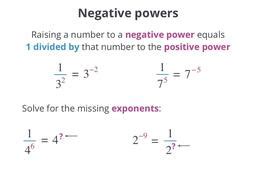
Negative distribution, a concept often misunderstood in the realm of business and logistics, plays a crucial role in the strategic planning and execution of supply chain management. At its core, negative distribution refers to the practice of deliberately avoiding or limiting the distribution of products or services to certain markets, customers, or geographical areas. This strategy is employed for various reasons, including but not limited to, regulatory compliance, market saturation, competitive advantage, and resource optimization. Understanding how negative distribution works is essential for businesses aiming to maximize their market presence and profitability while minimizing potential risks and liabilities.
Key Points
- Strategic avoidance of certain markets or customer segments to maintain profitability and competitive edge.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements by limiting distribution in restricted areas.
- Optimization of resources by focusing on high-potential markets and segments.
- Enhancement of brand image and exclusivity through selective distribution.
- Minimization of operational and logistical complexities in challenging or low-yield areas.
Market Segmentation and Exclusion
One of the primary ways negative distribution works is through the careful segmentation of markets and the deliberate exclusion of certain segments. This approach allows businesses to focus their resources on the most profitable and promising markets, thereby maximizing returns on investment. By analyzing market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive dynamics, companies can identify areas where their products or services may not be well-received or may face significant competition, and thus, decide to limit or avoid distribution in these areas.
Regulatory Compliance
Negative distribution also plays a critical role in ensuring regulatory compliance. In many industries, products or services are subject to stringent regulations that dictate where and how they can be sold. For instance, certain pharmaceuticals may be restricted in certain countries due to legal or safety concerns. By employing negative distribution strategies, companies can avoid the legal and financial risks associated with non-compliance, ensuring that their operations remain within the bounds of the law.
| Industry | Regulatory Considerations | Distribution Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Drug safety and efficacy standards | Restrict distribution to countries with approved regulatory frameworks |
| Financial Services | Anti-money laundering and know-your-customer laws | Avoid markets with high risk of non-compliance |
| Technology | Intellectual property rights and data privacy laws | Limit distribution in areas with stringent IP protection and data privacy regulations |
Resource Optimization and Competitive Advantage

Another way negative distribution works is by enabling businesses to optimize their resources and gain a competitive advantage. By focusing distribution efforts on high-potential markets and segments, companies can allocate their resources more efficiently, thereby enhancing their competitive edge. This selective approach to distribution allows businesses to concentrate on areas where they can achieve the greatest impact, improving brand visibility, customer satisfaction, and ultimately, revenue.
Brand Exclusivity and Image Enhancement
Negative distribution can also be used as a tool to enhance brand image and exclusivity. Luxury brands, for example, often limit their distribution to high-end retailers and select locations to maintain an aura of exclusivity and premium quality. This strategy helps to protect the brand’s image and appeal to its target market, which values uniqueness and scarcity. By being selective about where and how their products are sold, luxury brands can control their brand narrative and perceived value.
In conclusion, negative distribution is a multifaceted strategy that, when employed thoughtfully, can offer businesses a range of benefits, from regulatory compliance and resource optimization to competitive advantage and brand image enhancement. By understanding the complexities of market dynamics and consumer behavior, and by making informed decisions about where and how to distribute their products or services, companies can navigate the challenges of the global marketplace more effectively, ultimately driving growth and profitability.
How does negative distribution contribute to regulatory compliance?
+Negative distribution helps in ensuring regulatory compliance by limiting or avoiding the distribution of products or services in areas where they may not meet legal or safety standards, thus reducing the risk of legal and financial penalties.
Can negative distribution be used to enhance brand image?
+Yes, by selectively distributing products or services, especially in the case of luxury brands, companies can create an aura of exclusivity and premium quality, thereby enhancing their brand image and appeal to their target market.
How does negative distribution aid in resource optimization?
+Negative distribution allows businesses to focus their resources on the most promising markets and segments, thereby optimizing resource allocation and maximizing returns on investment.