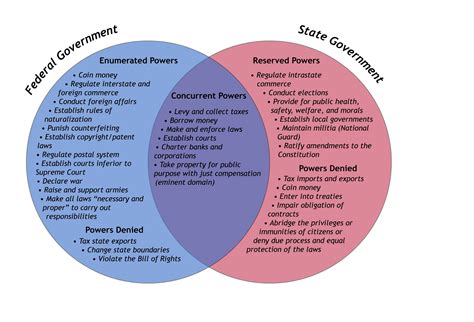
The concept of concurrent powers refers to the shared authority between two or more branches of government, or between the federal government and the states, to make laws and implement policies on specific matters. In the United States, the Constitution outlines several areas where the federal government and the states have concurrent powers, allowing them to work together to address common issues. One of the most significant examples of concurrent powers is the ability of both the federal government and the states to tax their citizens.
Concurrent powers are essential in ensuring that the federal government and the states can respond effectively to the needs of their citizens, while also preventing any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. By sharing authority, the federal government and the states can work together to achieve common goals, such as providing for the general welfare, regulating commerce, and ensuring national security. However, concurrent powers can also lead to conflicts and overlaps between the federal government and the states, highlighting the need for careful coordination and cooperation.
Key Points
- The concept of concurrent powers refers to the shared authority between two or more branches of government, or between the federal government and the states.
- Concurrent powers are essential in ensuring that the federal government and the states can respond effectively to the needs of their citizens.
- The federal government and the states have concurrent powers to tax their citizens, regulate commerce, and provide for the general welfare.
- Concurrent powers can lead to conflicts and overlaps between the federal government and the states, highlighting the need for careful coordination and cooperation.
- Examples of concurrent powers include the ability to regulate elections, enforce laws, and provide for public health and safety.
Types of Concurrent Powers
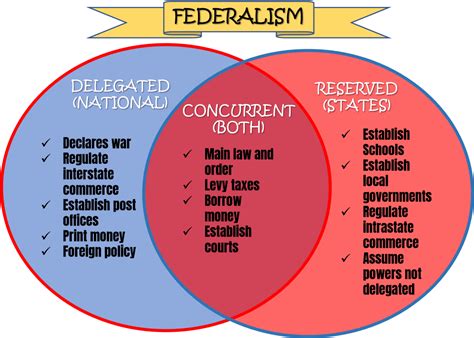
There are several types of concurrent powers, including the power to tax, the power to regulate commerce, and the power to provide for the general welfare. The power to tax is one of the most significant concurrent powers, as it allows both the federal government and the states to raise revenue to fund their activities. The federal government has the power to tax income, while the states have the power to tax property and sales.
The power to regulate commerce is another important concurrent power, as it allows both the federal government and the states to regulate businesses and industries that operate within their borders. The federal government has the power to regulate interstate commerce, while the states have the power to regulate intrastate commerce. This means that businesses that operate in multiple states must comply with both federal and state regulations.
Regulation of Elections
The regulation of elections is another area where the federal government and the states have concurrent powers. The federal government has the power to regulate federal elections, such as presidential and congressional elections, while the states have the power to regulate state and local elections. This means that the federal government and the states must work together to ensure that elections are fair and transparent.
| Level of Government | Concurrent Power |
|---|---|
| Federal Government | Power to tax income, regulate interstate commerce, and provide for national security |
| State Government | Power to tax property and sales, regulate intrastate commerce, and provide for public health and safety |
| Local Government | Power to regulate local businesses, provide for public services, and enforce local ordinances |

Examples of Concurrent Powers

There are many examples of concurrent powers in action, including the regulation of environmental protection, education, and public health. The federal government has the power to regulate environmental protection, while the states have the power to regulate environmental protection within their borders. This means that the federal government and the states must work together to develop and implement policies that protect the environment.
The regulation of education is another area where the federal government and the states have concurrent powers. The federal government has the power to regulate education at the federal level, while the states have the power to regulate education within their borders. This means that the federal government and the states must work together to develop and implement policies that improve education outcomes for all students.
Enforcement of Laws
The enforcement of laws is another area where the federal government and the states have concurrent powers. The federal government has the power to enforce federal laws, while the states have the power to enforce state laws. This means that the federal government and the states must work together to ensure that laws are enforced fairly and consistently.
In conclusion, concurrent powers are an essential part of the federal system, allowing the federal government and the states to work together to address common issues and provide for the needs of their citizens. By understanding the different types of concurrent powers and how they are exercised, citizens can better appreciate the complexities of the federal system and the importance of cooperation between different levels of government.
What is the concept of concurrent powers?
+The concept of concurrent powers refers to the shared authority between two or more branches of government, or between the federal government and the states, to make laws and implement policies on specific matters.
What are some examples of concurrent powers?
+Examples of concurrent powers include the power to tax, the power to regulate commerce, and the power to provide for the general welfare.
Why are concurrent powers important?
+Concurrent powers are important because they allow the federal government and the states to work together to address common issues and provide for the needs of their citizens.