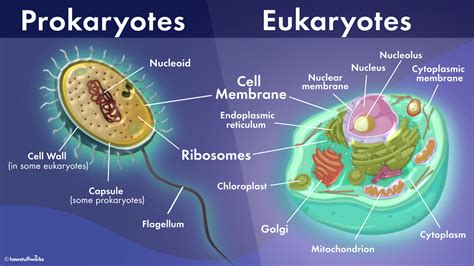
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the two fundamental forms of life on Earth, have been extensively studied to understand their unique characteristics and shared traits. Despite their distinct differences, both prokaryotes and eukaryotes possess certain commonalities that highlight their shared evolutionary history. This article aims to explore the shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, providing an in-depth analysis of their similarities and differences.
Cellular Structure and Function

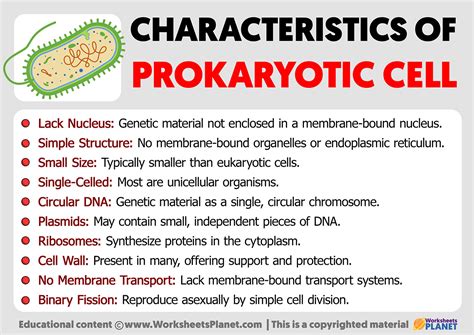
One of the primary shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is their cellular structure and function. Both types of cells are composed of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material, albeit with distinct differences in their organization and complexity. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, have a relatively simple cell structure with a single circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, have a more complex cell structure with multiple linear chromosomes and membrane-bound organelles.
Despite these differences, both prokaryotes and eukaryotes rely on similar cellular processes, such as metabolism, DNA replication, and protein synthesis, to sustain life. The presence of ribosomes, the cellular organelles responsible for protein synthesis, is a shared trait between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, the structure and function of ribosomes differ slightly between the two, with prokaryotic ribosomes being smaller and more efficient than their eukaryotic counterparts.
Genetic Material and Replication
The genetic material of prokaryotes and eukaryotes is another area where shared traits are evident. Both types of cells have DNA as their primary genetic material, although the organization and complexity of their genomes differ significantly. Prokaryotes have a single circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes with complex chromatin structures.
The process of DNA replication is also similar between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, with both relying on semi-conservative replication to duplicate their genetic material. However, the mechanisms of DNA replication differ between the two, with prokaryotes using a single origin of replication and eukaryotes using multiple origins to initiate DNA replication.
| Cell Type | Genetic Material | DNA Replication Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Prokaryotes | Single circular chromosome | Semi-conservative replication with single origin |
| Eukaryotes | Multiple linear chromosomes | Semi-conservative replication with multiple origins |
Key Points
- Prokaryotes and eukaryotes share similar cellular structures and functions, including a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material.
- The presence of ribosomes is a shared trait between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, with both types of cells relying on protein synthesis to sustain life.
- Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have DNA as their primary genetic material, although the organization and complexity of their genomes differ significantly.
- The process of DNA replication is similar between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, with both relying on semi-conservative replication to duplicate their genetic material.
- Understanding the shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes can provide valuable insights into the fundamental processes of life and the origins of cellular diversity.
Metabolic Processes and Energy Production
Metabolic processes and energy production are essential functions that are shared between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Both types of cells rely on metabolic pathways to convert energy and nutrients into the building blocks of life. Prokaryotes, such as bacteria, are capable of performing a wide range of metabolic processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and fermentation, whereas eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, rely on more complex metabolic pathways to sustain life.
The process of cellular respiration, which involves the conversion of glucose into energy, is a shared trait between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, the mechanisms of cellular respiration differ between the two, with prokaryotes using a single electron transport chain and eukaryotes using a more complex electron transport chain with multiple electron carriers.
Response to Environmental Stimuli
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes also share the ability to respond to environmental stimuli, such as changes in temperature, pH, and nutrient availability. Both types of cells have developed complex signaling pathways to sense and respond to their environment, although the mechanisms of these pathways differ significantly between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
The presence of sensory receptors and signal transduction pathways is a shared trait between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, with both types of cells relying on these pathways to respond to environmental stimuli. However, the complexity and specificity of these pathways differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, with eukaryotes having more complex and specialized signaling pathways.
What are the main differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
+The main differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes lie in their cellular structure and function, with prokaryotes having a simpler cell structure and eukaryotes having a more complex cell structure with membrane-bound organelles.
What are the shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
+The shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes include their cellular structure and function, genetic material, metabolic processes, and response to environmental stimuli.
Why is it important to understand the shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
+Understanding the shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes can provide valuable insights into the fundamental processes of life and the origins of cellular diversity, which is essential for advancing our knowledge of biology and improving our understanding of the natural world.
In conclusion, the shared traits between prokaryotes and eukaryotes highlight their evolutionary relationship and demonstrate that, despite their differences, they share a common ancestor. Understanding these shared traits can provide valuable insights into the fundamental processes of life and the origins of cellular diversity, which is essential for advancing our knowledge of biology and improving our understanding of the natural world.