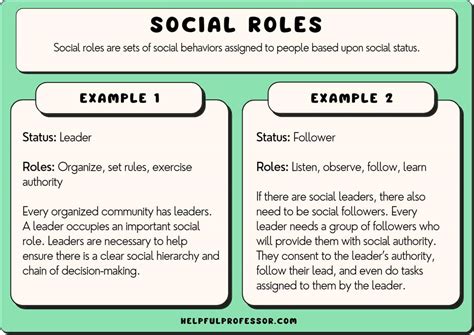
A social role refers to the patterns of behavior, expectations, and responsibilities associated with a particular position or status within a social group or society. Social roles are the building blocks of social structure, defining how individuals interact with each other and their environment. They provide a framework for understanding the social norms, values, and beliefs that shape human behavior and social interactions. In essence, social roles are the scripts that guide our actions, decisions, and relationships, influencing how we perceive ourselves and others.
Key Components of Social Roles
Social roles consist of several key components, including:
- Role expectations: The behaviors, attitudes, and values that are expected from an individual occupying a particular social role.
- Role responsibilities: The tasks, duties, and obligations associated with a social role.
- Role identity: The sense of self and identity that is tied to a particular social role.
- Role performance: The actual behavior and actions exhibited by an individual in a social role.
Types of Social Roles
There are various types of social roles, including:
- Ascribed roles: Roles that are assigned to individuals based on their birth, family, or social status.
- Achieved roles: Roles that are acquired through personal effort, education, or experience.
- Formal roles: Roles that are officially recognized and defined within an organization or institution.
- Informal roles: Roles that emerge through social interactions and are not formally recognized.
| Role Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Ascribed | Assigned at birth, based on family or social status |
| Achieved | Acquired through personal effort, education, or experience |
| Formal | Officially recognized, defined within an organization or institution |
| Informal | Emerges through social interactions, not formally recognized |
Key Points
- Social roles are patterns of behavior, expectations, and responsibilities associated with a particular position or status.
- Role expectations, responsibilities, identity, and performance are key components of social roles.
- Ascribed, achieved, formal, and informal roles are different types of social roles.
- Understanding social roles is essential for effective social interaction and relationship building.
- Social roles are dynamic and can change over time, influenced by personal, social, and cultural factors.
Social roles are not fixed entities, but rather dynamic and context-dependent constructs that evolve over time. As individuals navigate different social situations and interact with various groups, their social roles may shift, and new roles may emerge. Furthermore, social roles are influenced by a complex array of factors, including personal characteristics, social norms, cultural values, and institutional expectations.
The Impact of Social Roles on Individuals and Society
Social roles have a profound impact on both individuals and society as a whole. They shape our sense of identity, influence our behaviors and attitudes, and determine our access to resources, opportunities, and social connections. Social roles also contribute to social cohesion, as they provide a shared framework for understanding and interacting with each other. However, social roles can also be a source of conflict, inequality, and social change, as individuals and groups challenge existing role expectations and strive for greater autonomy, equality, and social justice.
Social Role Theory and Research
Social role theory has been extensively researched in various fields, including sociology, psychology, anthropology, and organizational studies. Researchers have explored the ways in which social roles are constructed, negotiated, and performed, as well as the consequences of social roles for individuals, groups, and societies. Some key findings include:
- Social roles are often associated with specific social norms, values, and expectations.
- Individuals may occupy multiple social roles, which can lead to role conflict or role strain.
- Social roles can be a source of social identity, self-esteem, and motivation.
- Social roles are influenced by power dynamics, social inequality, and cultural context.
What is the difference between an ascribed and achieved social role?
+An ascribed social role is assigned to an individual based on their birth, family, or social status, whereas an achieved social role is acquired through personal effort, education, or experience.
How do social roles influence individual behavior and attitudes?
+Social roles shape our sense of identity, influence our behaviors and attitudes, and determine our access to resources, opportunities, and social connections. They provide a framework for understanding the social norms, values, and expectations that guide our actions and decisions.
What are the implications of social roles for social cohesion and social change?
+Social roles contribute to social cohesion by providing a shared framework for understanding and interacting with each other. However, social roles can also be a source of conflict, inequality, and social change, as individuals and groups challenge existing role expectations and strive for greater autonomy, equality, and social justice.
In conclusion, social roles are complex and multifaceted constructs that play a crucial role in shaping individual behavior, social interactions, and societal dynamics. By understanding the various types of social roles, their associated expectations, responsibilities, and identities, and the ways in which they influence individuals and society, we can better navigate the complexities of social life and work towards creating more inclusive, equitable, and just social systems.