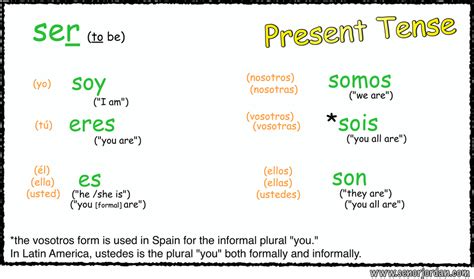
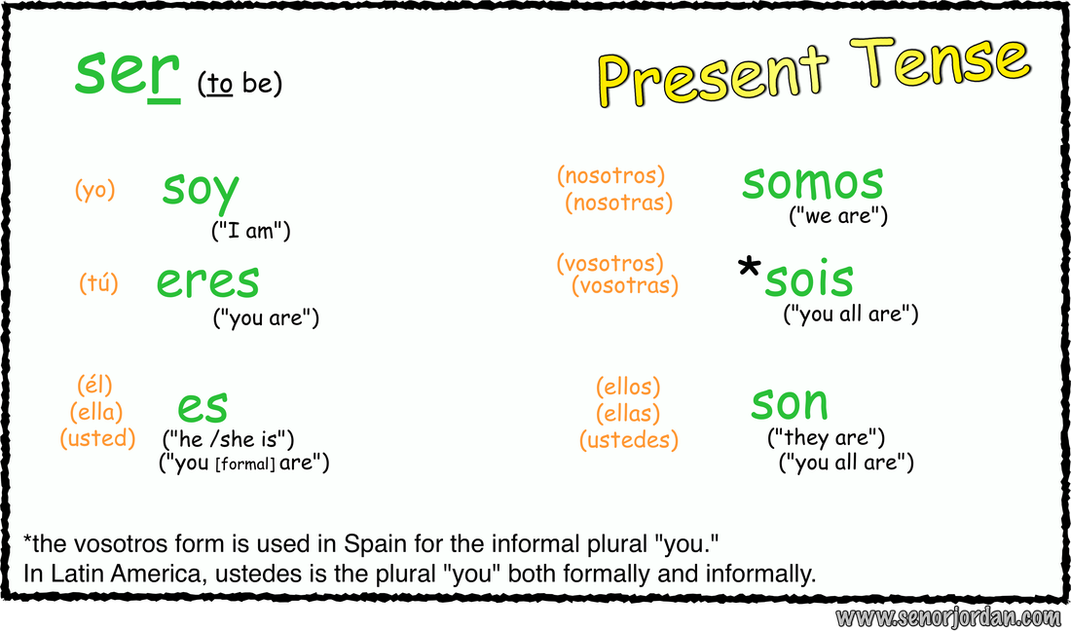
The Spanish verb "ser" is one of the most fundamental and complex verbs in the Spanish language, serving multiple purposes depending on the context in which it is used. At its core, "ser" translates to "to be" in English, but its application extends far beyond a simple translation due to the nuances of Spanish grammar and the distinction between "ser" and another verb that also means "to be," which is "estar".
Basic Uses of Ser

“Ser” is used to describe permanent or inherent qualities of something or someone, such as physical characteristics, nationality, occupation, or ownership. For example:
- Yo soy estudiante - I am a student. (Here, “ser” is used to describe an occupation or role.)
- Ella es alta - She is tall. (This describes a physical characteristic.)
- Él es médico - He is a doctor. (This describes a profession.)
- Esa casa es de mi familia - That house belongs to my family. (This describes ownership.)
Temporal and Spatial Uses
“Ser” can also be used to indicate the time of an event or the location where something happens, particularly in more formal or written contexts. For instance:
- La reunión es a las tres - The meeting is at three. (Here, “ser” is used to specify the time of an event.)
- La biblioteca es en el centro de la ciudad - The library is in the city center. (This describes a location.)
| Verb | Use |
|---|---|
| Ser | Permanent qualities, occupation, nationality, time, and location in formal contexts. |
| Estoy (from estar) | Temporary conditions, emotions, and locations in informal contexts. |
Idiomatic Expressions and Passive Voice

“Ser” is also used in various idiomatic expressions and to form the passive voice in Spanish. For example:
- Ser de can mean “to be from” or “to belong to,” as in Soy de Madrid - I am from Madrid.
- Ser como can mean “to be like,” as in Es como un hermano para mí - He is like a brother to me.
- For the passive voice, ser is used with the past participle of a verb, such as La casa fue vendida - The house was sold.
Key Points
- The verb "ser" in Spanish is used to describe permanent qualities, occupations, nationalities, and in formal contexts, time and location.
- It's essential to distinguish "ser" from "estar," as they have different applications based on the temporality and nature of the condition being described.
- "Ser" is used in idiomatic expressions and to form the passive voice.
- Understanding the uses of "ser" is fundamental for communicating effectively in Spanish.
- Practice is key to mastering the nuances of "ser" and "estar" in Spanish.
In conclusion, "ser" is a multifaceted verb that plays a critical role in Spanish grammar, covering a wide range of applications from describing inherent qualities to forming the passive voice. Its correct usage is vital for fluent and accurate communication in Spanish.
What are the main differences between “ser” and “estar” in Spanish?
+The primary difference between “ser” and “estar” is that “ser” is used for permanent or inherent qualities, occupations, and in some formal contexts, time and location, whereas “estar” is used for temporary conditions, emotions, and locations in informal contexts.
How do you use “ser” to describe someone’s profession?
+To describe someone’s profession using “ser,” you simply conjugate “ser” according to the subject and follow it with the profession. For example, “Yo soy médico” (I am a doctor) or “Ella es ingeniera” (She is an engineer).
Can “ser” be used to talk about the time of an event?
+Yes, “ser” can be used to indicate the time of an event, especially in formal or written contexts. For example, “La reunión es a las tres” (The meeting is at three).