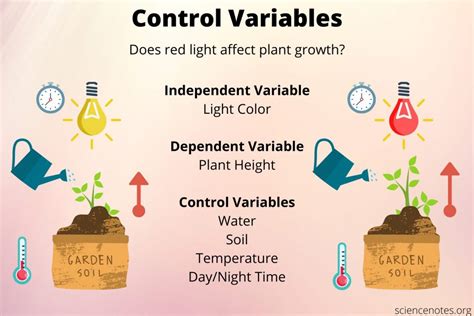
A controlled variable, also known as a constant variable, is a factor or element in an experiment or study that is kept constant or unchanged throughout the investigation. The purpose of controlling variables is to ensure that the results of the experiment are due to the manipulation of the independent variable, rather than other factors that could influence the outcome. By controlling variables, researchers can isolate the effect of the independent variable and draw conclusions about the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Importance of Controlled Variables
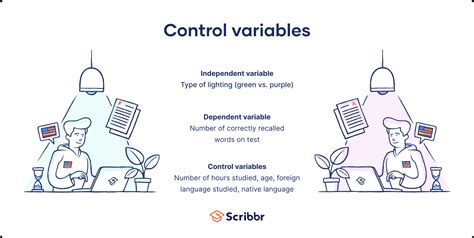
Controlled variables are crucial in scientific research because they help to:
- Eliminate confounding variables: Factors that could affect the outcome of the experiment and lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Increase internal validity: The extent to which the experiment is free from bias and error, and the results can be attributed to the manipulation of the independent variable.
- Improve reliability: The consistency of the results, which is essential for drawing conclusions and making predictions.
- Enhance external validity: The extent to which the results can be generalized to other populations, settings, or conditions.
Types of Controlled Variables
There are several types of controlled variables, including:
- Environmental variables: Factors such as temperature, humidity, and lighting that can affect the experiment.
- Instrumental variables: Factors related to the measurement tools or equipment used in the experiment.
- Participant variables: Characteristics of the participants, such as age, sex, or experience, that could influence the outcome.
- Procedural variables: Factors related to the experimental procedure, such as the order of tasks or the instructions provided.
| Variable Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Environmental variable | Temperature (20°C) |
| Instrumental variable | Calibrated measurement tool |
| Participant variable | Age range (18-25 years) |
| Procedural variable | Randomized task order |
Key Points
- A controlled variable is a factor that is kept constant throughout an experiment to ensure the results are due to the manipulation of the independent variable.
- Controlled variables help eliminate confounding variables, increase internal validity, improve reliability, and enhance external validity.
- Types of controlled variables include environmental, instrumental, participant, and procedural variables.
- Controlling variables is essential for advancing knowledge and making informed decisions in various fields.
- By controlling variables, researchers can increase the validity and reliability of their findings.
Best Practices for Controlling Variables

To effectively control variables, researchers should:
- Identify potential variables: Recognize factors that could influence the outcome of the experiment.
- Develop a control plan: Determine how to control each variable, such as using a randomized design or matching participants.
- Implement control measures: Put the control plan into action, such as using a calibrated measurement tool or maintaining a consistent environmental condition.
- Monitor and adjust: Continuously monitor the experiment and make adjustments as needed to ensure variables remain controlled.
Common Challenges in Controlling Variables
Despite the importance of controlling variables, researchers often face challenges, such as:
- Unanticipated variables: Factors that arise during the experiment that were not initially considered.
- Limited resources: Constraints on time, funding, or equipment that can limit the ability to control variables.
- Complexity of the experiment: Experiments with multiple variables or complex procedures can be difficult to control.
What is the purpose of controlling variables in an experiment?
+The purpose of controlling variables is to ensure that the results of the experiment are due to the manipulation of the independent variable, rather than other factors that could influence the outcome.
What are some common types of controlled variables?
+Common types of controlled variables include environmental variables, instrumental variables, participant variables, and procedural variables.
Why is it important to control variables in an experiment?
+Controlling variables is essential for increasing the validity and reliability of the findings, which is crucial for advancing knowledge and making informed decisions in various fields.