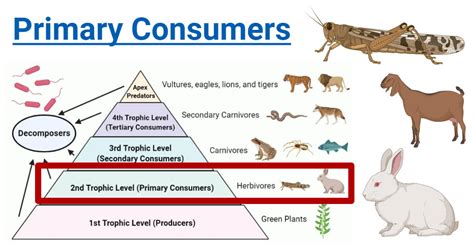
The concept of primary consumers is a fundamental aspect of ecology, playing a crucial role in understanding the flow of energy and nutrients through ecosystems. Primary consumers, also known as herbivores, are organisms that feed directly on producers, such as plants and algae, which form the base of the food chain. These consumers are essential for transferring energy from the primary producers to higher trophic levels, thus sustaining the complex web of relationships within an ecosystem.
In the context of ecological pyramids, primary consumers occupy the second trophic level, positioned above the primary producers. They convert the chemical energy stored in plants into a form that can be utilized by other organisms, facilitating the energy transfer process. This conversion is not entirely efficient, as a significant amount of energy is lost as heat, supporting the second law of thermodynamics. However, the energy that is retained and passed on to higher trophic levels is crucial for the survival and diversity of ecosystems.
Key Points
- Primary consumers are herbivores that feed directly on primary producers.
- Examples of primary consumers include zooplankton, insects, and large herbivorous mammals.
- Primary consumers are essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and diversity.
- The efficiency of energy transfer by primary consumers is limited, with significant energy loss as heat.
Characteristics and Examples of Primary Consumers
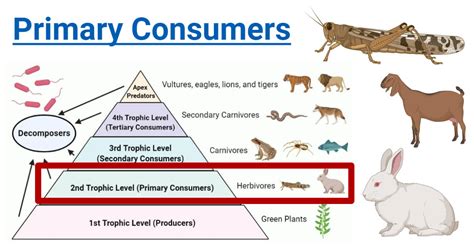
Primary consumers exhibit a range of characteristics that enable them to feed on primary producers efficiently. These characteristics include specialized digestive systems capable of breaking down cellulose in plant cell walls, as well as various adaptations that help them avoid predators. Examples of primary consumers are diverse and include zooplankton in aquatic ecosystems, insects such as grasshoppers and caterpillars, and large herbivorous mammals like deer and elephants.
Role of Primary Consumers in Ecosystems
The role of primary consumers in ecosystems is multifaceted. Not only do they facilitate the transfer of energy from primary producers to higher trophic levels, but they also influence the composition and structure of plant communities. Through their feeding activities, primary consumers can select for certain plant species over others, thereby affecting the diversity and distribution of vegetation. Additionally, primary consumers contribute to nutrient cycling by consuming and processing nutrients that would otherwise be locked in plant biomass, making these nutrients available to other organisms.
| Category of Primary Consumer | Examples | Ecosystem Role |
|---|---|---|
| Microscopic | Zooplankton | Base of aquatic food webs |
| Insectivorous | Grasshoppers, Caterpillars | Decomposition, nutrient cycling |
| Large Herbivores | Deer, Elephants | Ecosystem engineering, habitat creation |
Challenges and Conservation of Primary Consumers

Primary consumers face numerous challenges, including habitat destruction, climate change, and overhunting, which can lead to population declines and even extinctions. The conservation of primary consumers is essential for maintaining the integrity of ecosystems. Efforts to protect and restore habitats, manage hunting practices sustainably, and mitigate the impacts of climate change are critical for preserving the diversity and function of primary consumer populations.
In conclusion, primary consumers are vital components of ecosystems, playing a pivotal role in the flow of energy and nutrients. Their activities influence the structure and diversity of plant communities, and their loss can have cascading effects throughout ecosystems. Understanding the complex relationships between primary consumers and their environments is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and managing ecosystems sustainably.
What is the primary role of primary consumers in an ecosystem?
+Primary consumers play a crucial role in transferring energy from primary producers to higher trophic levels, facilitating the flow of energy through the ecosystem.
Can primary consumers influence the composition of plant communities?
+Yes, through their feeding activities, primary consumers can select for certain plant species over others, thereby affecting the diversity and distribution of vegetation.
Why is the conservation of primary consumers important?
+The conservation of primary consumers is essential for maintaining the integrity and function of ecosystems. Losses in primary consumer populations can have cascading effects, leading to changes in ecosystem processes and potentially resulting in the degradation of habitats and loss of biodiversity.