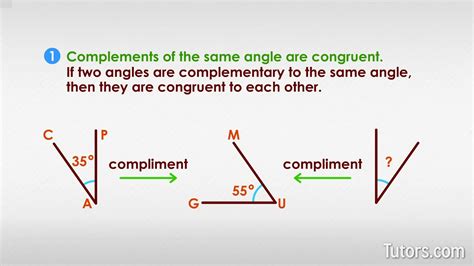
The concept of angle complement is a fundamental idea in geometry, particularly in the study of angles and their relationships. An angle complement refers to the angle that, when added to a given angle, results in a sum of 90 degrees. In other words, the complement of an angle is the angle that completes it to form a right angle. This concept is crucial in various geometric calculations and theorems, as it helps in understanding the properties and relationships between different angles in a plane.
Understanding Angle Complement
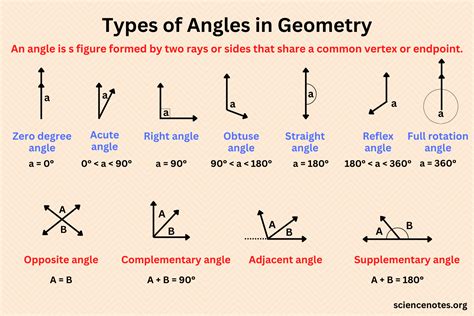
To grasp the concept of angle complement, it’s essential to start with the basics of angles. An angle is formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, known as the vertex. The size of an angle is measured in degrees, with a full circle being 360 degrees and a straight line being 180 degrees. A right angle, which is 90 degrees, serves as a reference point for defining complementary angles. If we have an angle A, its complement is the angle B such that A + B = 90 degrees.
Properties of Complementary Angles
Complementary angles have several key properties that make them useful in geometric analyses. Firstly, the sum of two complementary angles is always 90 degrees. Secondly, complementary angles do not have to be adjacent or share a common vertex; they can be anywhere in the plane as long as their sum is 90 degrees. Lastly, each angle has only one complement. For example, if we have an angle of 30 degrees, its complement is 60 degrees because 30 + 60 = 90 degrees.
| Angle | Complement |
|---|---|
| 20 degrees | 70 degrees |
| 45 degrees | 45 degrees |
| 60 degrees | 30 degrees |
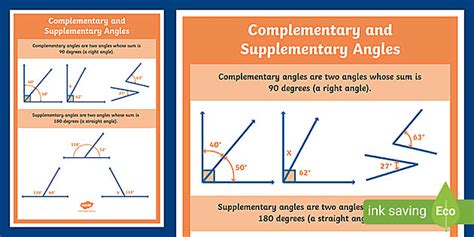
Applications of Complementary Angles
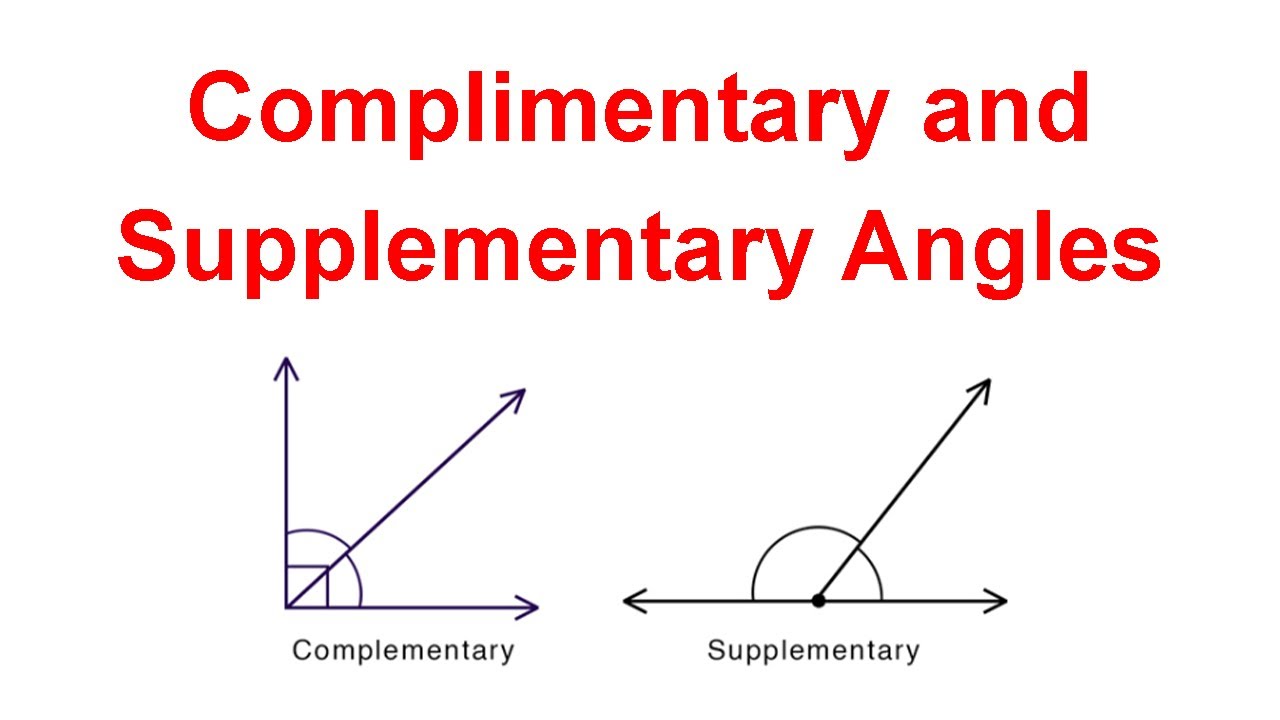
Complementary angles find applications in various areas of mathematics and real-world problems. In trigonometry, the relationships between complementary angles are used to derive identities and solve problems involving right triangles. In geometry, understanding complementary angles is essential for proving theorems related to angles in triangles and polygons. Furthermore, in physics and engineering, the concept of complementary angles is used in the study of motion, forces, and the design of mechanical systems.
Key Points
- The complement of an angle is the angle that, when added to it, equals 90 degrees.
- Complementary angles do not have to be adjacent or share a common vertex.
- Each angle has only one complement.
- Understanding complementary angles is crucial for geometric calculations and theorems.
- Complementary angles have practical applications in architecture, engineering, and design.
Calculating Complementary Angles
Calculating the complement of an angle is straightforward. If we know the measure of an angle, we can find its complement by subtracting the angle measure from 90 degrees. For instance, to find the complement of a 25-degree angle, we calculate 90 - 25 = 65 degrees. Therefore, the complement of a 25-degree angle is 65 degrees.
In conclusion, the concept of angle complement is a fundamental principle in geometry that has far-reaching implications in various fields. Understanding complementary angles and their properties is essential for solving geometric problems, proving theorems, and applying geometric principles in real-world scenarios.
What is the definition of complementary angles?
+Complementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees.
How do you find the complement of an angle?
+To find the complement of an angle, subtract the angle measure from 90 degrees.
Do complementary angles have to be adjacent?
+No, complementary angles do not have to be adjacent or share a common vertex; they can be anywhere in the plane as long as their sum is 90 degrees.