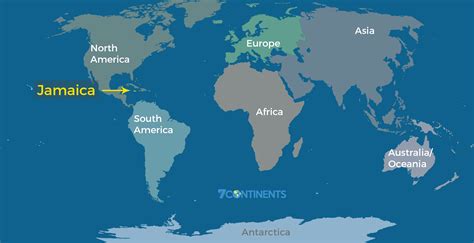
Jamaica, an island nation located in the Caribbean Sea, is often misunderstood in terms of its geographical classification. While it is true that Jamaica is situated in the northern hemisphere and is part of the Greater Antilles, it is not typically considered part of the continent of North America in the classical sense. North America is generally defined as comprising the United States, Canada, Mexico, and the countries of Central America, including Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama.
Geographical Classification of Jamaica
Jamaica is more accurately described as being part of the Caribbean region, which is sometimes considered a subregion of North America but is culturally, historically, and geographically distinct. The Caribbean region includes the Caribbean Sea, its islands, and the surrounding coasts. It is situated southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America and north of South America. Jamaica, along with other Caribbean islands, shares historical, linguistic, and cultural ties that are unique to the region.
Regional Identity and Classification
The classification of Jamaica as part of the Caribbean rather than North America reflects its unique cultural, historical, and geographical characteristics. While Jamaica does participate in regional organizations that include North American countries, such as the Organization of American States (OAS), its primary regional identity and affiliations are with other Caribbean nations. The Caribbean Community (CARICOM), for example, is a regional organization that aims to promote economic integration and cooperation among its member states, which include Jamaica and other Caribbean countries.
| Region | Description |
|---|---|
| North America | Comprises the United States, Canada, Mexico, and Central America. |
| Caribbean | Includes the Caribbean Sea, its islands, and the surrounding coasts, distinct from North America. |
Key Points
- Jamaica is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea, not part of the North American continent in the classical sense.
- The Caribbean region is distinct from North America, with its own unique cultural, historical, and geographical characteristics.
- Jamaica's regional identity and affiliations are primarily with other Caribbean nations, through organizations like CARICOM.
- Geographical classifications can be nuanced, reflecting both physical location and cultural/historical identities.
- Understanding these nuances is important for appreciating the complexities of regional identities and affiliations.
In conclusion, while Jamaica's geographical location might suggest a connection to North America, its cultural, historical, and regional affiliations clearly identify it as part of the Caribbean. This distinction is not merely semantic; it reflects the unique characteristics and relationships that define Jamaica and its place within the global community.
Is Jamaica considered part of North America?
+No, Jamaica is not considered part of the North American continent in the classical sense. It is part of the Caribbean region, which is culturally, historically, and geographically distinct from North America.
What region does Jamaica belong to?
+Jamaica belongs to the Caribbean region, which includes the Caribbean Sea, its islands, and the surrounding coasts. This region is distinct from North America and has its own unique cultural, historical, and geographical characteristics.
Why is the Caribbean region distinct from North America?
+The Caribbean region is distinct due to its unique cultural, historical, and geographical characteristics. These islands have shared historical experiences, such as colonialism, and have developed distinct cultural identities that are separate from those of North America.