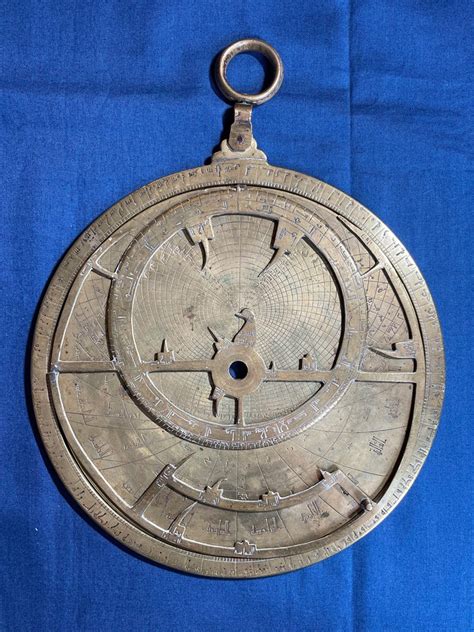
The astrolabe, an ancient astronomical instrument, has been a cornerstone of navigation and stargazing for centuries. Its intricate design and multifaceted functionality have allowed users to pinpoint their location, determine the time, and identify celestial bodies with remarkable accuracy. In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of the astrolabe, exploring its components and the principles that govern its operation. By examining the astrolabe's mechanics and applications, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the ingenuity and craftsmanship that went into its creation.
Understanding the Astrolabe’s Components
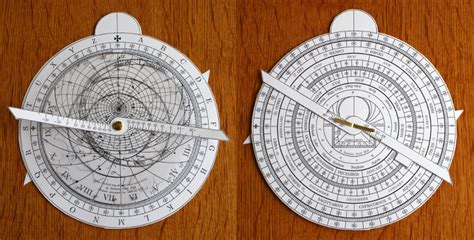
The astrolabe consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in its overall functionality. The mater, or mother, is the base plate of the astrolabe, which features a series of concentric circles and scales. The rete, or net, is a rotating overlay that contains pointers for various stars and constellations. The altitude ring is a circular scale that measures the angle of celestial bodies above the horizon. By combining these components, the astrolabe can provide a wealth of information about the user’s surroundings and the night sky.
Key Points
- The astrolabe is an ancient astronomical instrument used for navigation and stargazing.
- The instrument consists of several key components, including the mater, rete, and altitude ring.
- The astrolabe can be used to determine the user's location, time, and the position of celestial bodies.
- The instrument relies on the principles of astronomy and geometry to provide accurate measurements.
- The astrolabe has been used for centuries, with its design and functionality evolving over time.
Measuring Altitude and Azimuth
One of the primary functions of the astrolabe is to measure the altitude and azimuth of celestial bodies. By aligning the rete with the desired star or constellation, the user can determine its position in the sky. The altitude ring provides a scale for measuring the angle of the celestial body above the horizon, while the azimuth ring measures its direction from the user’s location. By combining these measurements, the user can calculate the celestial body’s position in terms of its declination and right ascension.
| Celestial Body | Altitude | Azimuth |
|---|---|---|
| Sirius | 30° | 120° |
| Orion's Belt | 40° | 90° |
| North Star | 50° | 0° |

Determining Time and Location
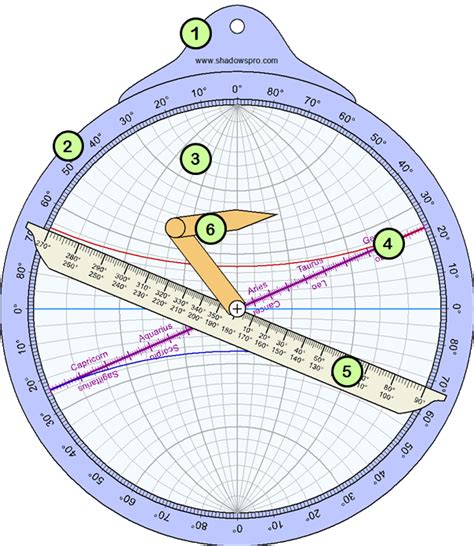
In addition to measuring the position of celestial bodies, the astrolabe can also be used to determine the time and the user’s location. By observing the position of the sun or stars, the user can calculate the local time and their latitude. The hour lines on the astrolabe’s face provide a scale for measuring the time, while the latitude lines provide a scale for measuring the user’s distance from the equator. By combining these measurements, the user can determine their precise location and the current time.
Using the Astrolabe for Navigation
The astrolabe’s ability to measure altitude, azimuth, time, and location makes it an essential tool for navigation. By using the instrument to determine their position and the position of celestial bodies, sailors, travelers, and explorers can chart their course and stay on track. The astrolabe’s compact size and durability also make it an ideal instrument for use in the field, where it can be used to make precise measurements and calculations.
In conclusion, the astrolabe is a remarkable instrument that has been used for centuries to navigate the night sky and determine the user's location. By understanding the principles behind its operation and the components that make it up, users can unlock the full potential of the astrolabe and gain a deeper appreciation for the art of astronomy and navigation.
What is the primary function of the astrolabe?
+The primary function of the astrolabe is to measure the altitude and azimuth of celestial bodies, which can be used to determine the user’s location, time, and the position of celestial bodies.
How does the astrolabe measure altitude and azimuth?
+The astrolabe measures altitude and azimuth using the rete and altitude ring. The rete is aligned with the desired star or constellation, and the altitude ring provides a scale for measuring the angle of the celestial body above the horizon.
Can the astrolabe be used for navigation?
+Yes, the astrolabe can be used for navigation. By determining the user’s location and the position of celestial bodies, the astrolabe can be used to chart a course and stay on track.