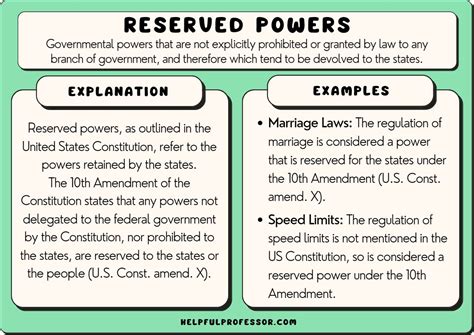
The concept of reserved powers is a fundamental aspect of constitutional law, particularly in federal systems where power is divided between a central government and constituent units, such as states or provinces. Reserved powers refer to the authority that is not explicitly granted to the central government by the constitution and is therefore retained by the constituent units. In the context of the United States, for example, the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution addresses reserved powers, stating, "The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people."
Key Points
- The concept of reserved powers is crucial in federal systems, where it defines the limits of central government authority.
- Reserved powers are not explicitly granted to the central government and are retained by the constituent units, such as states.
- The Tenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution is a key example of how reserved powers are addressed in a federal system.
- Reserved powers can include a wide range of authorities, such as education, transportation, and law enforcement, depending on the constitution and legal framework of the country.
- The balance between the central government's powers and reserved powers is critical for maintaining federalism and protecting the autonomy of constituent units.
Understanding Reserved Powers

Reserved powers are essential for maintaining the balance of power in a federal system. They ensure that the central government does not overstep its constitutional authority and that the constituent units have the autonomy to manage their internal affairs. The nature and extent of reserved powers can vary significantly from one country to another, depending on the specific provisions of the constitution and the historical, political, and social context in which the federal system operates.
Examples of Reserved Powers
In the United States, examples of reserved powers include the regulation of intrastate commerce, education, and law enforcement. These powers are not granted to the federal government by the Constitution and are therefore reserved to the states. For instance, while the federal government has the power to regulate interstate commerce, the regulation of commerce that takes place entirely within a state’s borders is generally reserved to the state. Similarly, the provision of public education is primarily a state and local responsibility, with the federal government playing a more limited role.
| Category of Power | Example |
|---|---|
| Regulation of Intrastate Commerce | Licensing of professions within a state |
| Education | Establishment and funding of public schools |
| Law Enforcement | Operation of state and local police departments |

Importance of Reserved Powers

Reserved powers are crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they help to prevent the concentration of power in the central government, thereby protecting the autonomy of the constituent units. This is essential for maintaining the principles of federalism, which is based on the idea of dividing power between different levels of government to protect individual rights and promote democratic governance. Secondly, reserved powers allow for diversity and innovation at the state and local levels, as different jurisdictions can experiment with different policies and approaches to addressing common problems.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite their importance, reserved powers can also be a source of controversy and conflict. One of the main challenges is determining the precise boundaries between federal and state authority. This can lead to disputes over which level of government has the power to regulate certain activities or address particular issues. Additionally, the existence of reserved powers can sometimes hinder the ability of the federal government to address national problems that require a coordinated response across different jurisdictions.
What are reserved powers in the context of federalism?
+Reserved powers refer to the authority that is not explicitly granted to the central government by the constitution and is therefore retained by the constituent units, such as states or provinces.
Why are reserved powers important in a federal system?
+Reserved powers are important because they help to prevent the concentration of power in the central government, protect the autonomy of the constituent units, and allow for diversity and innovation at the state and local levels.
How are reserved powers addressed in the U.S. Constitution?
+Reserved powers are addressed in the Tenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, which states that the powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.
In conclusion, reserved powers play a vital role in the functioning of federal systems, ensuring that power is distributed in a way that respects the autonomy of constituent units while also allowing for national coordination and cooperation. Understanding the concept of reserved powers and their implications is essential for navigating the complexities of federalism and for addressing the challenges that arise from the division of power between different levels of government.