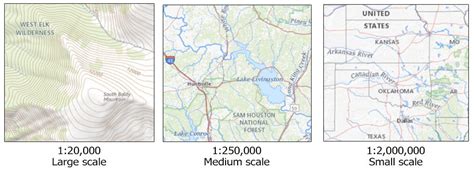
Map numbers representation is a critical aspect of cartography, geography, and data visualization. The effective use of numbers on maps can significantly enhance the comprehension and interpretation of spatial data, making it an indispensable tool for researchers, policymakers, and the general public. This article aims to delve into the principles, best practices, and recent advancements in map numbers representation, providing a comprehensive overview of its importance and applications.
Introduction to Map Numbers Representation
At its core, map numbers representation involves the use of numerical values to convey information about geographic phenomena, such as population density, climate data, or economic indicators. The challenge lies in presenting these numbers in a way that is both visually appealing and easily understandable, without overwhelming the viewer with too much information. Cartographers and data analysts employ various techniques to achieve this balance, including the strategic placement of labels, the use of color-coded legends, and the selection of appropriate scales.
Key Points
- The effective representation of numbers on maps is crucial for clear communication of spatial data.
- Cartographers use various techniques, including labeling, color coding, and scaling, to present numerical information.
- Recent advancements in data visualization and geographic information systems (GIS) have expanded the possibilities for map numbers representation.
- Understanding the principles of map numbers representation is essential for creating informative and engaging maps.
- Applications of map numbers representation include urban planning, environmental monitoring, and socio-economic research.
Principles of Map Numbers Representation
The principles guiding map numbers representation are rooted in the broader field of data visualization. They include clarity, simplicity, and the avoidance of visual noise. By carefully considering the size, color, and placement of numerical labels, cartographers can ensure that the map communicates its message effectively. Furthermore, the integration of these principles with the latest technologies in GIS and data visualization software has enabled the creation of dynamic, interactive maps that can be tailored to specific user needs.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Labeling | The strategic placement of numerical labels to avoid clutter and enhance readability. |
| Color Coding | The use of different colors to categorize and distinguish between various numerical values or ranges. |
| Scaling | The selection of an appropriate scale to ensure that the numerical information is presented in a contextually relevant manner. |
Applications and Advancements

The applications of map numbers representation are diverse and widespread, ranging from urban planning and environmental monitoring to socio-economic research and policy development. Recent advancements in data visualization and GIS have significantly expanded the capabilities of map numbers representation, allowing for the integration of real-time data, the creation of 3D visualizations, and the development of interactive web maps. These advancements have not only improved the aesthetic appeal of maps but have also enhanced their functionality, making them more accessible and useful to a broader audience.
Case Studies and Examples
Several case studies and examples illustrate the effective use of map numbers representation in various contexts. For instance, in urban planning, maps can be used to visualize population growth, demographic changes, and infrastructure development, providing valuable insights for policymakers and urban developers. In environmental monitoring, maps can display data on air quality, water pollution, and climate change, helping to identify areas of concern and track the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
What are the primary challenges in map numbers representation?
+The primary challenges include balancing the amount of information with visual clarity, selecting appropriate scales and colors, and ensuring that the map is accessible and understandable to its intended audience.
How have recent advancements in GIS and data visualization impacted map numbers representation?
+Recent advancements have enabled the creation of more dynamic, interactive, and visually appealing maps. They have also improved the integration of real-time data, enhanced the possibilities for 3D visualizations, and expanded the accessibility of maps through web-based platforms.
What are some of the key applications of map numbers representation?
+Key applications include urban planning, environmental monitoring, socio-economic research, and policy development. Map numbers representation is used to visualize and analyze spatial data, providing insights that can inform decision-making and policy interventions.
In conclusion, map numbers representation is a vital component of cartography and data visualization, offering a powerful tool for communicating complex spatial information. By understanding the principles, techniques, and recent advancements in this field, professionals and researchers can create maps that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also informative and engaging, thereby enhancing our understanding of the world and facilitating more informed decision-making.