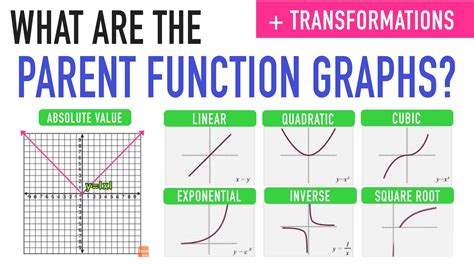
Parent functions are a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in algebra and calculus. They serve as the foundation for more complex functions and are used to model real-world phenomena. In essence, parent functions are the simplest form of a function, and all other functions can be derived from them through transformations. Understanding how parent functions work is crucial for students and professionals alike, as it enables them to analyze and solve problems in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics. In this article, we will delve into the world of parent functions, exploring their characteristics, types, and applications, as well as providing examples and illustrations to facilitate a deeper understanding of this essential mathematical concept.
Key Points
- Parent functions are the simplest form of a function and serve as the foundation for more complex functions.
- There are several types of parent functions, including linear, quadratic, polynomial, rational, and exponential functions.
- Transformations, such as vertical and horizontal shifts, stretches, and compressions, can be applied to parent functions to create more complex functions.
- Parent functions can be used to model real-world phenomena, such as population growth, financial transactions, and physical systems.
- Understanding parent functions is essential for solving problems in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics.
Types of Parent Functions
There are several types of parent functions, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The most common types of parent functions include linear, quadratic, polynomial, rational, and exponential functions. Linear functions, for example, are used to model situations where the rate of change is constant, such as the distance traveled by a car at a constant speed. Quadratic functions, on the other hand, are used to model situations where the rate of change is not constant, such as the trajectory of a projectile. Polynomial functions are used to model more complex situations, such as the growth of a population or the behavior of a physical system. Rational functions are used to model situations where the output is a fraction, such as the ratio of two quantities. Exponential functions are used to model situations where the rate of change is proportional to the current value, such as population growth or financial transactions.
Characteristics of Parent Functions
Parent functions have several characteristics that make them useful for modeling real-world phenomena. They are typically continuous, meaning that they have no gaps or jumps, and they are defined for all real numbers. They also have a unique shape, which can be used to identify the type of function. For example, linear functions have a straight line shape, while quadratic functions have a parabolic shape. Parent functions can also be transformed in various ways, such as vertical and horizontal shifts, stretches, and compressions, to create more complex functions. These transformations can be used to model real-world phenomena, such as the effect of a change in temperature on a physical system or the impact of a change in interest rates on financial transactions.
| Type of Function | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Function | Constant rate of change, straight line shape | Modeling distance traveled, cost of production |
| Quadratic Function | Non-constant rate of change, parabolic shape | Modeling projectile motion, population growth |
| Polynomial Function | Complex shape, multiple turning points | Modeling population growth, physical systems |
| Rational Function | Fractional output, discontinuities | Modeling ratios, financial transactions |
| Exponential Function | Proportional rate of change, exponential growth | Modeling population growth, financial transactions |
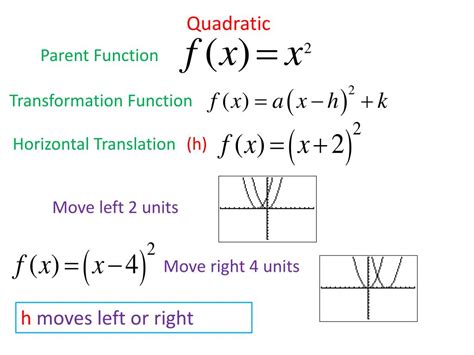
Transformations of Parent Functions

Transformations are used to create more complex functions from parent functions. There are several types of transformations, including vertical and horizontal shifts, stretches, and compressions. Vertical shifts involve moving the function up or down, while horizontal shifts involve moving the function left or right. Stretches and compressions involve changing the scale of the function, making it wider or narrower. These transformations can be used to model real-world phenomena, such as the effect of a change in temperature on a physical system or the impact of a change in interest rates on financial transactions.
Applications of Parent Functions
Parent functions have numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, economics, and finance. They are used to model real-world phenomena, such as population growth, financial transactions, and physical systems. For example, exponential functions are used to model population growth, while rational functions are used to model financial transactions. Polynomial functions are used to model complex physical systems, such as the motion of a pendulum or the behavior of a circuit. By understanding parent functions and their transformations, professionals can analyze and solve problems in these fields, making accurate predictions and decisions.
What are parent functions, and why are they important?
+Parent functions are the simplest form of a function and serve as the foundation for more complex functions. They are important because they are used to model real-world phenomena and solve problems in various fields, including physics, engineering, and economics.
What are the different types of parent functions?
+The most common types of parent functions include linear, quadratic, polynomial, rational, and exponential functions. Each type of function has its unique characteristics and applications.
How are parent functions transformed to create more complex functions?
+Parent functions can be transformed through vertical and horizontal shifts, stretches, and compressions. These transformations can be used to model real-world phenomena and solve problems in various fields.
In conclusion, parent functions are a fundamental concept in mathematics, and understanding their characteristics, types, and applications is essential for solving problems in various fields. By recognizing the type of function and its characteristics, professionals can choose the most appropriate model for a given situation and make accurate predictions and decisions. The transformations of parent functions, such as vertical and horizontal shifts, stretches, and compressions, can be used to create more complex functions and model real-world phenomena. As we continue to develop and apply mathematical models to real-world problems, the importance of parent functions will only continue to grow.