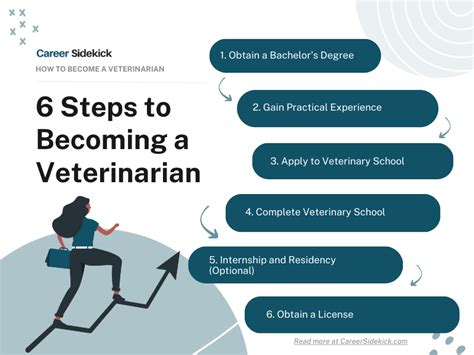
To become a veterinarian, one must undergo a rigorous educational process that combines academic coursework with hands-on clinical experience. The journey to earning a veterinarian degree is lengthy and demanding, but it is a necessary step for those who wish to pursue a career in animal healthcare. In this article, we will delve into the veterinarian degree requirements, exploring the various steps involved in becoming a licensed veterinarian.
Undergraduate Degree Requirements

Before applying to veterinary school, aspiring veterinarians must first complete a bachelor’s degree program. While there is no specific major required for veterinary school, most students choose to major in biology, chemistry, or animal science. The undergraduate degree program typically takes four years to complete and must include a set of prerequisite courses, such as biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics. These courses provide a solid foundation in the sciences and help prepare students for the rigors of veterinary school. According to the Association of American Veterinary Medical Colleges (AAVMC), the average GPA for students accepted into veterinary school is around 3.5, with a science GPA of 3.4.
Prerequisite Courses
The prerequisite courses required for veterinary school vary from institution to institution, but most programs require students to complete a set of core courses, including:
- Two semesters of biology with lab
- Two semesters of chemistry with lab
- Two semesters of organic chemistry with lab
- Two semesters of physics with lab
- One semester of biochemistry
- One semester of genetics
- One semester of mathematics (calculus or statistics)
These courses provide students with a strong foundation in the sciences and help prepare them for the challenging coursework they will encounter in veterinary school.
| Course | Credit Hours |
|---|---|
| Biology I with lab | 4 |
| Biology II with lab | 4 |
| Chemistry I with lab | 4 |
| Chemistry II with lab | 4 |
| Organic Chemistry I with lab | 4 |
| Organic Chemistry II with lab | 4 |

Veterinary School Requirements

After completing the undergraduate degree and prerequisite courses, students can apply to veterinary school. The Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) program typically takes four years to complete and includes both classroom and clinical instruction. The first two years of veterinary school focus on foundational coursework, such as anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology. The final two years of the program are dedicated to clinical rotations, where students work directly with animals and gain hands-on experience in a variety of settings, including private practices, hospitals, and research institutions.
Clinical Rotations
The clinical rotations are a critical component of veterinary school, as they provide students with the opportunity to apply the knowledge and skills they have acquired in a real-world setting. Students typically participate in a variety of rotations, including:
- Small animal medicine and surgery
- Large animal medicine and surgery
- Equine medicine and surgery
- Food animal medicine and surgery
- Exotic animal medicine and surgery
- Emergency and critical care
These rotations help students develop the skills and confidence they need to succeed as practicing veterinarians.
Key Points
- Earning a bachelor's degree with a strong foundation in the sciences is essential for veterinary school
- Completing the prerequisite courses is crucial for success in veterinary school
- The DVM program typically takes four years to complete and includes both classroom and clinical instruction
- Clinical rotations provide students with hands-on experience in a variety of settings
- Obtaining a license to practice veterinary medicine requires passing the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE)
Licensure Requirements
After graduating from veterinary school, students must obtain a license to practice veterinary medicine. In the United States, this typically involves passing the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE). The NAVLE is a comprehensive exam that tests a student’s knowledge and skills in a variety of areas, including animal anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology. According to the National Board of Veterinary Medical Examiners (NBVME), the NAVLE has a pass rate of around 90% for first-time test-takers.
NAVLE Exam Format
The NAVLE is a multiple-choice exam that consists of 360 questions. The exam is divided into two sections: the basic and clinical sciences section and the clinical proficiency section. The basic and clinical sciences section tests a student’s knowledge of animal anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology, while the clinical proficiency section tests a student’s ability to apply this knowledge in a clinical setting.
| Section | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Basic and Clinical Sciences | 200 |
| Clinical Proficiency | 160 |
What are the prerequisite courses for veterinary school?
+The prerequisite courses for veterinary school typically include biology, chemistry, organic chemistry, physics, biochemistry, genetics, and mathematics.
How long does it take to complete the DVM program?
+The DVM program typically takes four years to complete.
What is the NAVLE exam?
+The NAVLE is a comprehensive exam that tests a student's knowledge and skills in a variety of areas, including animal anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology.
In conclusion, becoming a veterinarian requires a significant amount of education, training, and dedication. By understanding the veterinarian degree requirements and the various steps involved in becoming a licensed veterinarian, aspiring veterinarians can better prepare themselves for the challenges and rewards of this rewarding career.