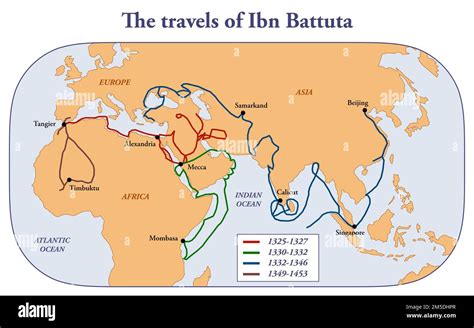
The city of Mecca, a place of profound spiritual significance, has been a beacon for pilgrims and travelers for centuries. One such traveler, Ibn Battuta, a Moroccan explorer and scholar, found himself in Mecca in the year 1326, during the reign of the Mamluk Sultanate. Ibn Battuta's journey to Mecca was a pivotal moment in his life, marking the beginning of his extensive travels across the Islamic world. As he arrived in the city, he was struck by the grandeur of the Masjid al-Haram, the largest mosque in the world, and the Kaaba, the holiest site in Islam.
The Spiritual Significance of Mecca

For Ibn Battuta, Mecca was more than just a destination; it was a spiritual experience that would shape his understanding of the Islamic faith. The city’s rich history, dating back to the time of the Prophet Muhammad, was palpable in every corner. Ibn Battuta spent several weeks in Mecca, performing the rituals of the Hajj, the Islamic pilgrimage, and immersing himself in the city’s vibrant cultural and intellectual scene. He was particularly drawn to the scholars and theologians who had gathered in Mecca from all over the Islamic world, and he spent many hours engaging in debates and discussions with them.
Ibn Battuta’s Interactions with the Local Population
During his stay in Mecca, Ibn Battuta had the opportunity to interact with people from diverse backgrounds, including merchants, traders, and pilgrims. He was struck by the city’s cosmopolitan nature, with people from all over the world converging on Mecca to perform the Hajj. Ibn Battuta’s interactions with the local population provided him with valuable insights into the social, economic, and cultural dynamics of the city. He was particularly impressed by the generosity and hospitality of the Meccans, who welcomed him and other pilgrims with open arms.
| Year | Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 1326 | Ibn Battuta's arrival in Mecca | Marked the beginning of his extensive travels across the Islamic world |
| 1327 | Performance of the Hajj | Deepened Ibn Battuta's understanding of the Islamic faith and its rituals |
| 1328 | Departure from Mecca | Marked the beginning of Ibn Battuta's journey to other parts of the Islamic world, including Egypt, Syria, and Anatolia |

Key Points
- Ibn Battuta's journey to Mecca marked the beginning of his extensive travels across the Islamic world, which would take him to over 40 countries and last for nearly three decades.
- The city of Mecca played a significant role in shaping Ibn Battuta's understanding of the Islamic faith and its rituals, particularly the Hajj.
- Ibn Battuta's interactions with the local population in Mecca provided him with valuable insights into the social, economic, and cultural dynamics of the city.
- The experience of performing the Hajj had a profound impact on Ibn Battuta's spiritual and intellectual development, influencing his views on the nature of faith, community, and identity.
- Ibn Battuta's time in Mecca was also marked by significant cultural and intellectual exchange, as he engaged with scholars, theologians, and other travelers from diverse backgrounds.
The Cultural and Intellectual Landscape of Mecca
Mecca, during the time of Ibn Battuta’s visit, was a thriving cultural and intellectual center, attracting scholars, theologians, and artists from all over the Islamic world. The city’s vibrant marketplace, the Suq al-Arab, was a hub of commercial and cultural activity, with merchants and traders from different regions offering a wide range of goods, including textiles, spices, and precious stones. Ibn Battuta was fascinated by the city’s rich cultural heritage, which was reflected in its architecture, literature, and art.
The Significance of the Kaaba and the Masjid al-Haram
The Kaaba, the holiest site in Islam, was the focal point of Ibn Battuta’s spiritual journey in Mecca. He was deeply moved by the experience of circumambulating the Kaaba, which he believed was a symbol of the unity and solidarity of the Islamic community. The Masjid al-Haram, the largest mosque in the world, was another significant landmark that Ibn Battuta visited during his stay in Mecca. He was impressed by the mosque’s grandeur and beauty, which reflected the wealth and power of the Islamic world during that period.
Ibn Battuta's experience in Mecca had a profound impact on his life and work, shaping his views on the nature of faith, community, and identity. His journey to Mecca marked the beginning of his extensive travels across the Islamic world, which would take him to over 40 countries and last for nearly three decades. As a scholar and traveler, Ibn Battuta's legacy continues to inspire and inform our understanding of the Islamic world and its rich cultural heritage.
What was the significance of Ibn Battuta’s journey to Mecca?
+Ibn Battuta’s journey to Mecca marked the beginning of his extensive travels across the Islamic world, which would take him to over 40 countries and last for nearly three decades. The experience of performing the Hajj had a profound impact on his spiritual and intellectual development, influencing his views on the nature of faith, community, and identity.
What was the cultural and intellectual landscape of Mecca like during Ibn Battuta’s visit?
+Mecca, during the time of Ibn Battuta’s visit, was a thriving cultural and intellectual center, attracting scholars, theologians, and artists from all over the Islamic world. The city’s vibrant marketplace, the Suq al-Arab, was a hub of commercial and cultural activity, with merchants and traders from different regions offering a wide range of goods.
What was the significance of the Kaaba and the Masjid al-Haram in Ibn Battuta’s spiritual journey?
+The Kaaba, the holiest site in Islam, was the focal point of Ibn Battuta’s spiritual journey in Mecca. He was deeply moved by the experience of circumambulating the Kaaba, which he believed was a symbol of the unity and solidarity of the Islamic community. The Masjid al-Haram, the largest mosque in the world, was another significant landmark that Ibn Battuta visited during his stay in Mecca.