The cell theory, a fundamental concept in biology, consists of three primary parts that have been extensively researched and validated through numerous scientific experiments and observations. The theory, which was first proposed by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann in the 19th century, has undergone significant revisions and expansions since its inception. At its core, the cell theory provides a framework for understanding the structure, function, and behavior of cells, which are the basic building blocks of all living organisms.
The first part of the cell theory states that all living organisms are composed of one or more cells. This concept is often referred to as the "cellular basis of life." It suggests that cells are the fundamental units of life and that all living organisms, from simple bacteria to complex multicellular organisms, are comprised of cells. This idea is supported by a vast amount of evidence from various fields of biology, including microscopy, biochemistry, and genetics. For instance, the discovery of cells by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century, using his handmade microscopes, marked the beginning of a new era in biology and provided significant evidence for the cellular basis of life.
Key Points
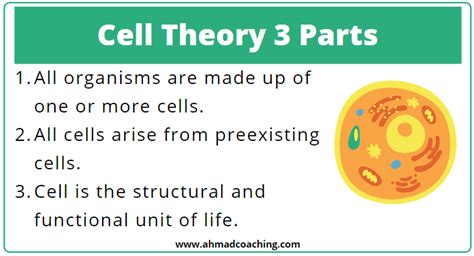
- The cell theory consists of three primary parts: all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic units of life and all cells arise from pre-existing cells, and all cells come from pre-existing cells.
- The cellular basis of life is supported by a vast amount of evidence from various fields of biology, including microscopy, biochemistry, and genetics.
- The concept of cells as the basic units of life and all cells arising from pre-existing cells is crucial in understanding the structure, function, and behavior of cells.
- The cell theory has undergone significant revisions and expansions since its inception, with new discoveries and advances in technology continuing to shape our understanding of cells and their role in living organisms.
- Understanding the cell theory is essential for understanding the principles of biology and for developing new treatments and therapies for various diseases.
The Cellular Basis of Life
The second part of the cell theory states that cells are the basic units of life and that all cells arise from pre-existing cells. This concept is often referred to as the “cellular continuity” or “biogenesis.” It suggests that cells are the fundamental units of life and that all living organisms, from simple bacteria to complex multicellular organisms, are comprised of cells that have arisen from pre-existing cells. This idea is supported by a vast amount of evidence from various fields of biology, including cell biology, genetics, and evolutionary biology. For example, the process of cell division, which is essential for the growth and development of living organisms, demonstrates the continuity of cells and the idea that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Cellular Continuity
The concept of cellular continuity is crucial in understanding the structure, function, and behavior of cells. It suggests that cells are not isolated entities, but rather are connected to other cells through a complex network of relationships. This idea is supported by the discovery of various cellular structures, such as the cytoskeleton, which provides a framework for cellular organization and movement. Additionally, the discovery of cellular signaling pathways, which allow cells to communicate with each other, has further supported the concept of cellular continuity.
| Cellular Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cytoskeleton | Provides a framework for cellular organization and movement |
| Cell membrane | Regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell |
| Nucleus | Contains the cell's genetic material and regulates cell growth and division |
Cellular Evolution
The third part of the cell theory states that all cells come from pre-existing cells. This concept is often referred to as the “cellular evolution” or “descent with modification.” It suggests that cells have evolved over time through a process of genetic variation, mutation, and natural selection. This idea is supported by a vast amount of evidence from various fields of biology, including evolutionary biology, genetics, and paleontology. For example, the discovery of fossil records, which provide evidence of the evolution of cells and organisms over time, has further supported the concept of cellular evolution.
In conclusion, the cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that consists of three primary parts: all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic units of life and all cells arise from pre-existing cells, and all cells come from pre-existing cells. Understanding the cell theory is essential for understanding the principles of biology and for developing new treatments and therapies for various diseases. The cell theory has undergone significant revisions and expansions since its inception, with new discoveries and advances in technology continuing to shape our understanding of cells and their role in living organisms.
What is the cell theory?
+The cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that consists of three primary parts: all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic units of life and all cells arise from pre-existing cells, and all cells come from pre-existing cells.
What is the significance of the cell theory?
+The cell theory is significant because it provides a framework for understanding the structure, function, and behavior of cells, which are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. Understanding the cell theory is essential for understanding the principles of biology and for developing new treatments and therapies for various diseases.
How has the cell theory evolved over time?
+The cell theory has undergone significant revisions and expansions since its inception, with new discoveries and advances in technology continuing to shape our understanding of cells and their role in living organisms. The discovery of cellular structures, such as the cytoskeleton, and cellular signaling pathways has further supported the concept of cellular continuity.



