Particles are the fundamental building blocks of matter, and they come in a variety of forms. Understanding the different types of particles is crucial in the field of physics, as it helps us comprehend the behavior of matter and energy at various scales. In this article, we will explore five types of particles that are widely recognized in the scientific community.
Introduction to Particle Types

The study of particles is a complex and fascinating field that has led to numerous breakthroughs in our understanding of the universe. From the tiny electrons that orbit the nucleus of an atom to the vast expanse of cosmic particles that fill the universe, particles are the basic units of matter and energy. In this section, we will provide an overview of the five types of particles that will be discussed in this article.
Key Points
- Elementary particles are the most basic building blocks of matter
- Composite particles are made up of two or more elementary particles
- Subatomic particles are smaller than atoms and include particles like electrons and protons
- Atomic particles are the building blocks of atoms and include particles like neutrons and protons
- Cosmic particles are high-energy particles that originate from outside the Earth's atmosphere
Elementary Particles
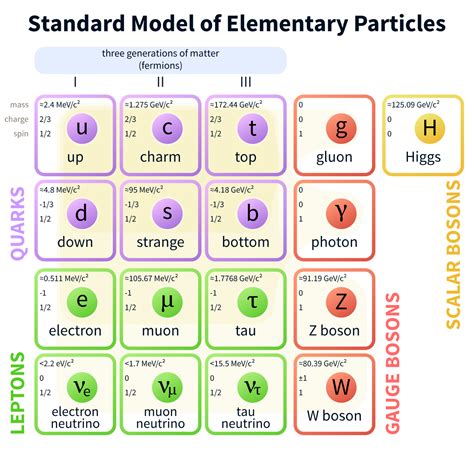
Elementary particles are the most basic building blocks of matter, and they cannot be broken down into smaller particles. They are the fundamental units of matter and energy, and they are the basis for all other particles. Examples of elementary particles include electrons, quarks, and photons. These particles are the foundation of the Standard Model of particle physics, which describes the behavior of fundamental particles and forces.
Properties of Elementary Particles
Elementary particles have unique properties that distinguish them from other types of particles. They have specific masses, charges, and spins, which determine their behavior in different situations. For example, electrons have a negative charge and a spin of 1⁄2, while photons have no charge and a spin of 1. Understanding the properties of elementary particles is essential for understanding the behavior of matter and energy at the most fundamental level.
| Particle Type | Mass | Charge | Spin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electron | 9.11 x 10^-31 kg | -1.6 x 10^-19 C | 1/2 |
| Quark | varies | varies | 1/2 |
| Photon | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Composite Particles
Composite particles are made up of two or more elementary particles. They can be formed through various processes, such as the combination of quarks to form protons and neutrons, or the combination of electrons and nuclei to form atoms. Composite particles can exhibit properties that are different from those of their constituent particles, and they play a crucial role in the structure and behavior of matter.
Examples of Composite Particles
Examples of composite particles include protons, neutrons, and atomic nuclei. Protons and neutrons are composed of quarks, while atomic nuclei are composed of protons and neutrons. These particles are the building blocks of atoms and molecules, and they determine the properties of matter at the atomic and molecular level.
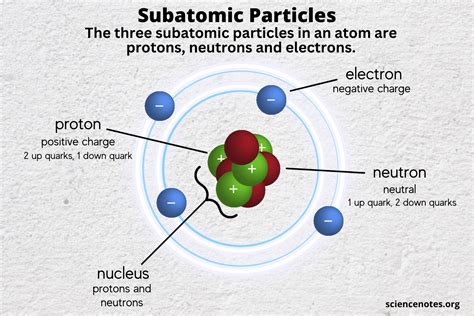
Subatomic Particles
Subatomic particles are smaller than atoms and include particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons. These particles are the building blocks of atoms and molecules, and they determine the properties of matter at the atomic and molecular level. Subatomic particles can be further divided into elementary particles, such as electrons and quarks, and composite particles, such as protons and neutrons.
Properties of Subatomic Particles
Subatomic particles have unique properties that distinguish them from other types of particles. They have specific masses, charges, and spins, which determine their behavior in different situations. For example, electrons have a negative charge and a spin of 1⁄2, while protons have a positive charge and a spin of 1⁄2. Understanding the properties of subatomic particles is essential for understanding the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and molecular level.
Atomic Particles

Atomic particles are the building blocks of atoms and include particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons. These particles are the foundation of the atomic structure, and they determine the properties of atoms and molecules. Atomic particles can be further divided into subatomic particles, such as electrons and quarks, and composite particles, such as protons and neutrons.
Properties of Atomic Particles
Atomic particles have unique properties that distinguish them from other types of particles. They have specific masses, charges, and spins, which determine their behavior in different situations. For example, protons have a positive charge and a spin of 1⁄2, while electrons have a negative charge and a spin of 1⁄2. Understanding the properties of atomic particles is essential for understanding the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and molecular level.
Cosmic Particles
Cosmic particles are high-energy particles that originate from outside the Earth’s atmosphere. They can be produced by various astrophysical processes, such as supernovae explosions or the collision of particles in high-energy accelerators. Cosmic particles can be detected using specialized instruments, such as particle detectors or telescopes, and they provide valuable insights into the behavior of matter and energy in extreme environments.
Properties of Cosmic Particles
Cosmic particles have unique properties that distinguish them from other types of particles. They have high energies, which can range from a few GeV to several TeV, and they can interact with matter in complex ways. Understanding the properties of cosmic particles is essential for understanding the behavior of matter and energy in extreme environments, such as black holes or neutron stars.
What are the most common types of particles?
+The most common types of particles include electrons, protons, neutrons, and photons. These particles are the building blocks of matter and energy, and they are the foundation of the Standard Model of particle physics.
What is the difference between elementary and composite particles?
+Elementary particles are the most basic building blocks of matter, and they cannot be broken down into smaller particles. Composite particles, on the other hand, are made up of two or more elementary particles. Examples of composite particles include protons, neutrons, and atomic nuclei.
What are cosmic particles, and how are they produced?
+Cosmic particles are high-energy particles that originate from outside the Earth’s atmosphere. They can be produced by various astrophysical processes, such as supernovae explosions or the collision of particles in high-energy accelerators.