When it comes to financing higher education, understanding the different types of loans available is crucial for making informed decisions. One common type of loan is the unsubsidized loan, which has distinct characteristics compared to its subsidized counterpart. Here are five key facts about unsubsidized loans that can help individuals navigate the complex landscape of student loan financing.
Key Points
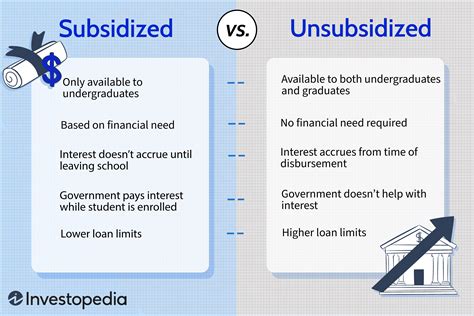
- Unsubsidized loans are not based on financial need and are available to all eligible students.
- Interest accrues on unsubsidized loans from the date of disbursement, and borrowers are responsible for paying this interest.
- The interest rates for unsubsidized loans are fixed and determined by the federal government for each academic year.
- Borrowers have the option to pay the interest as it accrues or allow it to capitalize, adding to the principal amount of the loan.
- Repayment terms for unsubsidized loans vary, with options including income-driven repayment plans and extended repayment periods.
Understanding Unsubsidized Loans

Unsubsidized loans are a type of federal student loan that is not based on financial need. This means that any eligible student can apply for and receive an unsubsidized loan, regardless of their family’s income level or financial situation. The primary difference between unsubsidized and subsidized loans lies in the treatment of interest. For subsidized loans, the government pays the interest while the student is in school and during certain periods of deferment. In contrast, interest on unsubsidized loans begins to accrue as soon as the loan is disbursed.
Interest Accrual and Payment
One of the critical aspects of unsubsidized loans is how interest accrues and is paid. Borrowers have two main options for handling the interest on their unsubsidized loans. They can choose to pay the interest as it accrues, which can help reduce the overall cost of the loan by preventing interest capitalization. Alternatively, borrowers can allow the interest to capitalize, which means it is added to the principal amount of the loan. This can result in paying more over the life of the loan because interest is then charged on the new, higher principal balance.
The interest rates for unsubsidized loans are fixed but can vary from year to year based on federal regulations. For the 2022-2023 academic year, for example, the interest rate for undergraduate unsubsidized loans was set at 4.99%. It's essential for borrowers to check the current interest rates for unsubsidized loans, as these rates can impact the total cost of borrowing.
| Loan Type | Interest Rate (2022-2023) |
|---|---|
| Undergraduate Unsubsidized Loan | 4.99% |
| Graduate Unsubsidized Loan | 6.54% |

Repayment Terms and Options
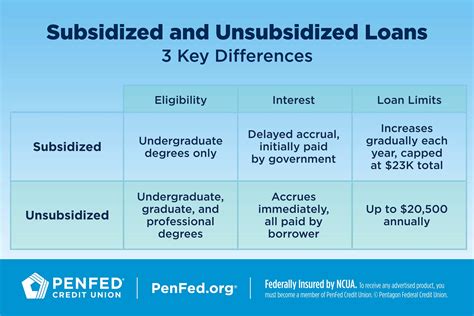
The repayment terms for unsubsidized loans can vary, offering borrowers flexibility in managing their debt. After graduating, leaving school, or dropping below half-time enrollment, borrowers typically enter a six-month grace period before they must start making payments. The standard repayment plan for federal student loans, including unsubsidized loans, spans ten years. However, borrowers may be eligible for income-driven repayment plans, which can extend the repayment period to 20 or 25 years, depending on the plan and the borrower’s income and family size.
Borrowers should carefully review their repayment options and consider factors such as the total interest paid over the life of the loan, monthly payment amounts, and potential forgiveness options. For those struggling to make payments, options like deferment or forbearance may be available, though these can have different implications for interest accrual and capitalization.
Strategic Considerations
When considering unsubsidized loans as part of a financial aid package, it’s crucial to approach the decision strategically. Borrowers should weigh the benefits of borrowing against the costs, considering both the principal amount and the interest that will accrue over time. Given that unsubsidized loans are available regardless of financial need, students and their families may use these loans as part of a broader strategy to finance education expenses, potentially in combination with scholarships, grants, and subsidized loans.
Understanding the terms and conditions of unsubsidized loans, including how interest works and the repayment options available, can empower borrowers to make informed decisions about their financial aid. By considering these factors and planning carefully, individuals can effectively manage their debt and make progress toward their educational and professional goals.
What is the main difference between subsidized and unsubsidized loans?
+The primary difference lies in the treatment of interest. Subsidized loans have their interest paid by the government while the student is in school, whereas interest on unsubsidized loans accrues from the date of disbursement, and borrowers are responsible for paying it.
Can I pay the interest on my unsubsidized loan while I’m in school?
+Yes, you can choose to pay the interest on your unsubsidized loan while you’re in school. This can help reduce the total cost of the loan by preventing interest capitalization.
What are my repayment options for unsubsidized loans?
+You have several repayment options, including the standard repayment plan, income-driven repayment plans, and extended repayment periods. The best option for you will depend on your financial situation and goals.