type of covalent bond (sigma or pi) affects the shape and reactivity of molecules.
- Covalent bond energy is a critical factor in determining the stability and reactivity of molecules.
Characteristics of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are characterized by the sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two atoms, leading to an attraction that holds the atoms together in a molecule. The characteristics of covalent bonds, such as their strength, length, and polarity, are determined by the atoms involved in the bond and their respective electronegativities. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. Differences in electronegativity between atoms in a bond lead to unequal sharing of electrons, resulting in polar covalent bonds. Nonpolar covalent bonds, on the other hand, occur when the electrons are shared equally between atoms of similar electronegativities.
Types of Covalent Bonds
There are two primary types of covalent bonds: sigma (σ) bonds and pi (π) bonds. Sigma bonds are formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals and are typically stronger than pi bonds. Pi bonds result from the sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals and are crucial in the formation of double and triple bonds. The combination and arrangement of sigma and pi bonds in a molecule influence its geometry, stability, and chemical reactivity.
| Covalent Bond Type | Description | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Sigma (σ) Bond | Head-on overlap of atomic orbitals | Stronger, typically single bonds |
| Pi (π) Bond | Sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals | Weaker, found in double and triple bonds |

Factors Influencing Covalent Bond Strength
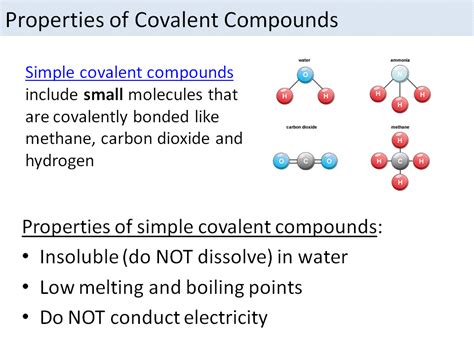
The strength of a covalent bond is influenced by several factors, including the electronegativities of the atoms involved, the size of the atoms, and the bond order. The bond order is the number of electron pairs shared between two atoms. Generally, higher bond orders result in stronger and shorter bonds. Additionally, the strength of a covalent bond can be affected by the hybridization state of the atoms involved, with bonds formed from more electronegative atoms or those with higher s-character tending to be stronger.
Covalent Bond Length and Energy
The length of a covalent bond, typically measured in angstroms (Å) or picometers (pm), is inversely related to its strength. Shorter bonds are usually stronger, indicating a more stable molecule. The energy required to break a covalent bond, known as the bond dissociation energy, is a critical parameter in understanding chemical reactivity. This energy varies significantly among different types of bonds and is influenced by the factors mentioned above.
| Bond Type | Average Bond Length (Å) | Average Bond Dissociation Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| C-C Single Bond | 1.54 | 83 |
| C=C Double Bond | 1.34 | 146 |
| C≡C Triple Bond | 1.20 | 200 |
What determines the polarity of a covalent bond?
+The polarity of a covalent bond is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved in the bond. A greater difference in electronegativity leads to a more polar bond.
How do sigma and pi bonds differ in terms of their formation?
+Sigma bonds are formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals, whereas pi bonds result from the sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals.
What factors influence the strength of a covalent bond?
+The strength of a covalent bond is influenced by the electronegativities of the atoms involved, the size of the atoms, the bond order, and the hybridization state of the atoms.
In conclusion, the properties of covalent bonds, including their strength, polarity, and the types of bonds (sigma and pi), play a crucial role in understanding the structure, stability, and reactivity of molecules. The factors influencing these properties, such as electronegativity differences, bond order, and atomic size, are essential considerations in chemistry. By grasping these concepts, one can better understand the complexities of molecular interactions and the principles guiding chemical reactions.