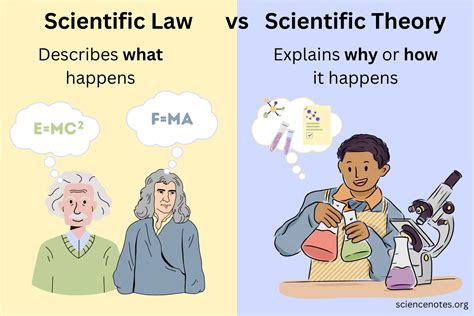
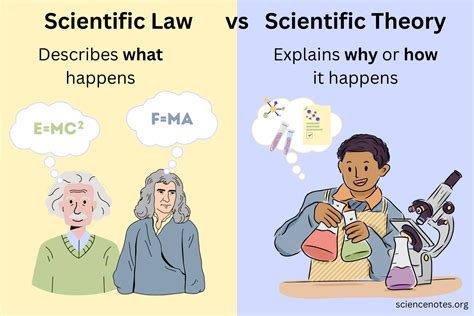
Scientific law, also known as a law of science or a scientific principle, is a statement that describes a fundamental principle or regularity in the natural world. These laws are derived from observations, experiments, and evidence-based reasoning, and they provide a framework for understanding and predicting natural phenomena. Scientific laws are often expressed mathematically, and they are typically universal, meaning they apply everywhere in the universe, at all times, and under all conditions.
Scientific laws are distinct from scientific theories, which are broader explanations for a set of phenomena. While theories provide a conceptual framework for understanding a particular aspect of the natural world, laws provide a specific, quantitative description of a particular phenomenon. Theories can be thought of as the "why" behind a phenomenon, while laws describe the "what" and "how" of the phenomenon. For example, the theory of gravity explains why objects attract each other, while the law of universal gravitation describes the mathematical relationship between the mass of two objects and the force of attraction between them.
Key Points
- Scientific laws describe fundamental principles or regularities in the natural world
- These laws are derived from observations, experiments, and evidence-based reasoning
- Scientific laws are often expressed mathematically and are universal in scope
- Scientific laws are distinct from scientific theories, which provide broader explanations for phenomena
- Theories explain the "why" behind a phenomenon, while laws describe the "what" and "how"
Characteristics of Scientific Laws
Scientific laws have several key characteristics that distinguish them from other types of statements. These characteristics include:
Universality: Scientific laws apply everywhere in the universe, at all times, and under all conditions. They are not limited to specific locations or circumstances.
Objectivity: Scientific laws are objective, meaning they are independent of personal opinions or biases. They are based on empirical evidence and are verifiable through experimentation and observation.
Predictive power: Scientific laws have predictive power, meaning they can be used to make accurate predictions about future events or phenomena. This predictive power is a key aspect of the scientific method, as it allows scientists to test hypotheses and refine their understanding of the natural world.
Mathematical expression: Many scientific laws are expressed mathematically, using equations or formulas to describe the relationships between variables. This mathematical expression provides a precise and quantitative description of the phenomenon, allowing for accurate predictions and calculations.
Examples of Scientific Laws
There are many examples of scientific laws that have been discovered and formulated over the years. Some notable examples include:
The law of universal gravitation, which describes the force of attraction between two objects as a function of their mass and distance apart.
The laws of motion, which describe the relationship between a force applied to an object and the resulting acceleration of the object.
The law of conservation of energy, which states that the total energy of a closed system remains constant over time, although it may be converted from one form to another.
| Scientific Law | Description |
|---|---|
| Law of Universal Gravitation | Describes the force of attraction between two objects as a function of their mass and distance apart |
| Laws of Motion | Describe the relationship between a force applied to an object and the resulting acceleration of the object |
| Law of Conservation of Energy | States that the total energy of a closed system remains constant over time, although it may be converted from one form to another |

Importance of Scientific Laws

Scientific laws play a crucial role in the development of scientific knowledge and technological innovation. By providing a precise and quantitative description of natural phenomena, scientific laws enable scientists to:
Predict future events: Scientific laws allow scientists to make accurate predictions about future events or phenomena, such as the motion of celestial bodies or the behavior of subatomic particles.
Develop new technologies: Scientific laws provide the foundation for the development of new technologies, such as GPS systems, medical imaging devices, and renewable energy systems.
Understand complex systems: Scientific laws help scientists understand complex systems, such as the behavior of ecosystems, the motion of fluids, and the properties of materials.
Advance our understanding of the universe: Scientific laws provide insights into the fundamental nature of the universe, from the behavior of subatomic particles to the expansion of the cosmos.
Challenges and Limitations
While scientific laws have been incredibly successful in describing and predicting natural phenomena, there are still challenges and limitations to their application. Some of these challenges include:
Complexity: Many natural systems are complex and difficult to model, making it challenging to apply scientific laws in a practical way.
Uncertainty: Scientific laws are often subject to uncertainty and error, particularly when dealing with complex or chaotic systems.
Contextual dependence: Scientific laws can be contextually dependent, meaning they may only apply under specific conditions or in certain environments.
Despite these challenges, scientific laws remain a fundamental aspect of scientific knowledge, providing a framework for understanding and predicting natural phenomena.
What is the difference between a scientific law and a scientific theory?
+A scientific law is a statement that describes a fundamental principle or regularity in the natural world, while a scientific theory is a broader explanation for a set of phenomena. Theories provide a conceptual framework for understanding a particular aspect of the natural world, while laws provide a specific, quantitative description of a particular phenomenon.
How are scientific laws developed and refined?
+Scientific laws are developed and refined through a process of observation, experimentation, and evidence-based reasoning. Scientists observe natural phenomena, develop hypotheses to explain their observations, and then test these hypotheses through experimentation and data analysis. As new evidence emerges, scientific laws are refined and updated to reflect our growing understanding of the natural world.
What is the importance of scientific laws in technological innovation?
+Scientific laws play a crucial role in technological innovation, as they provide the foundation for the development of new technologies. By understanding the fundamental principles and regularities of the natural world, scientists and engineers can design and develop new technologies, such as GPS systems, medical imaging devices, and renewable energy systems.