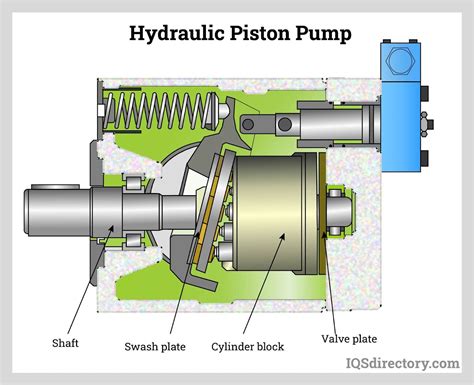
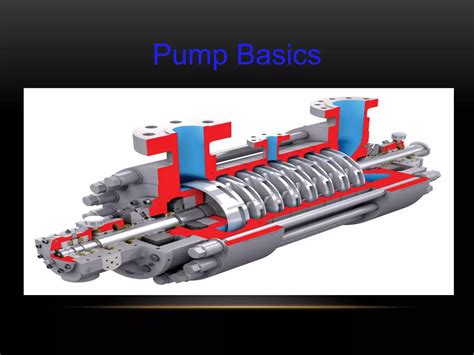
The concept of a pump is multifaceted and can be defined in various ways, depending on the context in which it is used. At its core, a pump is a device or mechanism that raises, transfers, or compresses fluids, gases, or sometimes even slurries, from one location to another. This can be achieved through mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, or even electromagnetic means. The diversity in pump applications ranges from industrial processes, such as oil extraction and water treatment, to biological systems, like the human heart, which pumps blood throughout the body.
Primary Definitions of Pump

A primary definition of a pump revolves around its mechanical function. Mechanically, a pump is an apparatus that uses suction or pressure to raise, move, or force a fluid, such as water or gas, from one place to another. This definition encompasses a wide range of devices, from small, handheld pumps used for inflating tires or operating spray bottles, to large, industrial pumps used in manufacturing, agriculture, and municipal water supply systems.
Types of Pumps Based on Operation
There are several types of pumps based on their operational mechanisms. These include centrifugal pumps, which use a spinning impeller to create suction and push the fluid through the pump, and positive displacement pumps, where a fixed volume of fluid is trapped and then forced out of the pump with each rotation or stroke. Other types include diaphragm pumps, which use a flexible membrane to create suction and discharge, and jet pumps, which use a high-velocity fluid jet to create a vacuum and draw in fluid.
| Type of Pump | Description |
|---|---|
| Centrifugal Pump | Uses an impeller to create suction and pressure |
| Positive Displacement Pump | Delivers a fixed volume of fluid with each rotation |
| Diaphragm Pump | Employs a flexible membrane for fluid movement |
| Jet Pump | Utilizes a high-velocity fluid jet for suction |

Biological Perspective
From a biological standpoint, a pump can refer to an organ or part of an organism that performs a pumping action, such as the heart in humans and other animals. The heart acts as a pump, using its muscular walls to contract and push blood through the circulatory system, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes. This biological definition highlights the critical role pumps play in sustaining life and maintaining physiological balance.
Chemical and Industrial Applications
In chemical and industrial contexts, pumps are essential for transporting and processing fluids. They are used in a wide range of applications, from chemical synthesis and pharmaceutical manufacturing to oil refining and water treatment. The choice of pump in these applications depends on factors such as the type of fluid being handled, the required flow rate and pressure, and the compatibility of the pump materials with the fluid.
Key Points
- The definition of a pump can vary significantly depending on the context, including mechanical, biological, and industrial applications.
- Understanding the different types of pumps and their operational principles is essential for selecting the right pump for a specific task.
- Pumps play a critical role in both biological systems, such as the circulatory system, and industrial processes, including manufacturing and water supply.
- The efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of a pump are influenced by its design, the materials used, and how well it is maintained.
- The selection and use of appropriate pumps are vital for ensuring the safety and environmental sustainability of industrial operations.
In conclusion, the concept of a pump is complex and multifaceted, encompassing a broad range of devices and biological systems that play critical roles in various aspects of life and industry. Whether in the human body, industrial processes, or everyday appliances, pumps are essential for the movement and processing of fluids, underscoring their importance in modern society.
What are the main types of pumps used in industrial applications?
+The main types include centrifugal pumps, positive displacement pumps, diaphragm pumps, and jet pumps, each with its unique operational mechanism and application suitability.
How does the heart act as a pump in the human body?
+The heart acts as a pump by using its muscular walls to contract and push blood through the circulatory system, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes.
What factors are considered when selecting a pump for an industrial application?
+Factors considered include the type of fluid being handled, the required flow rate and pressure, the compatibility of the pump materials with the fluid, and the efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of the pump.