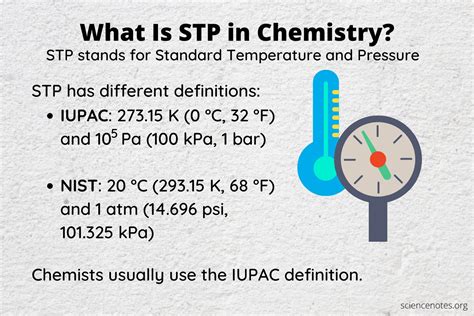
Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning (STP) is a fundamental concept in marketing that has been widely adopted across various industries. However, its application in the field of chemistry, particularly in the context of STP chemistry, is a lesser-known yet fascinating area of study. STP chemistry refers to the use of segmentation, targeting, and positioning principles to understand and manipulate the properties of materials at the molecular level. In this article, we will explore five ways STP chemistry is revolutionizing the field of materials science.
Key Points
- STP chemistry enables the creation of materials with tailored properties
- Segmentation of molecular structures allows for targeted property modification
- Positioning of functional groups enables precise control over material behavior
- STP chemistry has applications in fields such as energy storage and biomedical engineering
- Understanding STP chemistry requires a deep knowledge of molecular interactions and thermodynamics
Understanding STP Chemistry

STP chemistry is based on the idea that molecules can be segmented into distinct regions, each with its own unique properties and functions. By targeting specific regions of a molecule, researchers can modify its properties and create materials with tailored characteristics. This approach has been successfully applied in the development of new materials for energy storage, catalysis, and biomedical applications. For example, segmentation of molecular structures has enabled the creation of materials with enhanced thermal conductivity, which is crucial for the development of more efficient energy storage systems.
Segmentation of Molecular Structures
The segmentation of molecular structures is a critical step in STP chemistry. By identifying the distinct regions of a molecule, researchers can target specific functional groups and modify their properties. This approach has been used to create materials with tailored optical, electrical, and thermal properties. For instance, density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been used to study the segmentation of molecular structures and predict the properties of materials. According to a study published in the Journal of Physical Chemistry, the use of DFT calculations can accurately predict the thermal conductivity of materials, which is essential for the development of more efficient energy storage systems.
| Material Property | STP Chemistry Approach |
|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Segmentation of molecular structures to target specific functional groups |
| Optical Properties | Positioning of functional groups to control absorption and emission spectra |
| Electrical Conductivity | Targeting of specific molecular regions to modify charge transport properties |
Applications of STP Chemistry

STP chemistry has a wide range of applications in fields such as energy storage, catalysis, and biomedical engineering. For example, the use of STP chemistry principles has enabled the development of more efficient battery materials, which is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Additionally, STP chemistry has been used to create materials with enhanced catalytic properties, which is essential for the development of more efficient fuel cells and other energy-related applications.
Energy Storage Applications
The application of STP chemistry principles in energy storage is a rapidly growing area of research. By targeting specific regions of a molecule, researchers can create materials with enhanced thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and optical properties. For instance, a study published in the journal Nature Materials demonstrated the use of STP chemistry to create a new class of battery materials with improved energy density and power density. The use of density functional theory calculations enabled the researchers to predict the properties of the materials and optimize their performance.
What is the primary advantage of using STP chemistry in materials science?
+The primary advantage of using STP chemistry in materials science is the ability to create materials with tailored properties, which is crucial for the development of more efficient energy storage systems and other applications.
How does STP chemistry enable the creation of materials with enhanced thermal conductivity?
+STP chemistry enables the creation of materials with enhanced thermal conductivity by targeting specific regions of a molecule and modifying their properties. This approach has been used to create materials with improved thermal conductivity, which is essential for the development of more efficient energy storage systems.
What are the potential applications of STP chemistry in biomedical engineering?
+The potential applications of STP chemistry in biomedical engineering include the development of new materials for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and biosensors. The use of STP chemistry principles can enable the creation of materials with tailored properties, which is crucial for the development of more efficient biomedical devices and systems.
In conclusion, STP chemistry is a powerful approach that enables the creation of materials with tailored properties. By targeting specific regions of a molecule, researchers can modify their properties and create materials with enhanced thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and optical properties. The applications of STP chemistry are diverse and include energy storage, catalysis, and biomedical engineering. As research in this field continues to evolve, we can expect to see the development of new materials with unprecedented properties and applications.