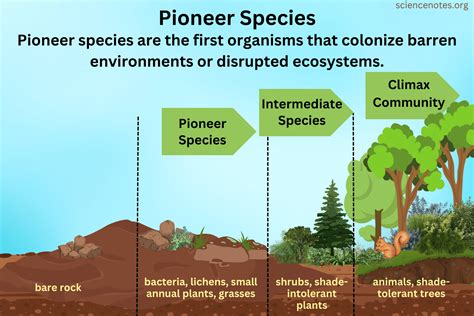
The concept of pioneer species is deeply rooted in the field of ecology, where these species play a crucial role in initiating the process of ecological succession. Pioneer species are the first to colonize a new or disturbed area, paving the way for other species to follow. Their ability to thrive in challenging environments makes them essential for the development of ecosystems. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of pioneer species, exploring their characteristics, roles, and examples.
Definition and Role of Pioneer Species
Pioneer species are typically hardy and adaptable, capable of surviving in areas with limited resources. They are often characterized by their ability to fix nitrogen, tolerate extreme temperatures, and withstand high levels of salinity or toxicity. These species are the vanguard of ecological succession, facilitating the creation of a more complex ecosystem. By altering their environment through processes such as nutrient cycling and soil modification, pioneer species create opportunities for other species to establish themselves.
Examples of Pioneer Species
One of the most well-known examples of pioneer species is the lichen. Lichens are composite organisms made up of fungi and algae or cyanobacteria, which work together to break down rocks and create soil. This process, known as weathering, is crucial for the establishment of plant life. Other examples of pioneer species include certain types of mosses, ferns, and grasses, which can thrive in areas with limited soil and harsh conditions.
| Species | Characteristics | Role in Ecological Succession |
|---|---|---|
| Lichens | Composite organisms, tolerant of extreme conditions | Soil creation through weathering |
| Mosses | Small, non-vascular plants, capable of growing in dense mats | Soil stabilization and retention of moisture |
| Ferns | Vascular plants, often found in shaded, moist areas | Contribution to soil development and increase in biodiversity |
Key Characteristics of Pioneer Species

Pioneer species possess a range of characteristics that enable them to thrive in challenging environments. These include the ability to tolerate extreme conditions, such as high temperatures, drought, or salinity, as well as the capacity to fix nitrogen and produce organic matter. Additionally, pioneer species often have adaptations that allow them to compete effectively for resources, such as deep roots or extensive root systems.
Adaptations of Pioneer Species
The adaptations of pioneer species are crucial to their success in disturbed or newly created environments. For example, some pioneer species have developed symbiotic relationships with microorganisms, which provide essential nutrients. Others have evolved unique morphological features, such as deep roots or small leaves, which enable them to conserve water and withstand extreme temperatures.
Key Points
- Pioneer species play a crucial role in initiating ecological succession and creating opportunities for other species to establish themselves.
- These species are often characterized by their ability to tolerate extreme conditions, fix nitrogen, and produce organic matter.
- Examples of pioneer species include lichens, mosses, ferns, and certain types of grasses.
- The adaptations of pioneer species, such as symbiotic relationships with microorganisms and unique morphological features, are essential for their success in challenging environments.
- Understanding the characteristics and functions of pioneer species can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of ecosystem development and the importance of conservation efforts.
Importance of Pioneer Species in Ecosystem Development
The importance of pioneer species in ecosystem development cannot be overstated. These species are the foundation upon which more complex ecosystems are built, providing a range of essential functions, including soil creation, nutrient cycling, and habitat provision. By facilitating the establishment of other species, pioneer species play a critical role in promoting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
Conservation Implications
The conservation of pioneer species is essential for maintaining healthy and resilient ecosystems. This can be achieved through the protection of habitats, the restoration of degraded areas, and the promotion of sustainable land-use practices. By conserving pioneer species and the ecosystems they inhabit, we can help to maintain the natural balance of ecosystems and ensure the long-term health of our planet.
What is the role of pioneer species in ecological succession?
+Pioneer species play a crucial role in initiating ecological succession, creating opportunities for other species to establish themselves and facilitating the development of more complex ecosystems.
What are some examples of pioneer species?
+Examples of pioneer species include lichens, mosses, ferns, and certain types of grasses. These species are often characterized by their ability to tolerate extreme conditions and facilitate the creation of soil and habitat for other species.
Why are pioneer species important for ecosystem development?
+Pioneer species are important for ecosystem development because they provide a range of essential functions, including soil creation, nutrient cycling, and habitat provision. They also facilitate the establishment of other species, promoting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
In conclusion, pioneer species play a vital role in the development of ecosystems, facilitating the creation of soil, habitat, and opportunities for other species to establish themselves. By understanding the characteristics and functions of these species, we can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of ecosystem development and the importance of conservation efforts. As we continue to face the challenges of environmental degradation and biodiversity loss, the conservation of pioneer species and the ecosystems they inhabit is more important than ever.



