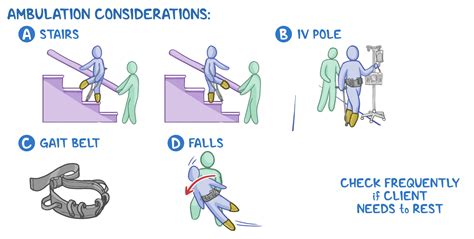
Ambulation refers to the act of walking or moving from one place to another on foot. It is a fundamental aspect of human mobility and is essential for maintaining physical health, independence, and overall well-being. Ambulation involves a complex interplay of physiological, biomechanical, and neurological processes, including muscle contractions, joint movements, and balance control. In the context of healthcare, ambulation is often used as an indicator of a person's functional ability and mobility status, with impaired ambulation being a common consequence of various medical conditions, injuries, or disabilities.
The process of ambulation involves a series of coordinated movements, including weight transfer, balance adjustments, and propulsion. It requires the integration of sensory inputs from the visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive systems, as well as the activation of specific muscle groups, such as the hip flexors, quadriceps, and calf muscles. Ambulation can be affected by various factors, including age, muscle strength, joint mobility, and neurological function, and is often assessed through clinical evaluations, such as gait analysis and mobility tests.
Key Points
- Ambulation is the act of walking or moving from one place to another on foot.
- It is a complex process involving physiological, biomechanical, and neurological components.
- Ambulation is an essential aspect of human mobility and is critical for maintaining physical health and independence.
- Impaired ambulation can result from various medical conditions, injuries, or disabilities.
- Clinical evaluations, such as gait analysis and mobility tests, are used to assess ambulation and functional ability.
Physiological and Biomechanical Aspects of Ambulation
The physiological and biomechanical aspects of ambulation are intricate and involve the coordinated functioning of multiple systems. The muscular system, for example, plays a crucial role in ambulation, with specific muscle groups responsible for hip flexion, knee extension, and ankle dorsiflexion. The skeletal system, comprising the bones and joints, provides the structural framework for movement, while the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, regulates and coordinates the various components of ambulation.
The biomechanics of ambulation involve the study of the movements and forces associated with walking. It encompasses the analysis of gait patterns, joint kinematics, and ground reaction forces, as well as the assessment of energy expenditure and metabolic costs. Understanding the biomechanical aspects of ambulation is essential for the development of effective rehabilitation strategies and the design of assistive devices, such as prosthetic limbs and orthotics.
Neurological Control of Ambulation
The neurological control of ambulation is a complex process involving the integration of sensory inputs, motor outputs, and cognitive processes. The brain plays a central role in regulating ambulation, with specific regions, such as the motor cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum, responsible for controlling movement, balance, and coordination. The spinal cord and peripheral nerves also contribute to the neurological control of ambulation, transmitting and processing sensory information and motor commands.
| System | Component | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Muscular | Hip flexors | Hip flexion |
| Skeletal | Joints | Provide structural framework for movement |
| Nervous | Brain | Regulates and coordinates ambulation |
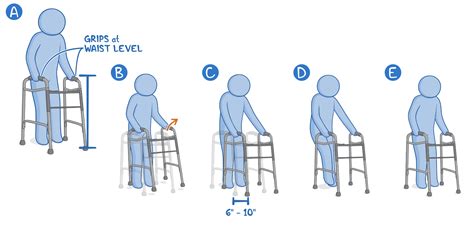
Clinical Significance of Ambulation

Ambulation is a critical aspect of functional ability and is often used as an indicator of a person’s overall health and well-being. Impaired ambulation can result from various medical conditions, such as stroke, spinal cord injury, or osteoarthritis, and can have significant consequences for an individual’s quality of life, independence, and mobility. Clinical evaluations, such as gait analysis and mobility tests, are used to assess ambulation and functional ability, providing valuable information for the development of rehabilitation strategies and treatment plans.
The clinical significance of ambulation is also reflected in its role as a predictor of health outcomes and mortality. Studies have shown that impaired ambulation is associated with an increased risk of falls, fractures, and other injuries, as well as a higher risk of mortality and morbidity. Therefore, maintaining ambulation and promoting mobility is essential for healthy aging and preventing disability.
Rehabilitation Strategies for Impaired Ambulation
Rehabilitation strategies for impaired ambulation are designed to promote mobility, strength, and functional ability. These strategies may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, as well as the use of assistive devices, such as canes, walkers, and wheelchairs. The goal of rehabilitation is to maximize an individual’s functional potential, promoting independence, mobility, and overall well-being.
Rehabilitation strategies for impaired ambulation often involve a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating the expertise of physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other healthcare professionals. These strategies may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and balance, as well as training in the use of assistive devices and adaptive equipment.
What is ambulation, and why is it important?
+Ambulation refers to the act of walking or moving from one place to another on foot. It is essential for maintaining physical health, independence, and overall well-being.
What are the physiological and biomechanical aspects of ambulation?
+The physiological and biomechanical aspects of ambulation involve the coordinated functioning of multiple systems, including the muscular, skeletal, and nervous systems.
How is ambulation assessed and evaluated in a clinical setting?
+Ambulation is assessed and evaluated through clinical evaluations, such as gait analysis and mobility tests, providing valuable information for the development of rehabilitation strategies and treatment plans.
In conclusion, ambulation is a complex and multifaceted process that is essential for maintaining physical health, independence, and overall well-being. Understanding the physiological, biomechanical, and neurological aspects of ambulation is critical for developing effective rehabilitation strategies and promoting mobility in individuals with impaired ambulation. By recognizing the clinical significance of ambulation and its role as a predictor of health outcomes and mortality, healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive care and support to individuals with mobility impairments, promoting healthy aging and preventing disability.