Extract files are a crucial component in various digital processes, serving as containers for data that needs to be transferred, stored, or executed. The term "extract" in this context refers to the process of pulling out specific data or files from a larger dataset or system, packaging them in a format that is easily manageable and transportable. Extract files are widely used in data exchange, software installation, and backup processes, making them an essential tool in the digital landscape.
Understanding Extract Files
At their core, extract files are archives that hold a collection of files and folders. They are created to facilitate the distribution of software, data, or documents in a compact and organized manner. Extract files can be compressed to reduce their size, making them easier to transfer over networks or store on physical media. The compression also serves to protect the integrity of the data by ensuring that all components are bundled together and can be restored in their original form.
Types of Extract Files
Several types of extract files are in use, each with its own set of features and uses. Some of the most common include:
- ZIP files: One of the most widely recognized and used formats, ZIP files are compressed archives that can contain numerous files and folders. They are supported by most operating systems and can be easily created and extracted using built-in tools or third-party software.
- RAR files: Similar to ZIP files, RAR (Roshal ARchive) files offer better compression ratios and additional features like encryption and password protection. They require specific software to create and extract, such as WinRAR.
- TAR files: Commonly used in Unix and Linux environments, TAR (Tape Archive) files are uncompressed archives. They are often compressed using gzip or bzip2 to reduce their size. TAR files are useful for distributing and backing up data in these operating systems.
- ISO files: These are disk images of optical discs like CDs, DVDs, or Blu-rays. ISO files contain the exact replica of a disc’s content and can be mounted as virtual drives or burned onto physical media.
| Type of Extract File | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| ZIP | Compressed archive | General data exchange and software distribution |
| RAR | Compressed archive with encryption | Secure data exchange and compression |
| TAR | Uncompressed archive | Backing up and distributing data in Unix/Linux environments |
| ISO | Disk image of optical discs | Distributing operating systems, software, and creating backups of discs |
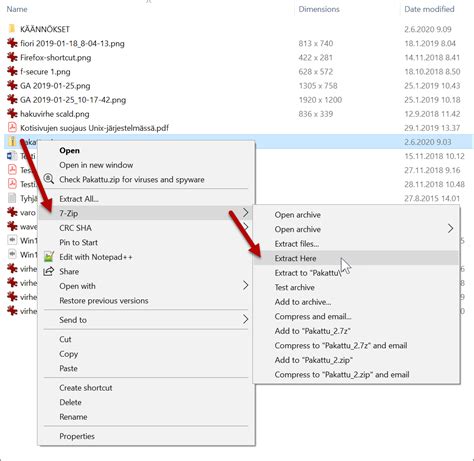
Creating and Extracting Files
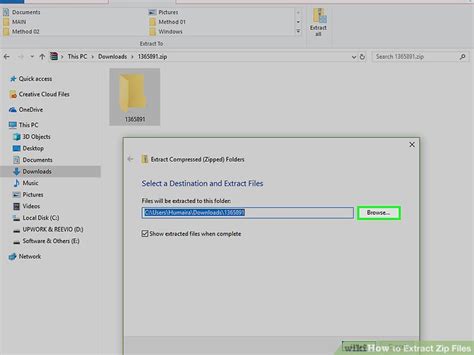
The process of creating an extract file involves selecting the files and folders you wish to archive, choosing the appropriate format (ZIP, RAR, TAR, etc.), and then using software to package and optionally compress these files. The steps can vary depending on the operating system and the tools being used. For extraction, most operating systems provide built-in utilities, or you can use third-party applications to unpack the archive and access its contents.
Best Practices for Working with Extract Files
To maximize the utility of extract files while minimizing potential risks, follow these best practices:
- Source Verification: Ensure that the extract files come from reputable sources to avoid malware and other security threats.
- Use Strong Passwords: If the extract file format supports encryption, use complex passwords to protect the contents from unauthorized access.
- Check Integrity: Verify the integrity of the extract file through checksums or digital signatures to ensure it has not been tampered with during transmission or storage.
- Update Software: Keep the software used to create and extract archives up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Key Points
- Extract files are used for data exchange, software distribution, and backup purposes.
- Different formats like ZIP, RAR, TAR, and ISO serve various needs and are supported by different operating systems and software.
- Verifying the source and integrity of extract files is crucial for security.
- Best practices include using strong passwords for encrypted archives and keeping relevant software up to date.
- Extract files can be compressed to reduce size and may require specific software for creation and extraction.
In conclusion, extract files play a vital role in digital data management, offering a convenient way to package, distribute, and store information. By understanding the different types of extract files, following best practices for their use, and being mindful of security considerations, individuals and organizations can leverage these tools effectively to streamline their data handling processes.
What is the primary purpose of extract files?
+The primary purpose of extract files is to facilitate the easy transfer, storage, and execution of data by packaging it into a single, manageable file or archive.
How do I create an extract file?
+To create an extract file, you typically select the files and folders you want to archive, choose the desired format (e.g., ZIP, RAR), and then use software to package and optionally compress these files.
What are some common types of extract files?
+Common types include ZIP, RAR, TAR, and ISO files, each serving different purposes such as general data exchange, secure compression, Unix/Linux data distribution, and disk imaging, respectively.