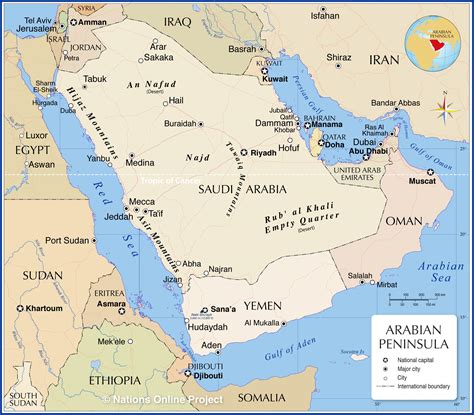
The Arabian Peninsula, situated in the southwestern corner of Asia, boasts a unique combination of geographic features that have contributed to its strategic importance and diverse economies. Stretching over 3 million square kilometers, the peninsula is bounded by the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden to the south, the Arabian Sea to the southeast, and the Persian Gulf to the northeast. This distinct geography has played a pivotal role in shaping the history, culture, and economic development of the region.
Natural Resources and Trade Routes
The Arabian Peninsula is endowed with an abundance of natural resources, including vast oil and gas reserves, which have been the backbone of the region’s economy for decades. The discovery of oil in the 20th century transformed the economic landscape of countries such as Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Qatar, enabling them to invest heavily in infrastructure, education, and healthcare. The peninsula’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa has also made it an important hub for international trade, with the Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz being critical waterways for global commerce.
Geographic Features and Climate
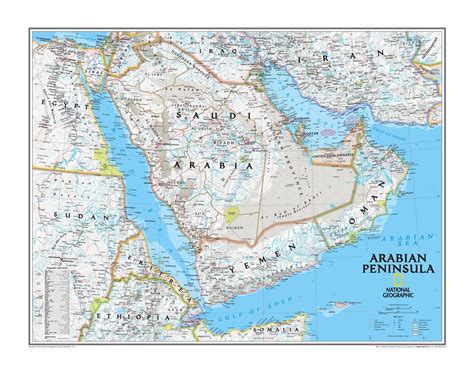
The Arabian Peninsula’s terrain is characterized by vast deserts, including the Rub’ al Khali, also known as the Empty Quarter, which is the largest sand desert in the world. The region’s climate is generally hot and dry, with very little rainfall throughout the year. However, the coastal areas and mountainous regions, such as the Sarawat Mountains in southwestern Saudi Arabia and the Hajar Mountains in Oman, experience a more moderate climate and are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. The peninsula’s unique geography and climate have necessitated the development of innovative solutions for water conservation, agriculture, and urban planning.
| Country | Oil Reserves (billion barrels) | Natural Gas Reserves (trillion cubic meters) |
|---|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | 298.3 | 7.17 |
| United Arab Emirates | 97.8 | 6.09 |
| Qatar | 25.4 | 23.86 |
| Oman | 5.3 | 0.68 |
| Kuwait | 102.5 | 1.81 |
Key Points
- The Arabian Peninsula is home to vast oil and gas reserves, which have driven the region's economic growth and development.
- The region's strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa makes it an important hub for international trade.
- The peninsula's unique geography and climate have necessitated the development of innovative solutions for water conservation, agriculture, and urban planning.
- Countries in the region, such as Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, have invested heavily in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, diversifying their economies and improving the standard of living for their citizens.
- The region's cultural and historical significance, including the birthplace of Islam and the ancient trade routes, continues to attract tourists and scholars from around the world.
Economic Diversification and Investment

In recent years, countries in the Arabian Peninsula have sought to diversify their economies, reducing their dependence on oil and gas exports. This has involved investing in sectors such as tourism, finance, and technology, as well as developing infrastructure projects such as airports, seaports, and logistics hubs. For example, the United Arab Emirates has established itself as a major tourism destination, with Dubai’s airport serving as a key transit hub for international travelers. Similarly, Saudi Arabia has launched a series of initiatives aimed at promoting foreign investment and developing its non-oil sectors, including the establishment of the Saudi Arabian General Investment Authority.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the many advantages of the Arabian Peninsula’s geography, the region also faces several challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and the impacts of climate change. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are expected to exacerbate these issues, making it essential for countries in the region to develop sustainable solutions for managing their natural resources. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and investment, particularly in the fields of renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and environmental conservation.
As the Arabian Peninsula continues to evolve and grow, its unique geography will remain a critical factor in shaping the region's economy, culture, and environment. By leveraging their natural resources, investing in infrastructure and innovation, and addressing the challenges posed by climate change, countries in the region can ensure a prosperous and sustainable future for their citizens.
What are the main natural resources found in the Arabian Peninsula?
+The Arabian Peninsula is rich in oil and natural gas reserves, with countries such as Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Qatar being among the largest producers in the world.
What are the main challenges facing the Arabian Peninsula due to its geography and climate?
+The region faces several challenges, including water scarcity, desertification, and the impacts of climate change, which are expected to exacerbate these issues and require innovative solutions for sustainable development.
How are countries in the Arabian Peninsula diversifying their economies and reducing their dependence on oil exports?
+Countries in the region are investing in sectors such as tourism, finance, and technology, as well as developing infrastructure projects and promoting foreign investment, to reduce their dependence on oil exports and create a more diversified economy.
Meta Description: Discover the Arabian Peninsula’s unique geographic advantages, including its strategic location, natural resources, and innovative solutions to environmental challenges, and learn how countries in the region are diversifying their economies and investing in sustainable development. (147 characters)