The concept of a science law definition is multifaceted, encompassing a broad range of principles and theories that govern the natural world. At its core, a science law is a statement that describes a fundamental relationship between variables or phenomena, often derived from empirical evidence and observation. Science laws, such as the laws of motion, thermodynamics, and gravity, provide a framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of physical systems, from the smallest subatomic particles to the vast expanse of the cosmos.
One of the key characteristics of science laws is their universality and consistency. They are believed to hold true regardless of time, location, or specific conditions, providing a consistent and reliable framework for scientific inquiry and experimentation. For instance, the law of universal gravitation, first formulated by Sir Isaac Newton, describes the gravitational force between two objects as a function of their mass and the distance between them. This law has been extensively tested and validated through numerous experiments and observations, and its principles are widely applied in fields such as astronomy, physics, and engineering.
Key Points
- Science laws are statements that describe fundamental relationships between variables or phenomena.
- They are derived from empirical evidence and observation, and are believed to be universal and consistent.
- Science laws provide a framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of physical systems.
- They are widely applied in various fields, including physics, astronomy, engineering, and more.
- Science laws are subject to refinement and revision as new evidence and observations become available.
Nature of Science Laws

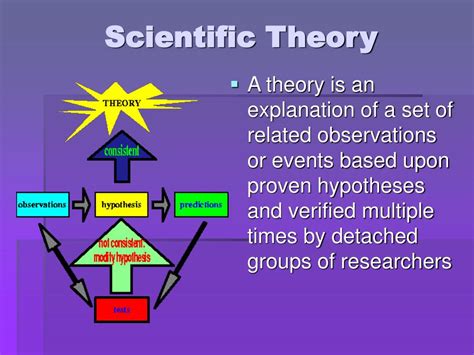
Science laws are often contrasted with scientific theories, which are more comprehensive and explanatory frameworks that attempt to explain the underlying mechanisms and principles that govern a particular phenomenon. While science laws provide a descriptive framework for understanding the behavior of physical systems, scientific theories provide a deeper understanding of the underlying causes and mechanisms that drive those behaviors. For example, the theory of evolution provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the diversity of life on Earth, while the laws of genetics and heredity describe the specific mechanisms that govern the transmission of traits from one generation to the next.
Types of Science Laws
There are several types of science laws, each describing a specific aspect of the natural world. Some of the most well-known science laws include:
- Physical laws, which describe the behavior of physical systems, such as the laws of motion, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism.
- Biological laws, which describe the behavior of living organisms, such as the laws of genetics, evolution, and ecology.
- Chemical laws, which describe the behavior of chemical reactions and processes, such as the laws of thermodynamics and chemical equilibrium.
| Science Law | Description |
|---|---|
| Law of Universal Gravitation | Describes the gravitational force between two objects as a function of their mass and distance. |
| Law of Conservation of Energy | States that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. |
| Law of Evolution | Describes the process by which species change and adapt over time through natural selection and genetic drift. |
Importance of Science Laws
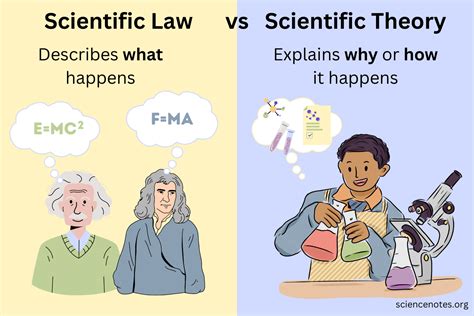
Science laws play a critical role in advancing our understanding of the natural world and driving technological innovation. By providing a framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of physical systems, science laws enable scientists and engineers to develop new technologies, materials, and processes that transform our daily lives. For example, the development of transistors and microchips, which are based on the principles of semiconductor physics, has revolutionized the field of electronics and enabled the creation of smaller, faster, and more powerful computing devices.
Applications of Science Laws
Science laws have numerous applications across a wide range of fields, including:
- Engineering, where science laws are used to design and develop new technologies, such as bridges, buildings, and electronic devices.
- Astronomy, where science laws are used to understand the behavior of celestial objects, such as stars, planets, and galaxies.
- Medicine, where science laws are used to understand the behavior of living organisms and develop new treatments and therapies.
What is the difference between a science law and a scientific theory?
+A science law is a statement that describes a fundamental relationship between variables or phenomena, while a scientific theory is a more comprehensive and explanatory framework that attempts to explain the underlying mechanisms and principles that govern a particular phenomenon.
How are science laws developed and refined?
+Science laws are developed and refined through a process of observation, experimentation, and evidence-based reasoning. As new evidence and observations become available, science laws are subject to refinement and revision to ensure that they remain consistent with the latest scientific understanding.
What are some examples of science laws in different fields?
+Examples of science laws include the laws of motion, thermodynamics, and gravity in physics, the laws of genetics and evolution in biology, and the laws of chemical equilibrium and thermodynamics in chemistry.
In conclusion, science laws are fundamental principles that govern the natural world, providing a framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of physical systems. By understanding and applying science laws, scientists and engineers can develop new technologies, materials, and processes that transform our daily lives and drive technological innovation. As our understanding of the natural world continues to evolve, science laws will remain a critical component of scientific inquiry and discovery.