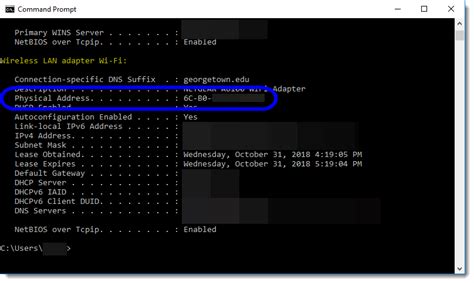
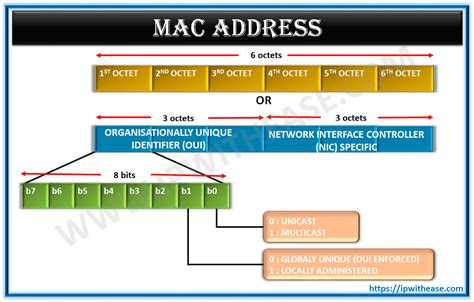
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communication at the data link layer of a network segment. It is used to identify devices on a network and is typically assigned by the manufacturer of the network interface card (NIC). The MAC address is a 48-bit address, usually represented as six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by colons or dashes. For example, a MAC address might look like this: 00:11:22:33:44:55.
The MAC address is an essential component of the OSI model, which is a conceptual framework used to understand how data is transmitted over a network. The MAC address is used to filter incoming data packets and determine where to send outgoing data packets. It is also used in various network protocols, such as Ethernet and Wi-Fi, to manage data transmission and ensure that data is delivered to the correct device.
MAC addresses are usually assigned by the manufacturer of the network interface card and are stored in the device's read-only memory (ROM). However, it is possible to change a MAC address using software or firmware modifications. This can be useful in certain situations, such as when a device is replaced or when a network administrator wants to assign a specific MAC address to a device.
Key Points
- A MAC address is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communication at the data link layer.
- MAC addresses are typically assigned by the manufacturer of the network interface card.
- MAC addresses are used to identify devices on a network and filter incoming data packets.
- MAC addresses are an essential component of the OSI model and are used in various network protocols.
- MAC addresses can be changed using software or firmware modifications in certain situations.
How MAC Addresses Work
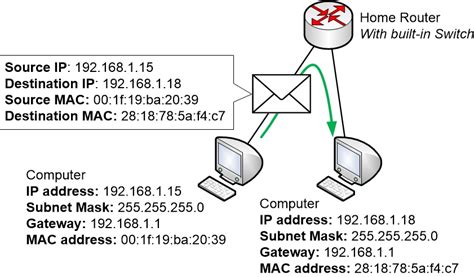
When a device is connected to a network, its MAC address is used to identify it and manage data transmission. Here’s how it works:
1. The device sends a request to the network to access the internet or other resources.
2. The network router or switch receives the request and checks the MAC address of the device.
3. The router or switch uses the MAC address to determine where to send the data packets.
4. The data packets are transmitted to the device with the matching MAC address.
This process is repeated for every data packet transmitted over the network, ensuring that data is delivered to the correct device.
MAC Address Formats
MAC addresses can be represented in several formats, including:
Unicast MAC address: a unique address assigned to a single device.
Multicast MAC address: an address shared by multiple devices, used for broadcasting data to multiple devices.
Broadcast MAC address: an address used to transmit data to all devices on a network.
| MAC Address Type | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Unicast | 00:11:22:33:44:55 | Unique address assigned to a single device |
| Multicast | 01:00:5E:00:00:00 | Address shared by multiple devices for broadcasting data |
| Broadcast | FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF | Address used to transmit data to all devices on a network |
MAC Address Security Concerns
MAC addresses can be used to improve network security, but they can also be vulnerable to attacks. Here are some security concerns related to MAC addresses:
MAC address spoofing: an attacker can pretend to be a legitimate device by using its MAC address.
MAC address filtering: a network can be configured to only allow devices with specific MAC addresses to connect.
MAC address authentication: a device can be required to authenticate its MAC address before being allowed to connect to a network.
Network administrators can take steps to mitigate these security concerns, such as implementing MAC address filtering and authentication, and monitoring network activity for suspicious behavior.
Best Practices for Managing MAC Addresses
Here are some best practices for managing MAC addresses:
Assign unique MAC addresses to devices: ensure that each device has a unique MAC address to prevent conflicts.
Use MAC address filtering: configure the network to only allow devices with specific MAC addresses to connect.
Monitor network activity: regularly monitor network activity to detect suspicious behavior and prevent MAC address spoofing attacks.
What is a MAC address used for?
+A MAC address is used to identify devices on a network and manage data transmission.
How is a MAC address assigned?
+A MAC address is typically assigned by the manufacturer of the network interface card.
Can a MAC address be changed?
+Yes, a MAC address can be changed using software or firmware modifications.
Meta Description: Learn about MAC addresses, including what they are, how they work, and their role in network communication. Discover best practices for managing MAC addresses and mitigating security concerns. (145 characters)