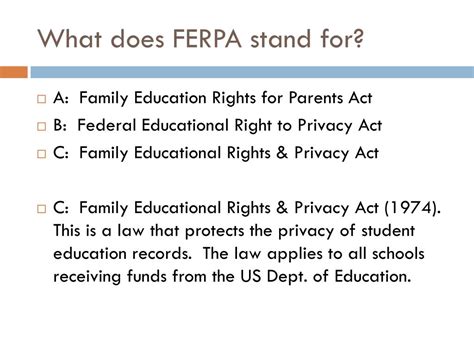
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act, commonly referred to as FERPA, is a federal law that protects the privacy of student education records. Enacted in 1974, FERPA applies to all educational agencies and institutions that receive federal funding, including elementary and secondary schools, colleges, and universities. The primary goal of FERPA is to ensure that students and their parents have control over their personal and academic information, maintaining the confidentiality and security of their education records.
Understanding FERPA’s Key Provisions

FERPA gives parents and eligible students (those who are 18 years old or attend a postsecondary institution) certain rights regarding their education records. These rights include the right to inspect and review their education records, the right to request amendment of their education records if they believe the records are inaccurate or misleading, and the right to consent to disclosure of personally identifiable information (PII) from their education records, except to the extent that FERPA authorizes disclosure without consent. One of the critical aspects of FERPA is its definition of education records, which includes any records that are directly related to a student and maintained by an educational agency or institution, or by a person acting for such agency or institution.
FERPA’s Impact on Educational Institutions
FERPA has significant implications for how educational institutions handle student data. Institutions must ensure that they have policies and procedures in place to protect the privacy of students’ education records. This includes training staff and faculty on FERPA requirements, implementing secure methods for storing and transmitting student data, and establishing procedures for responding to requests from parents and eligible students to exercise their FERPA rights. The law also allows for the disclosure of education records without consent under certain circumstances, such as to other school officials within the same institution who have a legitimate educational interest, to officials of another school where the student seeks or intends to enroll, or in connection with a student’s application for, or receipt of, financial aid.
| Key FERPA Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Right to Inspect and Review | Students and parents have the right to inspect and review the student's education records. |
| Right to Request Amendment | Students and parents can request that the school amend the student's education records if they believe the records are inaccurate or misleading. |
| Right to Consent to Disclosure | Generally, schools must have written permission from the parent or eligible student before releasing any personally identifiable information from the student's education record. |

Key Points
- FERPA protects the privacy of student education records, giving parents and eligible students certain rights.
- These rights include the right to inspect and review education records, request amendment of records, and consent to disclosure of personally identifiable information.
- FERPA applies to all educational agencies and institutions that receive federal funding.
- Institutions must have policies in place to protect student data and train staff on FERPA requirements.
- Disclosure of education records without consent is allowed under specific circumstances, such as for legitimate educational interests or in connection with financial aid.
FERPA's regulations have evolved over the years, with amendments and guidance provided by the U.S. Department of Education to clarify its provisions and ensure its enforcement. For instance, the Department has issued guidance on the application of FERPA to new technologies and on the handling of student records in the context of school safety and security. Educational institutions must stay abreast of these developments to ensure compliance and to maintain the trust of their students and parents.
Implementing FERPA in Educational Settings

Effective implementation of FERPA in educational settings involves a multifaceted approach. Institutions should develop comprehensive policies that outline procedures for managing student records, including how records are created, maintained, and destroyed. Training programs for faculty and staff are essential to ensure that all individuals handling student records understand their responsibilities under FERPA. Furthermore, institutions must establish clear protocols for responding to requests from parents and eligible students, including requests to inspect records, amend records, and consent to disclosure.
Challenges and Considerations
One of the challenges educational institutions face in implementing FERPA is balancing the need to protect student privacy with the need to share information for legitimate educational purposes. Institutions must carefully evaluate each request for disclosure to determine whether it meets the criteria for an exception under FERPA. Additionally, the rise of digital technologies and online learning platforms has introduced new complexities in managing student data privacy, requiring institutions to adopt robust cybersecurity measures and to ensure that third-party service providers comply with FERPA.
FERPA also intersects with other laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for institutions that serve international students, and state laws regarding student data privacy. Navigating these legal landscapes requires institutions to have a deep understanding of the regulatory environment and to be proactive in their compliance efforts.
What is the primary purpose of FERPA?
+The primary purpose of FERPA is to protect the privacy of student education records and to provide parents and eligible students with certain rights regarding their education records.
Who is protected under FERPA?
+FERPA protects the education records of students who are or have been in attendance at an educational agency or institution that receives federal funding, including elementary and secondary schools, colleges, and universities.
What constitutes an education record under FERPA?
+An education record is any record that is directly related to a student and maintained by an educational agency or institution, or by a person acting for such agency or institution.
In conclusion, FERPA is a critical federal law that safeguards the privacy of student education records, providing parents and eligible students with significant rights. Understanding and complying with FERPA’s provisions are essential for educational institutions to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and security of student data. By adopting comprehensive policies, providing training, and staying informed about regulatory developments, institutions can uphold their obligations under FERPA and foster a culture of privacy and respect for student information.