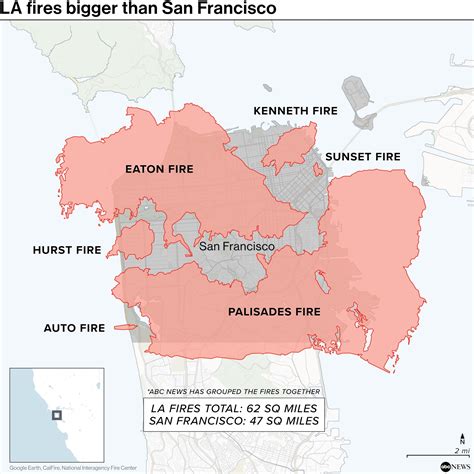
The state of California has been plagued by devastating wildfires in recent years, with the 2018 Camp Fire being the deadliest and most destructive wildfire in the state's history. The 2020 fire season was also particularly severe, with over 4 million acres burned and thousands of structures destroyed. While wildfires are a natural occurrence in California, human activities and climate change have significantly contributed to the increasing frequency and severity of these events. Here, we will explore the 5 primary causes of California fires, which are often interconnected and can exacerbate one another.
Natural Causes: Lightning and Drought
Lightning strikes are a major natural cause of wildfires in California. During the summer months, the state experiences a dry lightning season, where thunderstorms produce lightning but little to no rainfall. This can ignite wildfires in remote areas, which can then spread quickly due to strong winds and dry vegetation. Drought is another natural factor that contributes to the risk of wildfires. Prolonged droughts, like the one that affected California from 2012 to 2016, can dry out vegetation, making it more susceptible to ignition and rapid spread. According to data from the National Interagency Coordination Center, lightning-caused wildfires account for approximately 10% of all wildfires in California.
Human-Caused Ignitions: Arson, Accidental Ignitions, and Infrastructure
Human activities are responsible for the majority of wildfires in California. Arson, or intentionally set fires, is a significant cause of wildfires, accounting for around 5% of all fires. Accidental ignitions, such as those caused by discarded cigarettes, unattended campfires, or sparks from machinery, are also a major contributor. In addition, the state’s aging infrastructure, including power lines and transformers, can malfunction and ignite wildfires. For example, the 2018 Camp Fire was caused by a faulty power line owned by Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E). According to a report by the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CAL FIRE), human-caused ignitions account for approximately 95% of all wildfires in the state.
| Cause of Wildfire | Percentage of Total Wildfires |
|---|---|
| Human-Caused Ignitions | 95% |
| Lightning | 5% |
| Other Natural Causes | <1% |
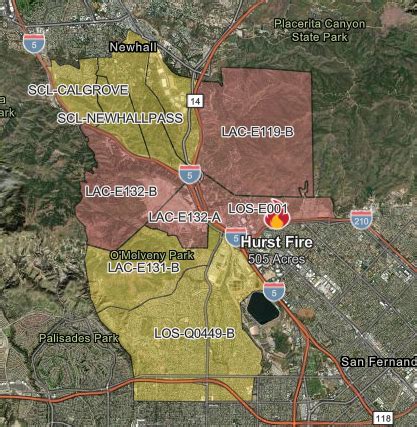
Climate Change: Rising Temperatures and Changing Precipitation Patterns
Climate change is a significant factor in the increasing risk of wildfires in California. Rising temperatures have led to an increase in the number of days with extreme heat, which can dry out vegetation and create conditions ripe for wildfires. Changing precipitation patterns, including more frequent and intense droughts, have also contributed to the risk of wildfires. According to a study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research, climate change has increased the risk of wildfires in California by 500% since the 1970s.
Land Use and Land Management Practices
The way land is used and managed in California also plays a significant role in the risk of wildfires. The state’s wildland-urban interface (WUI), where urban development meets wildland areas, is a high-risk zone for wildfires. In these areas, human activities such as construction, landscaping, and recreation can ignite wildfires, which can then spread quickly due to the presence of flammable vegetation and structures. Additionally, land management practices such as grazing, logging, and prescribed burning can also impact the risk of wildfires. For example, overgrazing can lead to an increase in invasive species, which can increase the risk of wildfires.
Key Points
- The 5 primary causes of California fires are natural causes (lightning and drought), human-caused ignitions (arson, accidental ignitions, and infrastructure), climate change, land use, and land management practices.
- Human activities are responsible for the majority of wildfires in California, accounting for approximately 95% of all fires.
- Climate change has increased the risk of wildfires in California by 500% since the 1970s.
- The wildland-urban interface (WUI) is a high-risk zone for wildfires, where human activities can ignite fires that can spread quickly due to the presence of flammable vegetation and structures.
- Land management practices such as grazing, logging, and prescribed burning can impact the risk of wildfires, and should be carefully managed to mitigate this risk.
In conclusion, the causes of California fires are complex and multifaceted, involving natural and human-caused factors. By understanding these causes, we can work to mitigate the risk of wildfires and reduce the impact of these devastating events on communities and the environment.
What is the primary cause of wildfires in California?
+Human-caused ignitions, including arson, accidental ignitions, and infrastructure, are the primary cause of wildfires in California, accounting for approximately 95% of all fires.
How does climate change impact the risk of wildfires in California?
+Climate change has increased the risk of wildfires in California by 500% since the 1970s, due to rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased fuel loads.
What can be done to mitigate the risk of wildfires in California?
+To mitigate the risk of wildfires in California, it’s essential to implement sustainable land use and land management practices, such as prescribed burning, grazing management, and logging. Additionally, human activities that can ignite wildfires, such as arson and accidental ignitions, must be prevented and addressed.