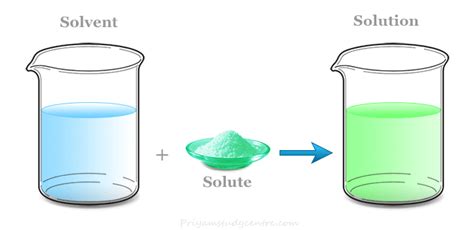
The concept of a chemistry solution is fundamental to understanding various chemical reactions and processes. A solution, in the context of chemistry, refers to a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where one substance (the solute) is dissolved in another substance (the solvent). The solute can be a solid, liquid, or gas, and the solvent is typically a liquid. The most common solvent used in chemistry is water, due to its high solubility and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances. However, other solvents like ethanol, acetone, and hexane are also commonly used, depending on the specific application and the properties of the solute.
Chemistry solutions are classified based on the concentration of the solute in the solvent. The concentration can be expressed in various units, such as molarity (moles of solute per liter of solution), molality (moles of solute per kilogram of solvent), or percentage composition (mass of solute per 100 grams of solution). Understanding the concentration of a solution is crucial in chemistry, as it affects the chemical properties and reactivity of the solution. For instance, the concentration of a solution can influence the rate of chemical reactions, the solubility of substances, and the stability of the solution. Moreover, the concentration of a solution is critical in various industrial and laboratory applications, such as the production of chemicals, the development of pharmaceuticals, and the analysis of environmental samples.
Key Points
- A chemistry solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where one substance (the solute) is dissolved in another substance (the solvent).
- The concentration of a solution can be expressed in various units, including molarity, molality, and percentage composition.
- The concentration of a solution affects its chemical properties and reactivity, and is critical in various industrial and laboratory applications.
- Water is the most common solvent used in chemistry, due to its high solubility and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
- Other solvents, such as ethanol, acetone, and hexane, are also commonly used, depending on the specific application and the properties of the solute.
Preparation of Chemistry Solutions
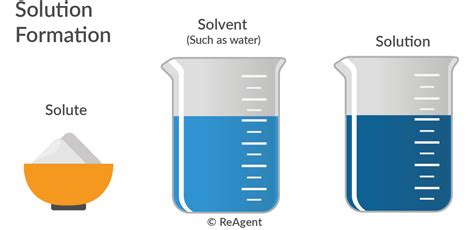
The preparation of chemistry solutions involves dissolving a known amount of solute in a solvent to produce a solution with a desired concentration. This can be achieved through various methods, including mixing the solute and solvent in a container, heating the mixture to facilitate dissolution, or using a solvent extraction technique to separate the solute from a solid matrix. The preparation of solutions is a critical step in many chemical analyses and reactions, as it allows chemists to control the concentration of reactants and products, and to study the properties of substances under different conditions. For example, the preparation of solutions is essential in titration reactions, where a known amount of a substance is added to a solution to determine the concentration of another substance.
Types of Chemistry Solutions
Chemistry solutions can be classified into several types based on their composition and properties. These include aqueous solutions, which are solutions where water is the solvent, and non-aqueous solutions, which are solutions where a solvent other than water is used. Other types of solutions include saturated solutions, which contain the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent, and unsaturated solutions, which contain less than the maximum amount of solute. Additionally, solutions can be classified as acidic, basic, or neutral, based on their pH level. Understanding the properties of different types of solutions is essential in chemistry, as it allows chemists to predict the behavior of substances under different conditions, and to design experiments and reactions that achieve specific outcomes.
| Type of Solution | Description |
|---|---|
| Aqueous Solution | A solution where water is the solvent. |
| Non-Aqueous Solution | A solution where a solvent other than water is used. |
| Saturated Solution | A solution that contains the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a solvent. |
| Unsaturated Solution | A solution that contains less than the maximum amount of solute. |
Applications of Chemistry Solutions

Chemistry solutions have a wide range of applications in various fields, including medicine, industry, and environmental science. In medicine, solutions are used as solvents for drugs, as diagnostic tools, and as treatments for diseases. In industry, solutions are used in the production of chemicals, textiles, and other materials. In environmental science, solutions are used to study the properties of pollutants, to monitor water quality, and to develop strategies for pollution control. Additionally, solutions are used in various laboratory techniques, such as chromatography and spectroscopy, to separate and analyze mixtures of substances. For example, solutions are used in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to separate and quantify the components of a mixture, and in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to determine the structure of molecules.
Importance of Chemistry Solutions in Everyday Life
Chemistry solutions play a vital role in everyday life, as they are used in a wide range of products and applications. For example, solutions are used in cleaning products, personal care products, and food processing. Additionally, solutions are used in the production of fuels, lubricants, and other energy-related products. The importance of chemistry solutions in everyday life cannot be overstated, as they have a significant impact on our daily lives, our health, and our environment. Furthermore, the development of new solutions and technologies has the potential to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges, such as climate change, energy security, and access to clean water.
In conclusion, chemistry solutions are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and their preparation, classification, and applications are critical to understanding various chemical reactions and processes. By understanding the properties of different types of solutions, chemists can control the concentration of reactants and products, and study the properties of substances under different conditions. The importance of chemistry solutions in everyday life is undeniable, and their applications in various fields will continue to grow and evolve as new technologies and discoveries are made.
What is a chemistry solution?
+A chemistry solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, where one substance (the solute) is dissolved in another substance (the solvent).
How are chemistry solutions classified?
+Chemistry solutions can be classified based on their composition and properties, including aqueous solutions, non-aqueous solutions, saturated solutions, and unsaturated solutions.
What are the applications of chemistry solutions?
+Chemistry solutions have a wide range of applications in various fields, including medicine, industry, and environmental science.
Why are chemistry solutions important in everyday life?
+Chemistry solutions play a vital role in everyday life, as they are used in a wide range of products and applications, including cleaning products, personal care products, and food processing.
How are chemistry solutions prepared?
+The preparation of chemistry solutions involves dissolving a known amount of solute in a solvent to produce a solution with a desired concentration.
Meta Description: Discover the concept of chemistry solutions, including their preparation, classification, and applications in various fields. Learn about the importance of chemistry solutions in everyday life and their impact on our health and environment.